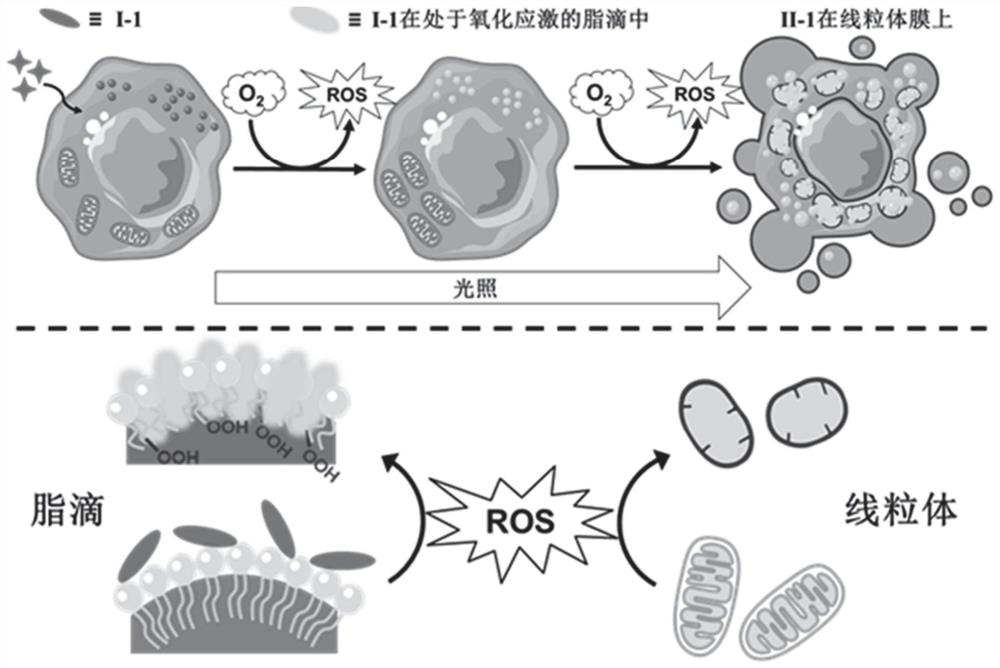
Light-activated probe with organelle sequential imaging and double-color imaging functions and application thereof
A two-color imaging and photoactivation technology, applied in the field of photoactivated probes, can solve the problems of differences in intake, poor residence capacity and photostability, adverse mitochondrial morphological changes, etc., and achieve the effect of a simple method.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
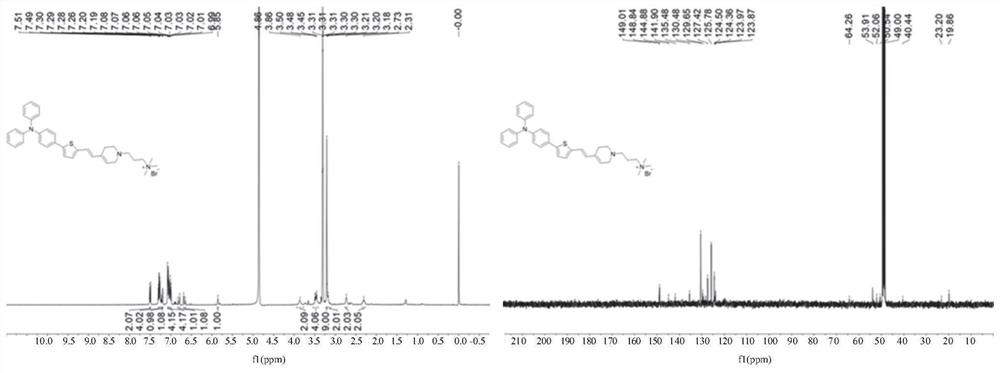
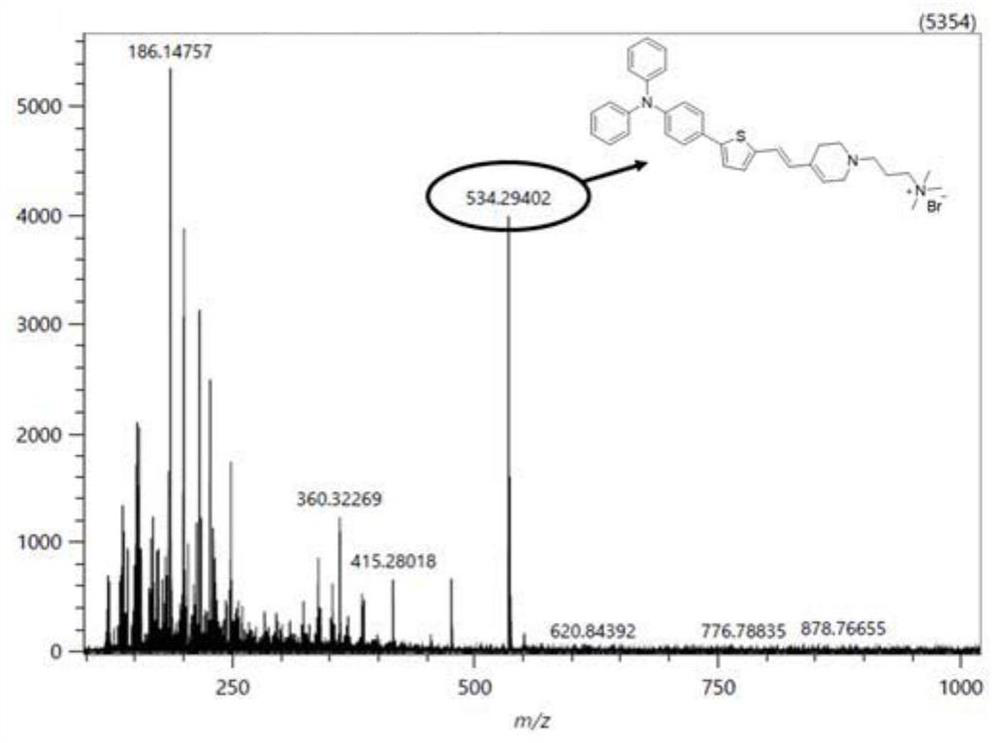
[0054] Preparation of Compound I-1:
[0055] Weigh compound II-1 (28.3mg, 0.04mmol) in a reaction vessel, add 5mL methanol to it, and ultrasonically dissolve the solid completely; weigh sodium borohydride (15.5mg, 0.41mmol) and add it to the reaction solution, and Stir the reaction at room temperature under nitrogen atmosphere for half an hour; after the reaction is completed, use a rotary evaporator to depressurize the reaction solution to obtain the crude product to be treated; add 10mL ultrapure water to the crude product, ultrasonicate, and filter to obtain a brown solid product. The precipitate was dried in vacuo to obtain compound I-1 in ~8.5% yield.
[0056] The structure of compound I-1 is
[0057] The structure of compound II-1 is
[0058] The chemical structure characterization data of the product are as follows:
[0059] 1 H NMR (MeOD, 400MHz): δ7.49(d, J=8.8Hz, 2H), 7.29(t, J 1 =15.6Hz,J 2 =8.4Hz, 4H), 7.22(d, J=8.0Hz, 2H), 7.19(d, J=3.6Hz, 2H), 7.07(d, J...
Embodiment 2
[0063] The characterization of compound I-1 and compound II-1 photophysical properties, as shown in Table 1:
[0064] Table 1 Characterization of photophysical properties of compound I-1 and compound II-1 in different solvents
[0065]
[0066] Figure 4 It is a characterization diagram of the photophysical properties of compound I-1; (A) the ultraviolet absorption spectrum of compound I-1, and its fluorescence emission spectrum (40μM) in phosphate buffer or 1,4-dioxane; (B) Fluorescence emission spectrum (40 μM) of compound I-1 in the mixed solution of 1,4-dioxane and water continuously increasing 1,4-dioxane content, and the excitation wavelength is 371nm; (C) Compound I-1 (10μM) in the mixed solution of 1,4-dioxane and water, the ratio change diagram of the fluorescence emission intensity at 463nm and the maximum emission wavelength change diagram with increasing 1,4-dioxane content ; (D) schematic diagram of LUMO and HOMO energy levels of compound I-1;
[0067] Fig...
Embodiment 3
[0073] Characterization of the photoactivation process of compound I-1:
[0074] Figure 7 It is a characterization diagram of the photoactivation process of compound I-1; (A) compound I-1 in liposome solution with light (40mW / cm 2 ) time-varying ultraviolet absorption spectrum (40μM); (B) compound I-1 in liposome solution with light (40mW / cm 2 ) time-varying fluorescence emission spectrum (40μM), the excitation wavelength is 371nm; (C) compound I-1 in liposome solution with light (40mW / cm 2 ) time-varying fluorescence emission spectrogram (40μM), the excitation wavelength is 488nm; (D) the absorption intensity of compound I-1 in liposome solution at 371nm and 481nm varies with light (40mW / cm 2 ) time ratio change figure; (E) Fluorescence emission intensity of compound I-1 in liposome solution at 445nm with light (40mW / cm 2 ) Ratio change figure of time, the excitation wavelength is 371nm; 2 ) time ratio diagram, the excitation wavelength is 488nm.
[0075] Such as Figu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com