Hyper-abrupt change variable capacitance diode
A varactor diode, N-type technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, circuits, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problem that the variable capacitance ratio of varactor diodes is difficult to increase, etc., to reduce series resistance, increase zero-bias junction capacitance, increase doping The effect of impurity concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
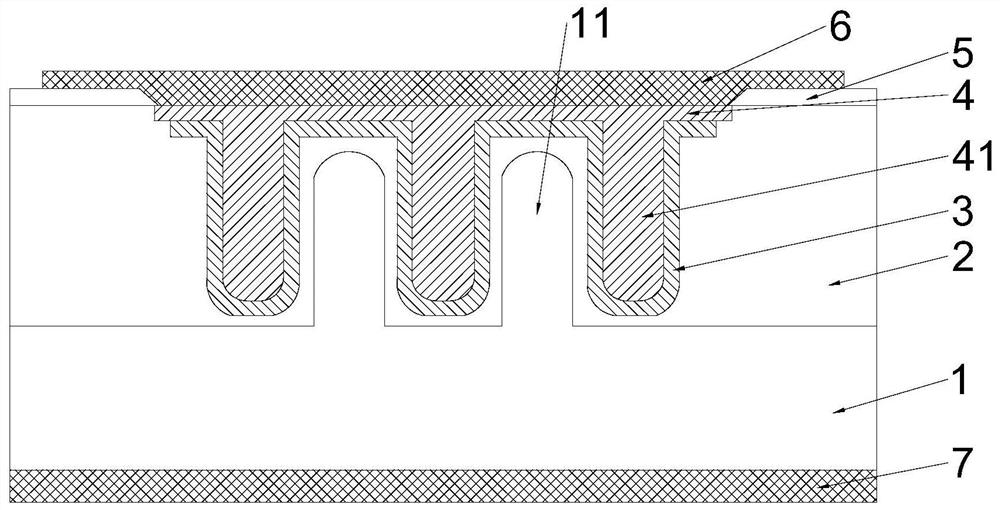
[0034] Such as figure 1 As shown, a hyperabrupt varactor diode, including: N-type heavily doped substrate 1, N-type lightly doped epitaxial layer 2, N-type doped buffer layer 3, P-type heavily doped layer 4, oxide layer 5 , the front multilayer metal 6 and the back multilayer metal 7; the N-type lightly doped epitaxial layer 2 is arranged on the N-type heavily doped substrate 1, and the N-type doped buffer layer 3 and the P-type heavily doped layer 4 are arranged on the In the upper part of the N-type lightly doped epitaxial layer 2, the N-type doped buffer layer 3 is arranged between the P-type heavily doped layer 4 and the N-type lightly doped epitaxial layer 2, and the oxide layer 5 is arranged on the N-type lightly doped epitaxial layer. On the upper surface of layer 2, the front multilayer metal 6 is arranged above the oxide layer 5 and communicated with the P-type heavily doped layer 4, and the back multilayer metal 7 is arranged under the N-type heavily doped substrate ...
Embodiment 2
[0043] This embodiment provides a method for preparing the hyperabrupt varactor diode as described in Embodiment 1, comprising the following steps:
[0044] Step 1: Forming an N-type heavily doped layer and bump 2 on an N-type heavily doped substrate by photolithography and etching;
[0045] Step 2: forming an N lightly doped epitaxial layer on the N type heavily doped substrate and the N type heavily doped layer;
[0046] Step 3: forming an oxide layer on the N lightly doped epitaxial layer;
[0047] Step 4: forming trenches on the oxide layer by photolithography and etching;
[0048] Step 5: epitaxially forming an N-type doped buffer layer above the trench;
[0049] Step 6: removing excess N-type doped buffer layer by photolithography and etching;
[0050] Step 7: Forming a P-type heavily doped layer by epitaxy above the N-type doped buffer layer and the N lightly doped epitaxial layer;
[0051] Step 8: removing the excess P-type heavily doped layer by etching;
[0052]...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com