Preparation method, product and application of antiferromagnetic nanoparticle biological imaging probe
A nanoparticle and antiferromagnetic technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of antiferromagnetic nanoparticle bioimaging probes, can solve the problem of difficulty in controlling the particle size of nanoparticles, the physicochemical properties of magnetization, and the biocompatibility of antiferromagnetic nanoparticles. Poor and difficult in vivo bioimaging and other problems, to achieve good biocompatibility and availability, reduce toxic side effects, and improve the effect of magnetic resonance imaging
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1: Synthesis of oil phase ferromagnetic nanoparticles
[0048] Dissolve 90 mg of iron acetylacetonate and 100 mg of platinum acetylacetonate in a mixed solution of 415 μl oleylamine, 400 μl oleic acid and 10 ml of dibenzyl ether, react for 30 minutes under an inert atmosphere at 300 ° C, and precipitate with ethanol after the reaction stops to obtain oil phase of antiferromagnetic nanoparticles.
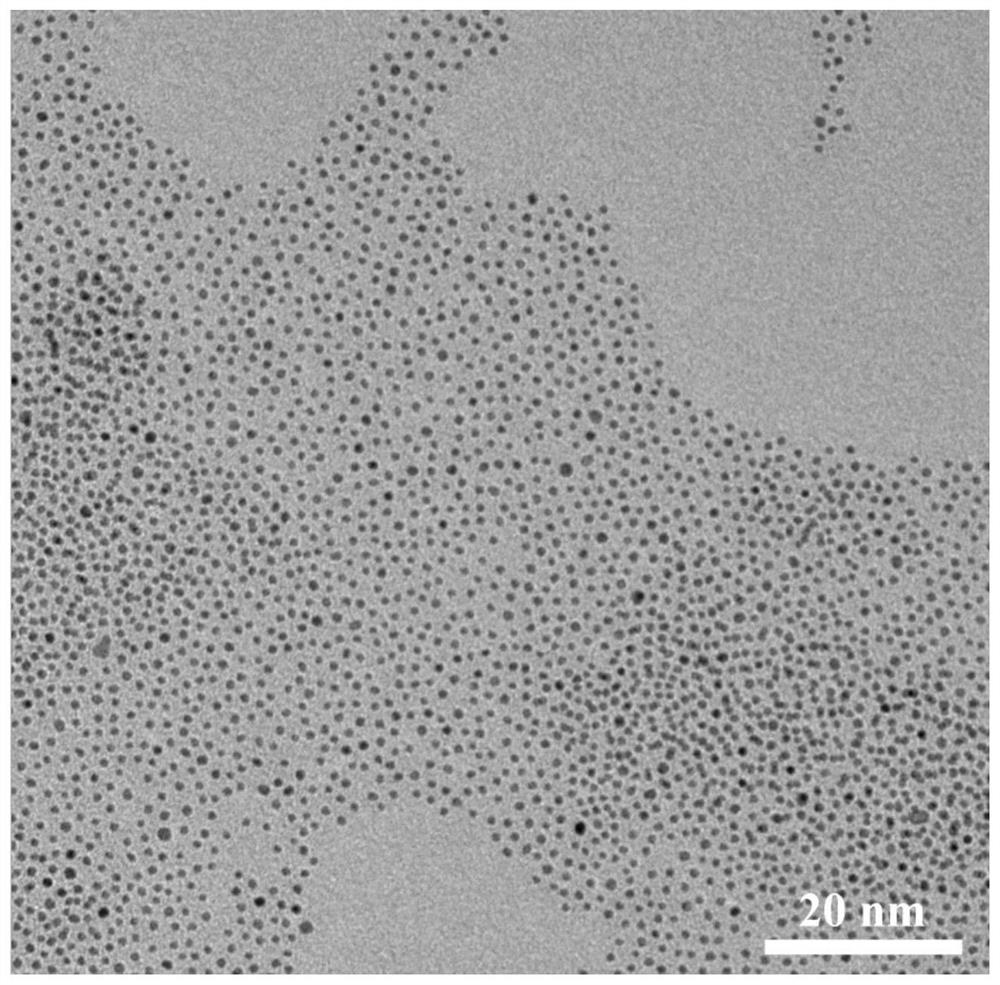
[0049] The morphology of the prepared oil phase ferromagnetic nanoparticles was characterized by transmission electron microscopy, as shown in figure 1 shown.
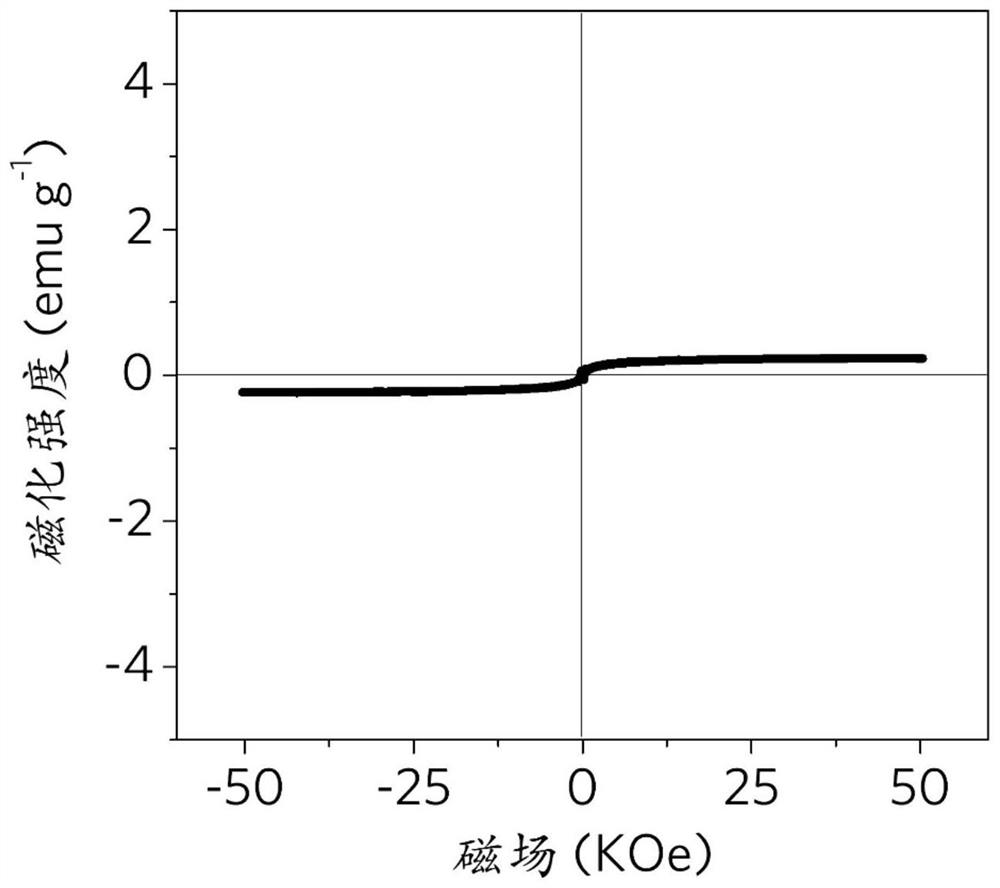
[0050] Using a vibrating sample magnetometer to test its magnetization, the results are as follows figure 2 shown.
[0051] The above results prove that the antiferromagnetic nanoparticles in the oil phase have relatively low magnetization, and the measured magnetization is 0.23 emu / g.
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2: Synthesis of oil phase ferromagnetic nanoparticles
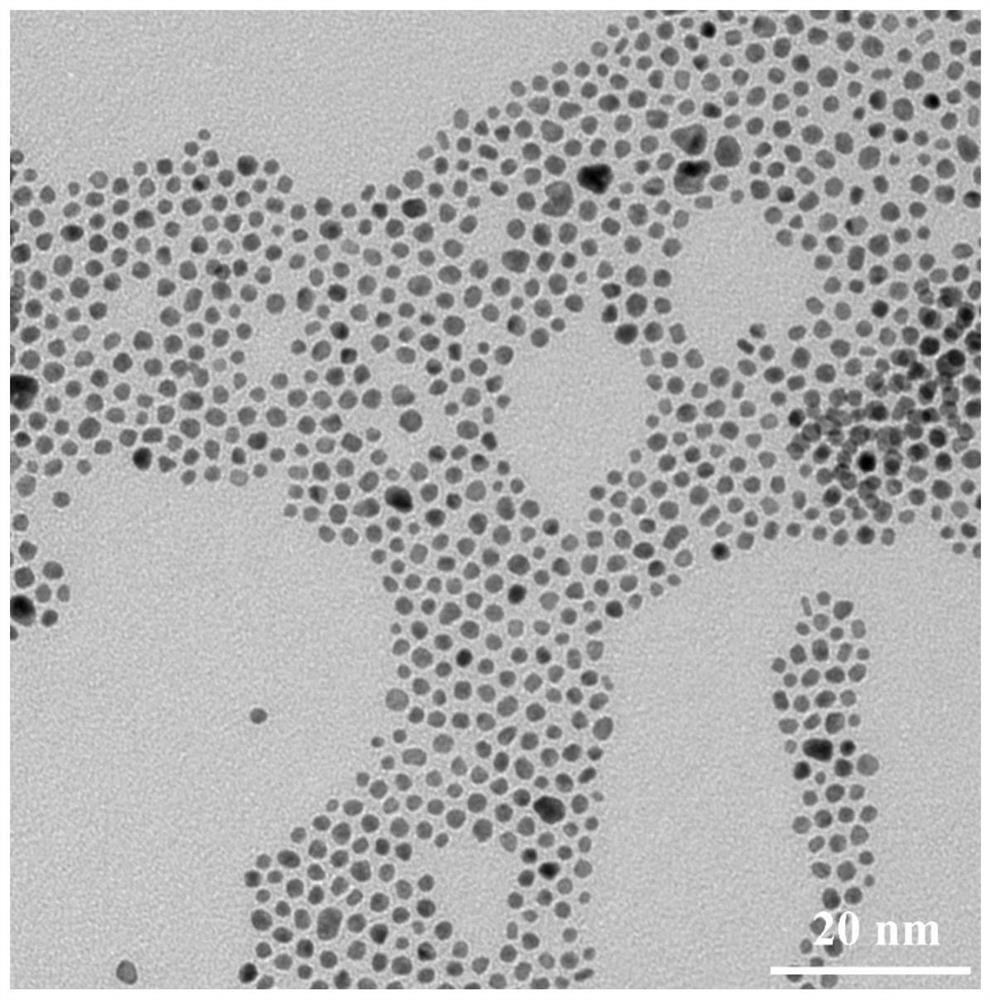
[0053] Synthesized with reference to the preparation process of Example 1, the difference is that the amount of oleylamine and oleic acid added was changed to 800 μl and 830 μl, and antiferromagnetic nanoparticles in the oil phase were also obtained, and the measured magnetization was 4.51 emu / g. Increasing the amount of oleylamine and oleic acid in Example 2 can increase the particle size of the antiferromagnetic nanoparticles in the oil phase.
[0054] The morphology of the oil-phase ferromagnetic nanoparticles prepared by changing the method was characterized by transmission electron microscopy, as shown in image 3 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0055] Example 3: Synthesis of oil-phase ferromagnetic nanoparticles
[0056] Synthesized with reference to the preparation process of Example 1, the difference is that the amount of oleylamine and oleic acid added was changed to 1250 μl and 1200 μl, and antiferromagnetic nanoparticles in the oil phase were also obtained, and the measured magnetization was 4.86 emu / g.
[0057] The morphology of the oil-phase ferromagnetic nanoparticles prepared by changing the method was characterized by transmission electron microscopy, as shown in Figure 4 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com