Method for detecting and evaluating levofloxacin environmental risk by using paramecium biomarkers and IBR
A biomarker, levofloxacin technology, applied in biological testing, measuring devices, material inspection products, etc., can solve the problems of lack of comprehensive analysis and evaluation of IBR, lack of pertinence, and low degree of standardization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
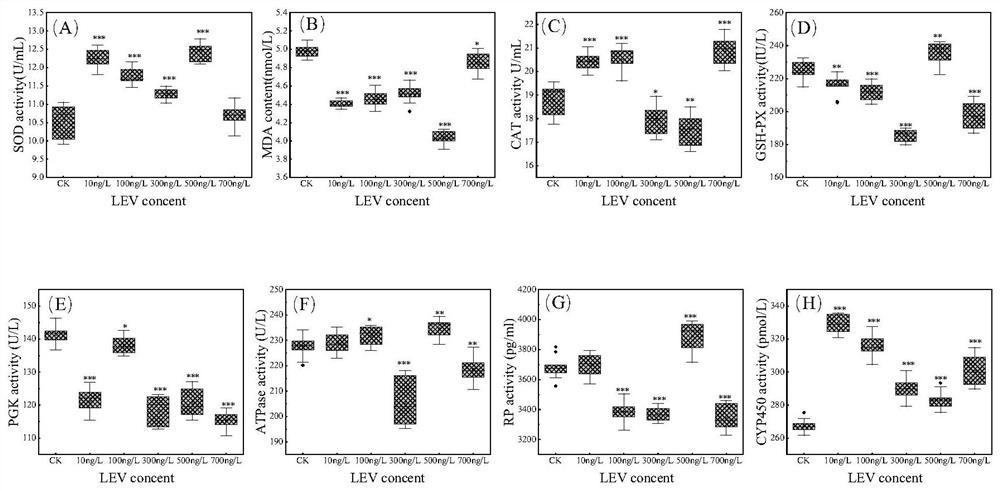
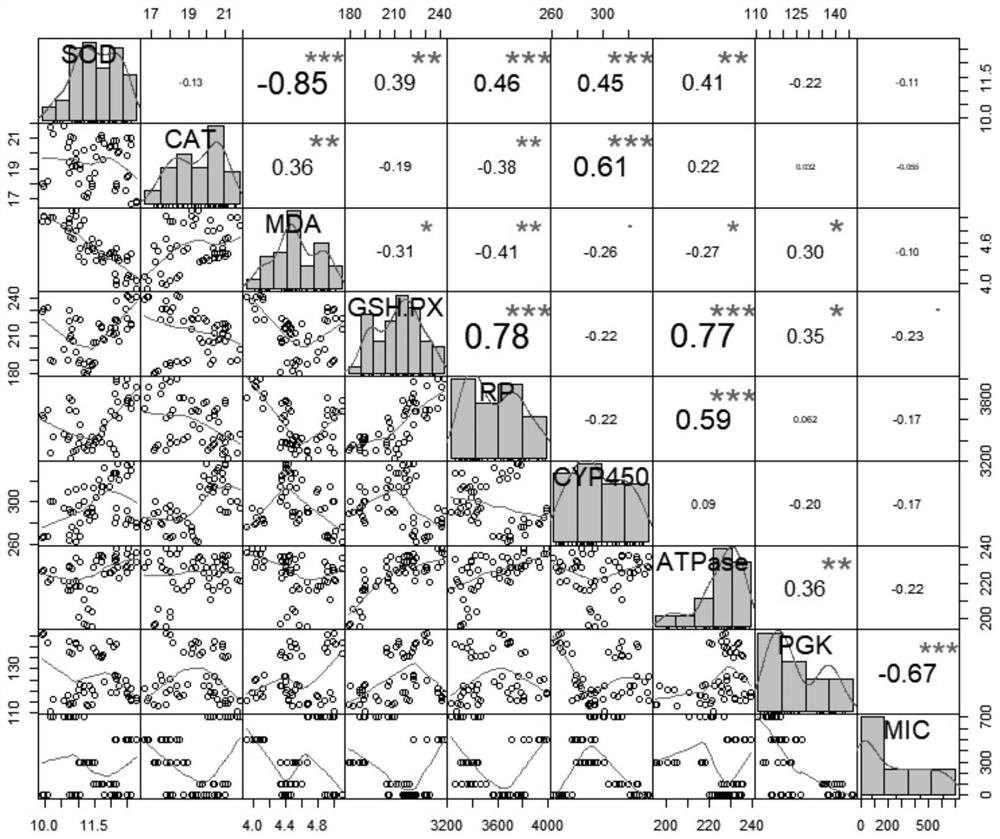
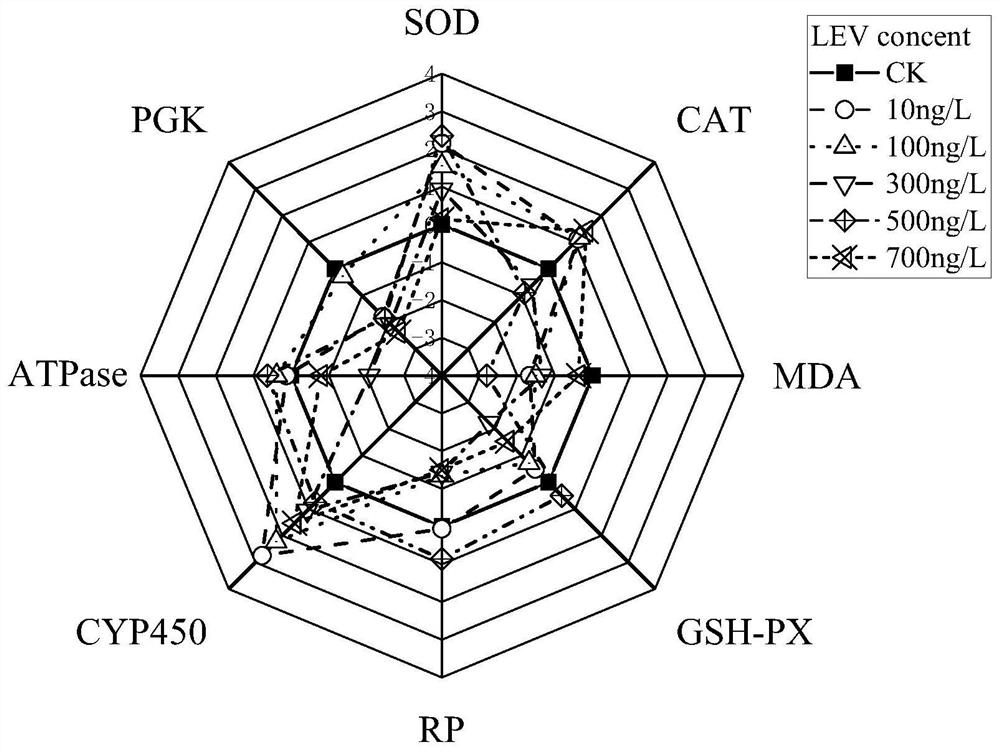
[0053] 1. Materials and methods
[0054] 1.1 Indicator organisms
[0055] Paramecia (Parameci μm ca μdat μm), Cilia, Oligomembrane, Hymenostomy, Paramecia, Paramecia genus. Widely distributed in still water bodies rich in organic matter. It is sensitive to the stimulation of environmental pollutants, so it is often used in the evaluation research of environmental pollutants.
[0056] 1.2 Cultivation of Paramecium
[0057] It can be collected in fresh water bodies rich in plankton, pick single cells, wheat grain culture medium, establish monoclonal culture lines in a constant temperature and humidity incubator at 20-25°C, starvation-induced conjugation, large-scale pure culture, and logarithmic growth Phase individuals were used for levofloxacin testing.
[0058] 1.3 Setting of detection concentration range of levofloxacin
[0059] According to various literature reports and environmental monitoring reports, the experimental concentration of levofloxacin in the water and soi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com