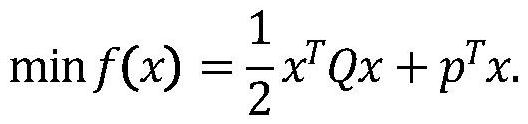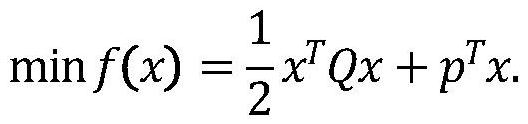Verifiable constrained quadratic programming safety outsourcing calculation method and system
A secondary planning and security outsourcing technology, which is applied in the fields of information security, privacy protection and cloud computing, can solve the problem of meaningless outsourcing, achieve the effect of improving robustness, solving resource constraints, and preventing collusion attacks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
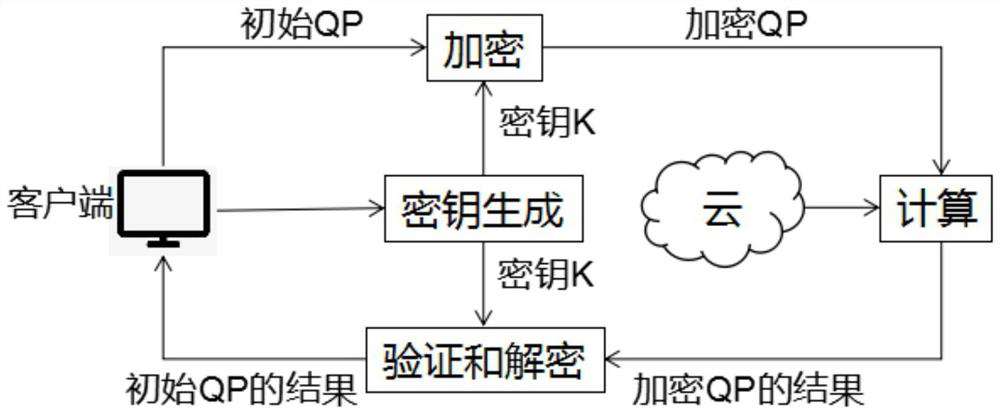
[0039] see figure 1 , a verifiable constrained quadratic programming secure outsourcing computing method, the client needs to hand over the complex task of quadratic programming to the cloud server for computing due to limited local resources. The steps of the entire outsourcing computing process are as follows:
[0040] In the first step, the client performs initialization settings, including generating three random elementary matrices and a random vector;
[0041] In the second step, the client uses the elementary matrix and random vector generated in the first step to construct a new encrypted quadratic programming problem and send it to the cloud server.
[0042] Step 3: After receiving the encrypted quadratic programming problem, the cloud server solves the problem according to the requirements, and returns the result to the client;
[0043] Step 4: After receiving the result, the client first verifies the result. If it passes the verification, it decrypts to get the ans...
Embodiment 2
[0046] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, and the special features are as follows:
[0047] In this embodiment, the first step includes three sub-steps:
[0048] Step a, generating a displacement map;
[0049] Step b, generating elementary matrices for encryption;
[0050] Step c, generate a random vector.
[0051] In this embodiment, the described step a is specifically:
[0052] For a given set S = {1, 2, 3, ..., n}, the permutation mapping is expressed as the following form Among them, π(i), i=1, 2,..., n is a certain arrangement of 1, 2,...n; the client needs to generate three permutation maps π 1 (k), π 2 (m), π 3 (n); wherein, π(n) represents a random permutation map, and k, m, and n respectively represent the number of set elements corresponding to the three random permutation maps.
[0053] In this embodiment, the bth step is specifically:
[0054] First, the client generates n random numbers ω 1 , ω 2 ,...,ω n ; Then use the Kronecker f...
Embodiment 3
[0062] This embodiment is basically the same as the above-mentioned embodiment, and the special features are as follows:
[0063] In this embodiment, a verifiable constrained quadratic programming secure outsourcing computing system includes an initialization module for implementing the verifiable constrained quadratic programming secure outsourcing computing method in the above embodiment.
[0064] The verifiable constrained quadratic programming security outsourcing computing system in this embodiment includes the following parts:
[0065] Initialization module: the client generates elementary matrices and random vectors, and stores them in the initial matrix pool to solve the subsequent encrypted initial quadratic programming problem;
[0066] Blind module: the user randomly selects the elementary matrix P from the elementary matrix pool 1 ,P 2 ,P 3 and random vector r to encrypt the original quadratic programming problem to protect the client's private information;
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com