Method for extracting metallic iron from zinc kiln slag
A technology for extracting metal and kiln slag, which is applied in the field of zinc kiln slag and metal iron extraction, can solve the problems of low utilization rate and waste of metal resources, achieve high recovery rate, increase reaction rate, and concise process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 A method for determining component components in a molten salt system
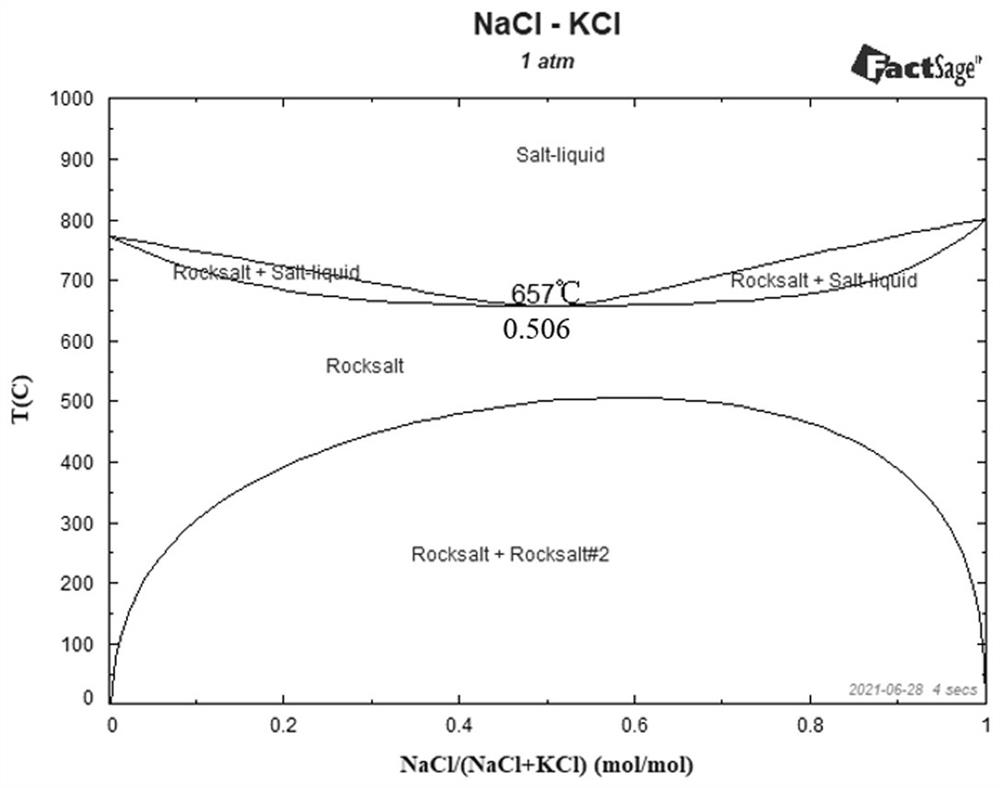
[0041] The following six groups of melting salt systems are prepared separately. 1 -α 6 And the melting of the six groups of solids were measured separately, as shown in Figure 1:
[0042] alpha 1 : 1 mol (58.5 g) no water chloride;
[0043] alpha 2 : 0.2 mol (11.7 g) No aqueous sodium chloride and 0.8 mol (59.6 g) potassium chloride;
[0044] alpha 3 : 0.4 mol (23.4 g) No aqueous sodium chloride and 0.6 mol (44.7 g) no water supply;
[0045] alpha 4 : 0.6 mol (35.1 g) No water sodium chloride and 0.4 mol (29.8 g) no water-free potassium chloride;
[0046] alpha 5 : 0.8 mol (46.8 g) No aqueous sodium chloride and 0.2 mol (14.9 g) potassium chloride;
[0047] alpha 6 : 1 mol (74.5 g) no water supply;
[0048] Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that the molar ratio of sodium chloride and potassium chloride is 1: 0.4-2.5, the state of the molten salt system reaches an optimum value, and the temper...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2 A method of extracting metal iron from a zinc kiln?
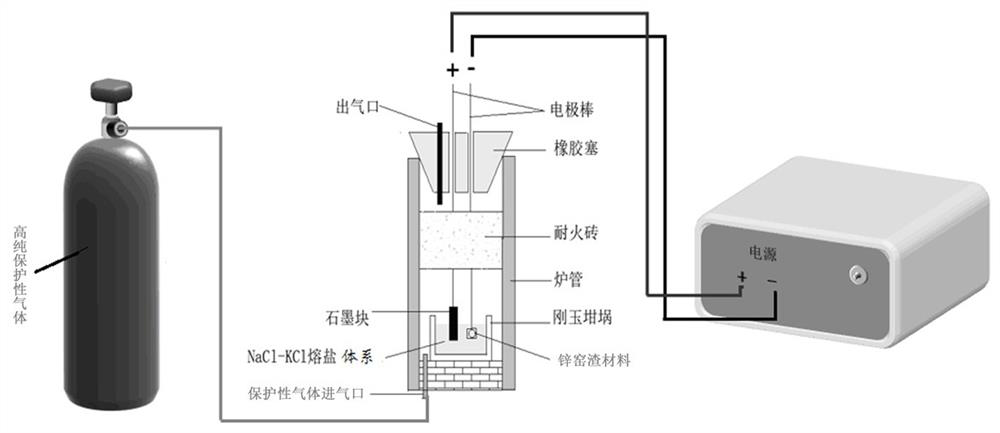
[0050] The reaction principle of this embodiment figure 2 .
[0051] This embodiment includes the following steps in turn:
[0052]a. Take zinc kiln slag (i.e., the leaching residue (zinc tailings) generated by the zinc mine (zinc tailings) is added to a quantity of coke, and the residue produced by metal recovery of zinc and lead is used in the rotary kiln. In the ball mill, the powder is made to a uniform particle size, and 10 kg is taken under the conditions of the pressure of 8 Mp into a block shape, and the hunch furnace is sintered at a temperature of 700 ° C for 6 h to enhance the hardness of the zinc kiln slag material. Zinc kiln slag material, spare; detected, the hardness of zinc kiln slag material is 7.8Hb;
[0053] b. Take 10,000 mol (585 kg) of anhydrous sodium chloride and 10000 mol (745 kg) of anhydrous hydrazed potassium chloride. After grinding, mix evenly, first rises to 160 ° C and heat insul...
Embodiment 3-7
[0057] Example 3-7 Method for extracting metal iron from zinc kiln
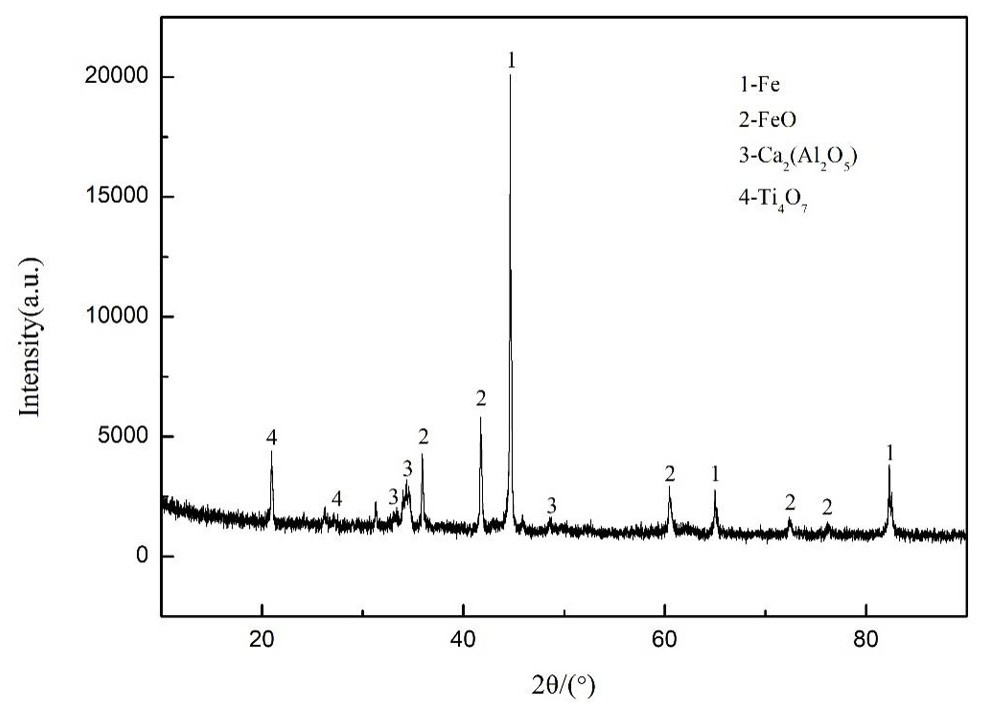
[0058] Examples 3-7 are a method of extracting metal iron from zinc kiln, and they are based on figure 2 The reacting principle shown is realized, and their steps are substantially the same as in Example 1, and the difference is only the different process parameters, and the details are shown in Table 1:
[0059]
[0060]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com