Foam microstructure modeling method based on foaming process
A technology of foaming process and mesostructure, applied in 3D modeling, image data processing, special data processing applications, etc., can solve the problems of difficult microstructure of foam, low porosity, high cost, etc., and achieve easy shape Simple regulation and modeling methods and wide application range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
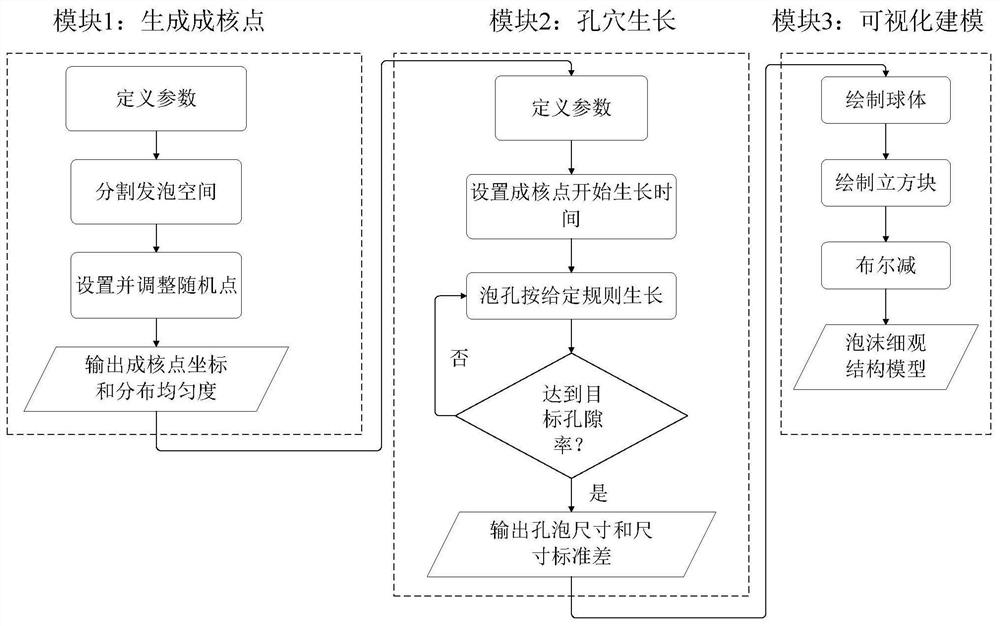
[0063] The superiority of the foam three-dimensional microstructure model modeling method of the present invention is verified.
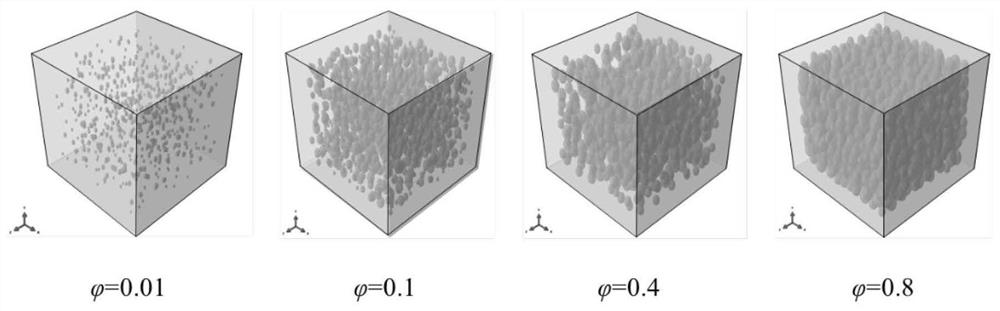
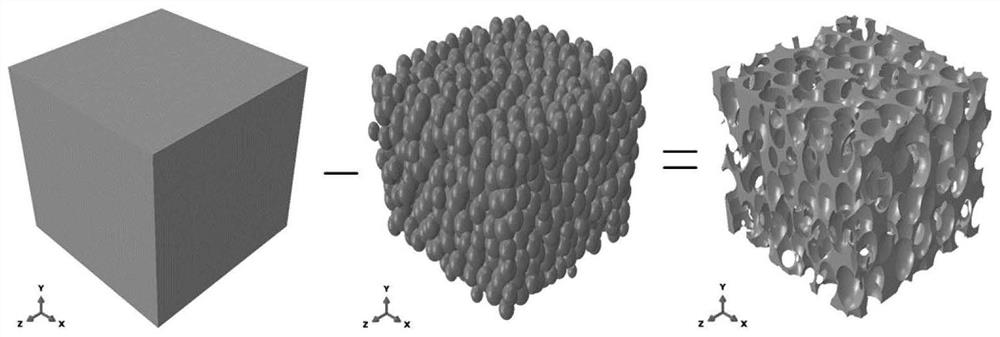
[0064] Consider the mesoscopic structural model of coal-based carbon foam with porosity equal to 0.8, ellipsoidal pores, and pore anisotropy rate equal to 1.83, and the size of the model is 2mm×2mm×2mm. figure 2 represents the porosity during cell growth The growth conditions of cells are equal to 0.01, 0.1, 0.4 and 0.8, respectively, where the ball represents the cell and the cube represents the foaming space. from porosity The distribution of nucleation points in the foaming space can be seen in the figure. image 3 Shown is the process of obtaining the foam mesostructure model by Boolean subtraction of the foaming region model and the cell model. First, all the cells are subjected to Boolean addition operation, and then the foaming region model is taken as the object, and the cell model after the Boolean addition is subtracted , to get the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com