Low-leakage amplifier biasing circuit
A bias circuit and amplifier technology, applied in amplifiers, parts of amplifying devices, improving amplifiers to reduce temperature/power supply voltage changes, etc. The effect of reducing static power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
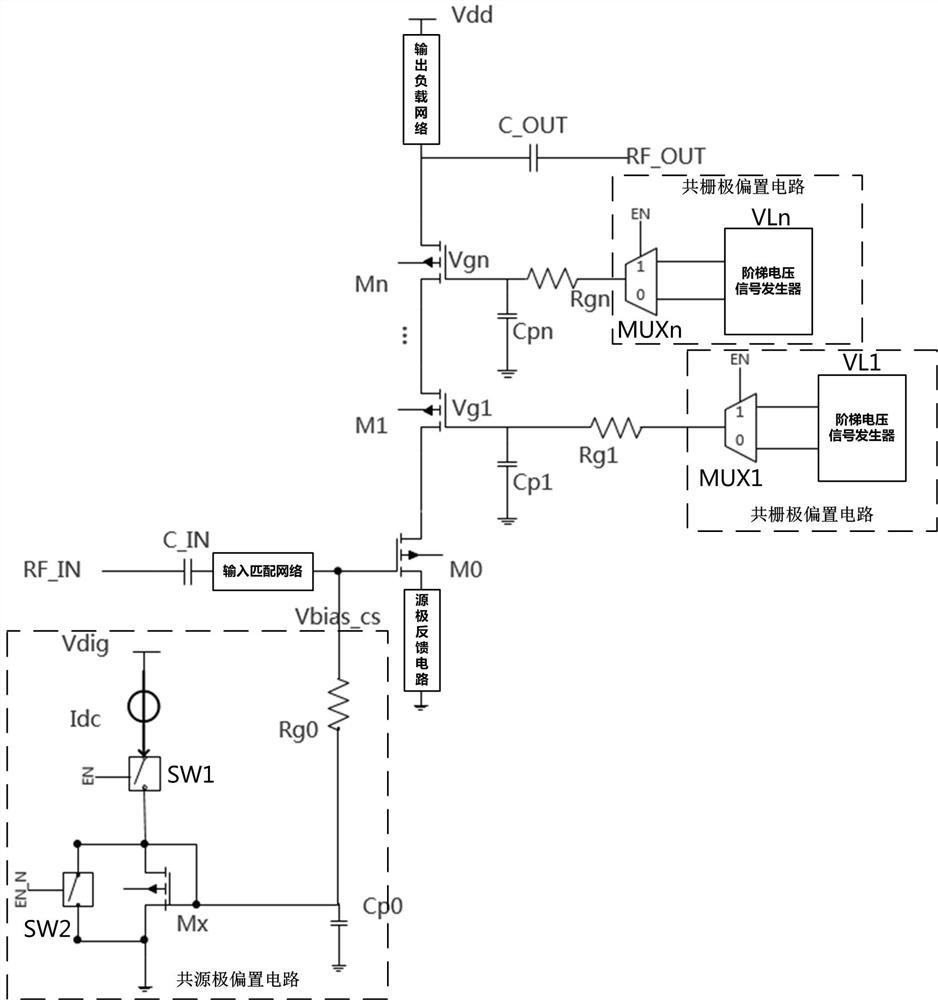
[0041] Figure 4 It is the bias circuit diagram of the low leakage amplifier according to the present invention, such as Figure 4 As shown, the low leakage amplifier bias circuit of the present invention includes a common source bias circuit and a plurality of common gate bias circuits, wherein,
[0042] The common source bias circuit, the output end of which is connected to the gate of the common source transistor M0 of the amplifier, provides source bias voltage for the common source transistor M0 of the amplifier.
[0043] A plurality of common-gate bias circuits are respectively connected to the gates of the common-gate transistors M1~Mn of the amplifier through the isolation resistors Rg1-Rgn to provide the common-gate bias voltage Vg1~Mn for the multiple common-gate transistors M1~Mn of the amplifier. Vgn.
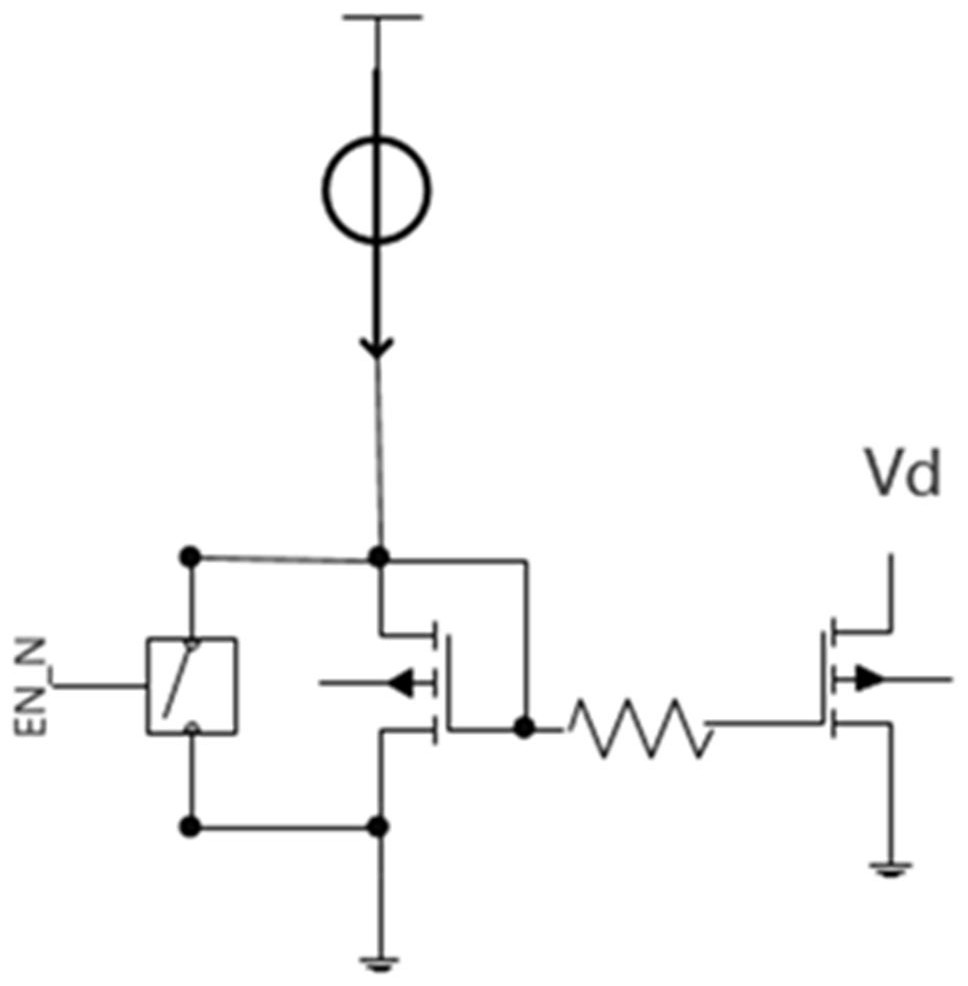
[0044] In the embodiment of the present invention, the common source bias circuit includes a common source bias transistor Mx, a current source Idc, an isolation ...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Figure 5 It is a circuit diagram of a ladder voltage signal generator according to the present invention, such as Figure 5 As shown, the ladder voltage signal generator (VL1-VLn) of the present invention includes a plurality of resistors (R0-Rn) with the same resistance value connected in series to divide the voltage of the logic power supply (Vdig), and extract the intermediate node to turn on the gate voltage Vgn and The turn-off voltage Voff is used as the common gate bias voltage:
[0055] Vgn=(n-1) / n*Vdig,
[0056] Voff=1 / n*Vdig,
[0057] In actual situations, any node Vg can be selected, wherein Vgn is the turn-on gate voltage, and Voff is the turn-off voltage.
Embodiment 3
[0059] Image 6 It is the gate circuit diagram according to the present invention, such as Image 6 As shown, the gating device (MUX1-MUXn) of the present invention is realized by two sets of NMOS and PMOS switches:
[0060] Vout=Vgn*EN+Voff*(1-EN),
[0061] When EN=1, the amplifier is enabled, and the strobe (MUX1-MUXn) outputs the on-gate voltage Vgn to the gate; when EN=0, the amplifier is turned off, and the strobe (MUX1-MUXn) outputs the off-voltage Voff.
[0062] In the embodiment of the present invention, the common-source bias circuit forms a current mirror by the common-source bias transistor Mx and the common-source transistor M0 of the amplifier, and the amplification part of the amplifier is the same as that of the existing amplifier.
[0063] In amplifier off state, EN=0:
[0064] The first switch SW1 is turned off, the current source Idc is turned off, the second switch SW2 is turned on, and the common source bias voltage Vbias_cs is pulled down to ground;
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com