5G network slice resource allocation method
A network slicing and resource allocation technology, applied in the field of 5G network slicing resource allocation, can solve the problems of being unable to meet different user service requests, ignoring user service quality, and small base station coverage, so as to achieve rapid resource allocation, good real-time performance and Global selectivity, the effect of improving expected returns
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
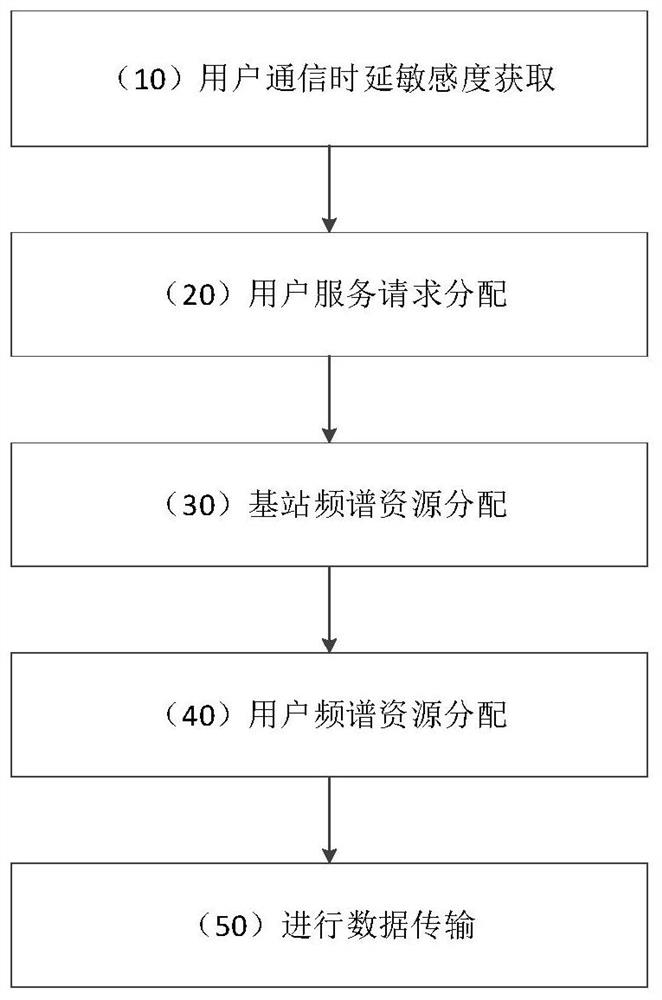
[0074] The specific conditions of this example are: the number of mobile users N within the coverage of a single physical macro base station is set to 12, the number of slices M is set to 3, that is, 3 network slices obtain spectrum resources from the physical macro base station to provide 12 mobile users Different data transfer services. In the simulation environment where the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is 1db to 20db, the channel fading obeys the Rayleigh distribution.
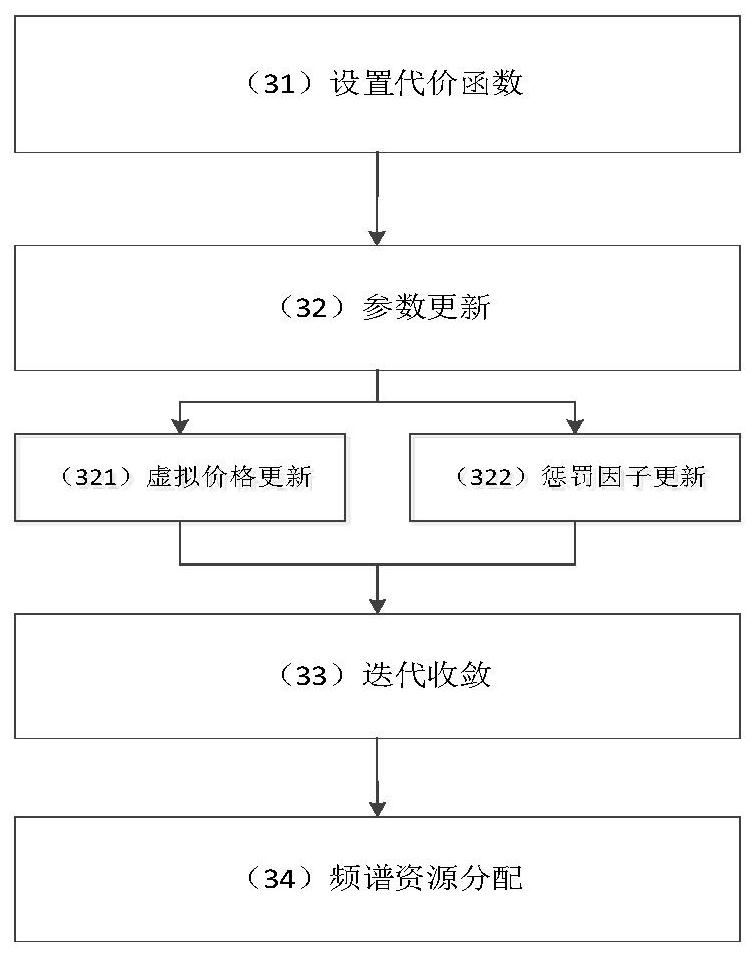
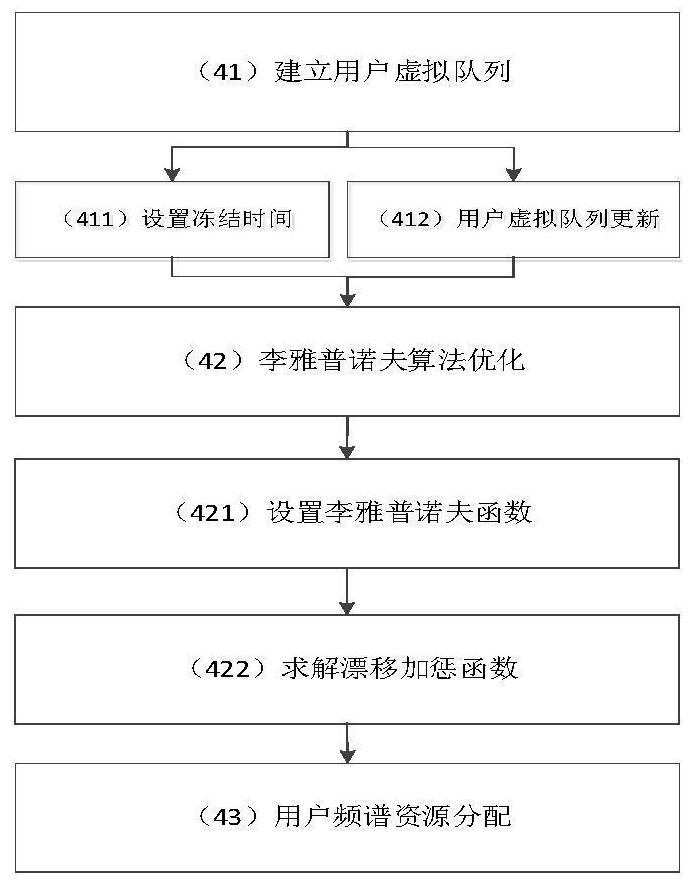
[0075] Based on the above experimental conditions, first obtain the delay sensitivity of different users, and quantify it as Then, the service request A made by the mobile user n assigned to different network slices. After the network slice receives the service request, it calculates the cost function μ m (ω m ), and sequentially update the virtual price ω m and penalty factor q m , until the virtual price converges, the base station allocates spectrum resource b according to the virtual price m Sli...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com