Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae and application thereof
A technology of Erysipelas erythematosus and a preservation number, which is applied in the field of biology, can solve the problems of poor immune effect of Erysipelas erythematosus type 1 and type 2 bacteria, etc., and achieves the effect of significant technological progress.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Embodiment 1 bacterial strain source background
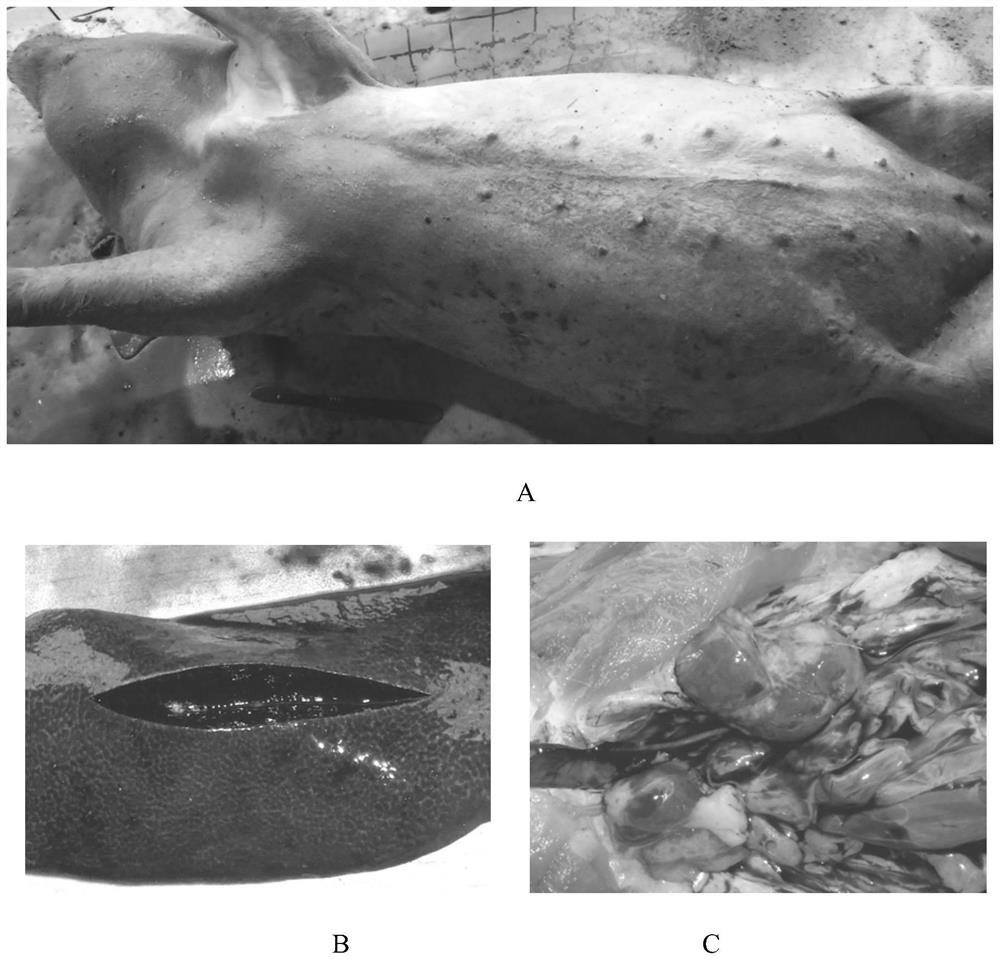
[0019] The strain was isolated in 2015 from the heart of a diseased fattening pig (above 100kg) raised in a pig farm in Fengxian, Shanghai. On the afternoon of the first day, the diseased pigs suffered from lack of energy, red skin, and a fever of 40°C to 41°C. They died suddenly the next morning. The autopsy found enlarged spleen and lymph nodes throughout the body, hemorrhage in the throat and heart, emphysema, and pancreatic edema. , Kidneys are fragile, and other organs have no obvious lesions. The body surface and main necropsy lesions of diseased pigs can be seen in figure 1 A, 1B and 1C.
Embodiment 2
[0020] Example 2 strain isolation and identification
[0021] 2.1 Isolation and culture of bacteria
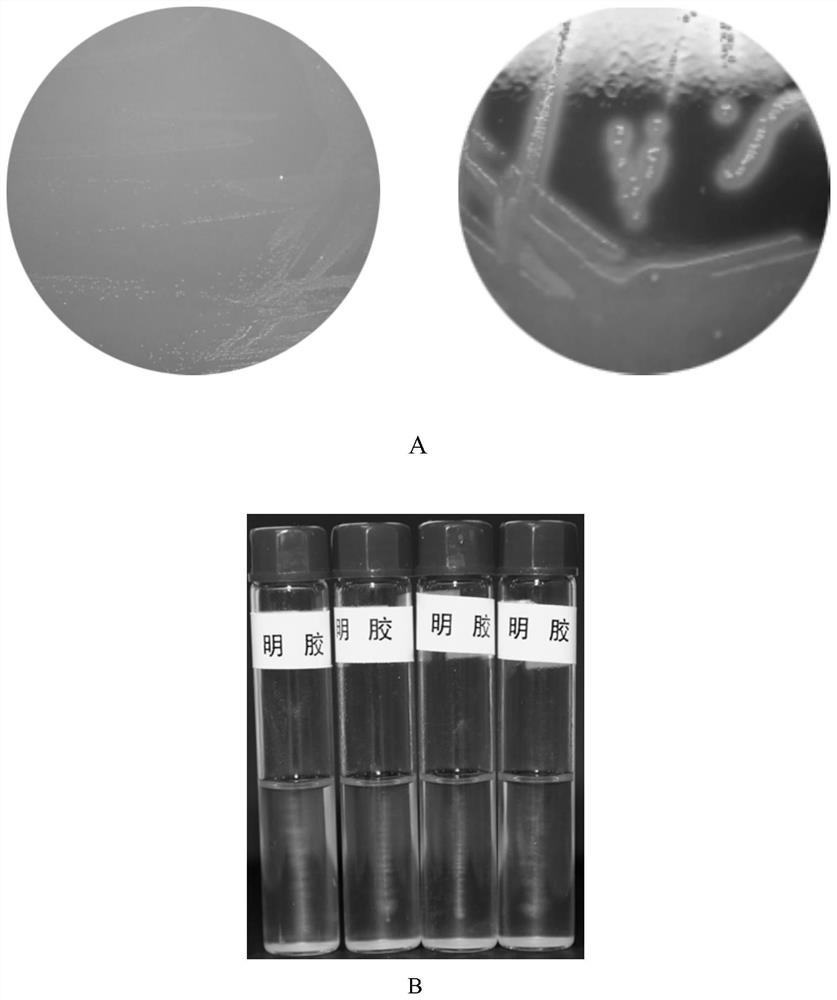
[0022] 2.1.1 Gently touch the aseptically collected infected pig disease material (including heart, liver, spleen, lung) to the culture medium of Columbia blood plate (added with 5% defibrated sheep blood), and inoculate it with a sterile inoculation loop. at 37°C and 5% CO 2 Environmental cultivation 24h ~ 48h. After culturing for 24 hours (the left picture), pinpoint-sized colonies can be seen at all the inoculation sites of the diseased materials on the medium, showing alpha hemolysis, and the hemolysis circle is narrow grass green; after culturing for 48 hours (the right picture), the colonies become larger to a diameter of 0.5 Around mm, the hemolytic circle becomes larger and the hemolysis is obvious. Such as figure 2 As shown in A.
[0023] 2.1.2 Inoculate suspicious colonies into gelatin medium by puncture, culture at 22°C for 48 hours, and grow like a test tube ...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3 Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae isolate mouse immune protection test
[0047] 3.1 Experimental animals
[0048] Clean grade BALB / c mice, 18-20g.
[0049] 3.2 Challenge strains
[0050] 3.2.1 Strain: CVCC 43005——type 2 (from China Veterinary Microorganism Culture Collection Management Center), the original 43-5 strain, an inactivated vaccine production strain, and a virulent strain.
[0051] CVCC 4060 (China Veterinary Microbiological Culture Collection and Management Center)—type 1a, former JD-2012 strain, clinical isolate, virulent strain.
[0052] 3.2.2 Determination of minimum lethal dose (MLD)
[0053] 3.2.2.1 Dilute the bacterial solution to 0.5McF (about 1×10 8 CFU / mL).
[0054] 3.2.2.2 Take 10 -3 、10 -4 、10 -5 、10 -6 Four dilutions, 3 mice for each dilution, and 0.1 mL was injected subcutaneously in the neck of each mouse.
[0055] 3.3 Preparation of vaccine
[0056] 3.3.1 Take the freeze-dried strain of SHFX14035B strain (CGMCC No: 23390), place ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com