Human body gait monitoring algorithm based on dynamic time planning
A technology of dynamic time planning and human body, applied in computing, complex mathematical operations, computer parts, etc., and can solve problems such as low recognition accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
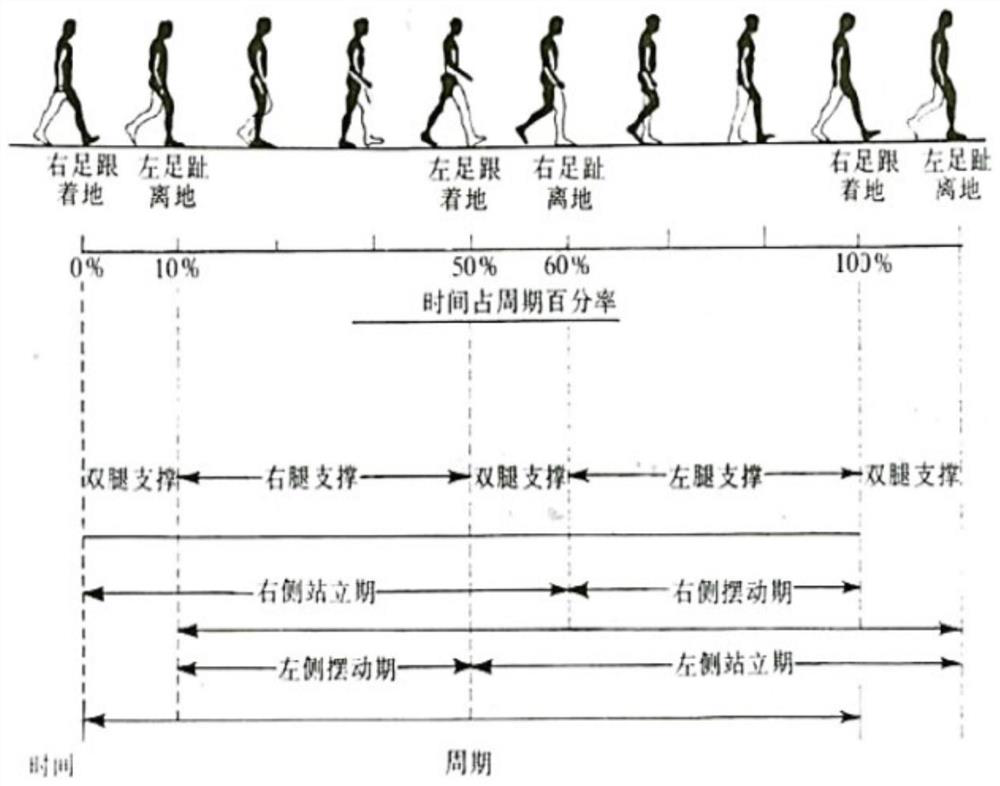
[0043] A human gait monitoring algorithm based on dynamic time planning in this embodiment, such as Figure 8 As shown, the algorithm is implemented through the following steps:
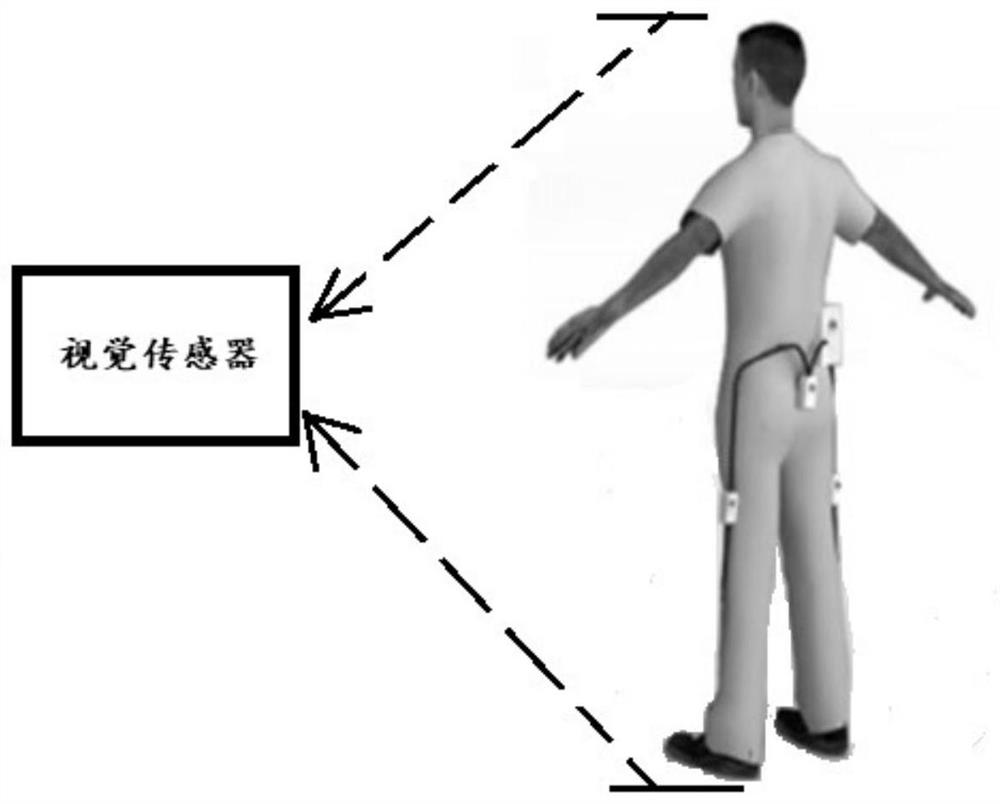
[0044] Human gait video acquisition using visual sensors, such as image 3 Shown, the steps of building a human gait model;
[0045] Based on the human gait video collected by the visual sensor, a human gait model including space, time, and motion trends is established through deep convolution, and the skeleton nodes of the human body during normal walking are obtained; 20 human skeletons are selected from these skeleton nodes through in-depth analysis Key nodes, and calculate the corresponding position of the key skeletal nodes of each gait; conduct in-depth analysis on the movement and position changes of human skeletal data nodes during walking, extract the characteristic parameters of human walking posture, and analyze based on the combination of dynamic time warping and gait parameters Under t...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0067] The difference from Embodiment 1 is that in this embodiment, a human gait monitoring algorithm based on dynamic time planning, the K-means clustering algorithm uses dynamic time warping, the full name is Dynamic Time Warping, abbreviated as DTW: Use dynamic programming (DP) to find the smallest matching path of two different sequences, eliminate the difference on the time axis, and expand or shorten the length of the unknown until it is consistent with the length of the reference template, this method can maximize the degree of overlap . Since the time for different people to perform the same action is not exactly the same, the general algorithm requires that the lengths of the feature quantities of the two sequences should be equal, and the feature values of the two sequences on the time axis should also correspond to each other. The DTW algorithm is currently the most effective solution to this problem. way.
[0068] Let the sequence of the reference template be X ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0077] The difference from Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2 is that in this embodiment, the human gait monitoring algorithm based on dynamic time planning, the human gait video collection using the visual sensor, and the establishment of the human gait model In the step, it is also necessary to assemble a PC, an infrared emitter and an infrared sensor;
[0078] The visual sensor adopts the Kinect somatosensory controller launched by Microsoft. The device is equipped with a three-dimensional somatosensory camera sensor, which can simultaneously obtain human body depth image information, color image information and human skeleton information, and can communicate with a PC through a USB interface. The infrared emitter is used in conjunction with the infrared sensor to obtain 3D depth information. According to the principle of infrared emission and reception, the closer the object is to the camera, the brighter it will be, otherwise it will be darker. Use the self-developed detection ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com