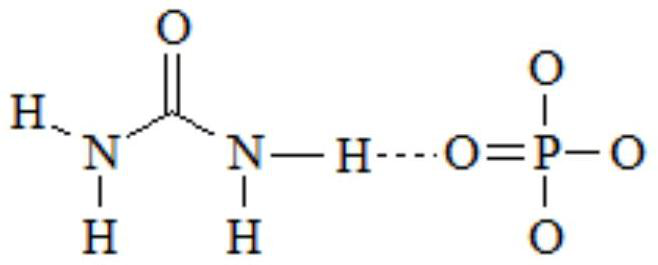Nano-hybrid N and P slow-release fertilizer and preparation method thereof
A slow-release fertilizer and hybrid technology, applied in nitrogen fertilizers, phosphate fertilizers, fertilization devices, etc., can solve the problems of narrow application range, high cost, complicated preparation process of slow-release fertilizers, etc., achieve high stability constant, reduce nitrogen fertilizer loss, avoid The effect of slowing down the loss of performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
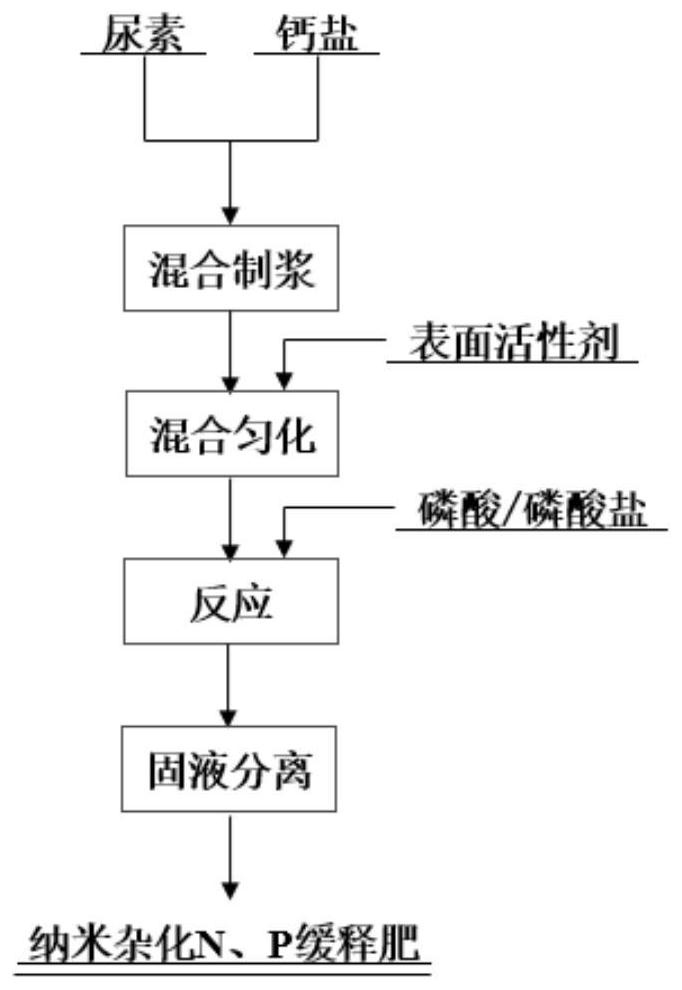
[0025] The present embodiment provides a kind of preparation method of nano-hybrid N, P slow-release fertilizer, such as figure 1 As shown, the specific process is:
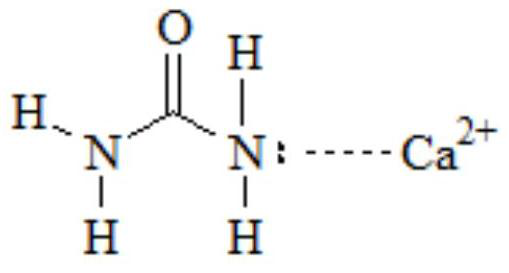
[0026] Add urea and slaked lime into water according to the molar ratio of urea: calcium ion is 5:1, stir vigorously and mix evenly to obtain a mixed slurry. Add cetyltrimethylsodium bromide (CTAB) in an amount of 2% of the mass of the calcium salt, and vigorously stir to dissolve CTAB. Prepare a mixture of phosphoric acid and potassium dihydrogen phosphate at a molar ratio of phosphate and calcium ions of 0.6:1, and dissolve it in water to obtain a phosphoric acid / potassium dihydrogen phosphate solution. Then the phosphoric acid / potassium dihydrogen phosphate solution, and the mixture of urea, slaked lime and CTAB are pumped into the reaction vessel that has been preheated to 90°C. After stirring and reacting at 90° C. for 60 minutes, spray drying is carried out to obtain nano-hybrid N, P slow-release fertiliz...
Embodiment 2
[0034] This embodiment provides a preparation method of nano-hybrid N, P slow-release fertilizer, the specific process is:
[0035] Add urea, calcium chloride, and lime into water according to the molar ratio of urea:calcium ion 2:1, stir vigorously and mix evenly to obtain a mixed slurry. Sodium dodecylsulfonate (SDS) was added in an amount of 2% of the mass of the calcium salt, and vigorously stirred to dissolve the SDS. Prepare a mixture of phosphoric acid and diammonium hydrogen phosphate at a molar ratio of phosphate to calcium ions of 0.55:1, and dissolve it in water to obtain a phosphoric acid / diammonium hydrogen phosphate solution. Then pump the mixture of urea, calcium chloride, lime mixed slurry and SDS, and phosphoric acid / diammonium hydrogen phosphate solution into the reaction vessel that has been preheated to 50°C. After stirring and reacting at 50° C. for 180 minutes, spray drying is carried out to obtain nano-hybrid N, P slow-release fertilizer.
Embodiment 3
[0037] This embodiment provides a preparation method of nano-hybrid N, P slow-release fertilizer, the specific process is:
[0038] Add urea and slaked lime into water according to the molar ratio of urea:calcium ion 4:1, stir vigorously and mix evenly to obtain a mixed slurry. Add the surfactant Tween 80 in an amount of 1.0% of the mass of the calcium salt, heat to 40° C. and vigorously stir to dissolve the Tween 80. Prepare a mixture of sodium hexametaphosphate and ammonium phosphate at a molar ratio of phosphate to calcium ions of 0.6:1, and dissolve it in water to obtain a sodium hexametaphosphate / ammonium phosphate solution. Put the mixture of urea, slaked lime mixed slurry and Tween 80, and sodium hexametaphosphate / ammonium phosphate solution into the reaction vessel that has been preheated to 60°C with a pump, and stir and react at 60°C for 120min. Spray-drying is carried out to obtain nano-hybrid N, P slow-release fertilizer.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com