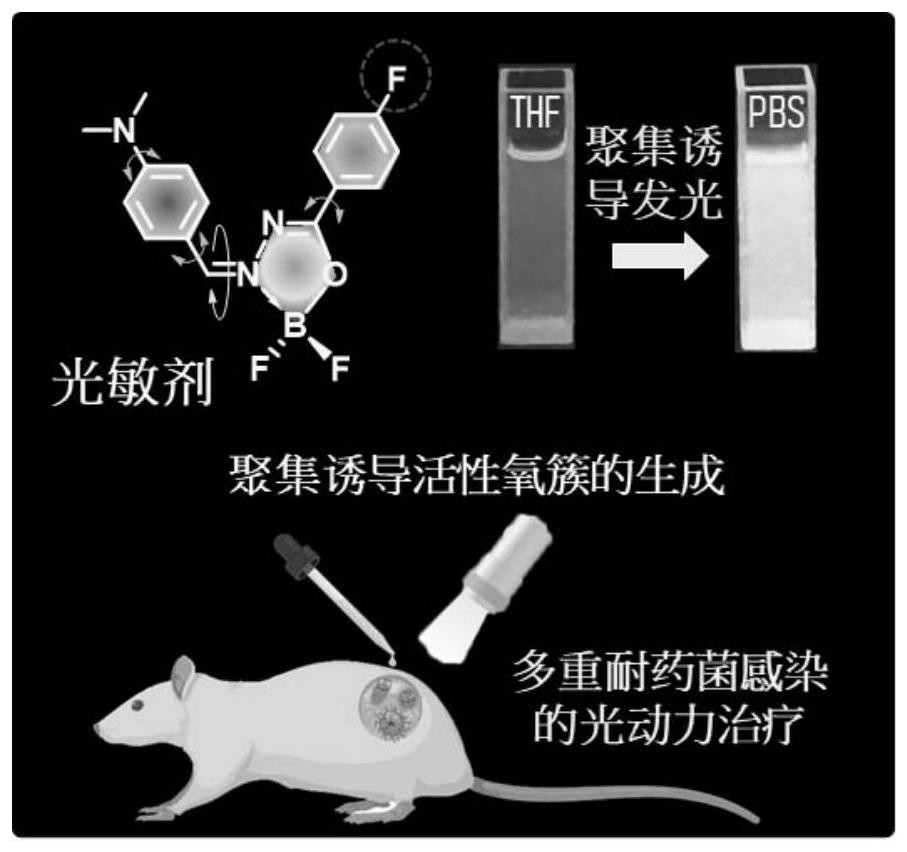
Organic boron photosensitizer based on aggregation-induced emission, and application thereof in treatment of multi-drug-resistant bacterium infection
A technology for aggregation-induced luminescence and multi-drug-resistant bacteria, which is applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of poor inhibition or killing of multi-drug-resistant bacteria, and achieve the effect of good generation of active oxygen clusters and easy synthesis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0084] Embodiment 1: the preparation of product
[0085] (1) Synthesis of DMA-AB
[0086] In a 100mL single-necked round bottom bottle equipped with a condenser, add 4-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde (4-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde, DMA-P-CHO; 1.5g, 10mmol), benzohydrazide (BHA; 1.36g , 10mmol) and ethanol (EtOH; 20mL) solvent, heated to reflux for 24 hours. After the reaction mixture was cooled back to room temperature, it was filtered and washed three times with cold ethanol solvent to obtain a white DMA-AH intermediate solid product, which was directly carried out to the next reaction without further purification after vacuum drying. Add DMA-AH allyltrimethylsilane (ATMS; 2.05mL, 12.9mmol), boron trifluoride diethyl ether (BF 3 OEt 2 1.87mL, 14.87mmol) and dry dichloroethane (DCE; 50 mL) solvent, after heating to reflux for more than two hours, the reaction was monitored with a silica gel plate (TLC); after confirming that the reaction was complete, the solvent was drained, And ...
Embodiment 2
[0103] Example 2: Research on the optics, aggregation-induced luminescence, and generation of active oxygen characteristics of the product
[0104] Two organoboron fluorescent products (DMA-AB-F and F-AB-DMA) are taken as examples to illustrate their optical properties, aggregation-induced luminescence, and generation of active oxygen. The same is true for other products, and details will not be repeated here.
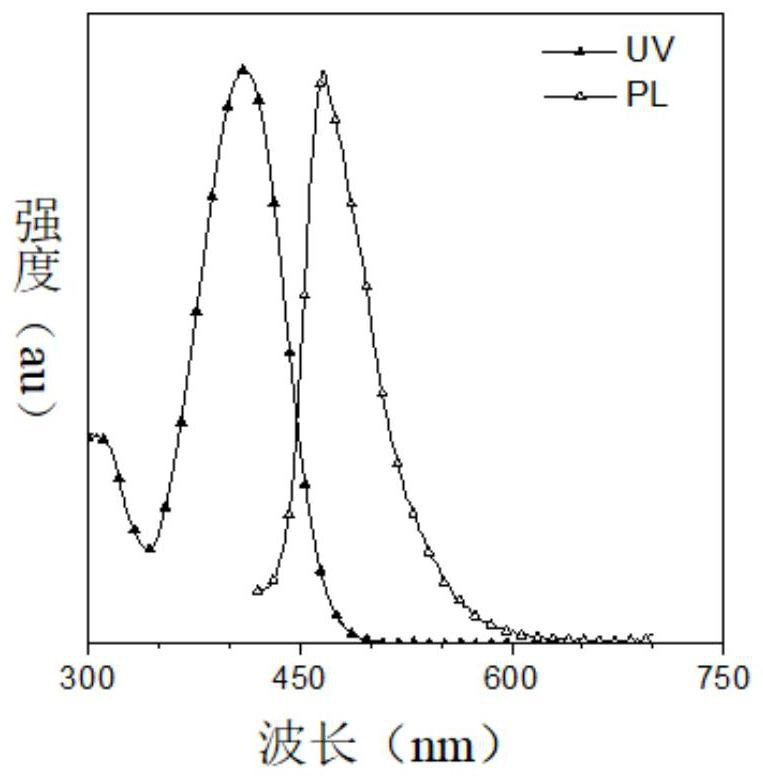
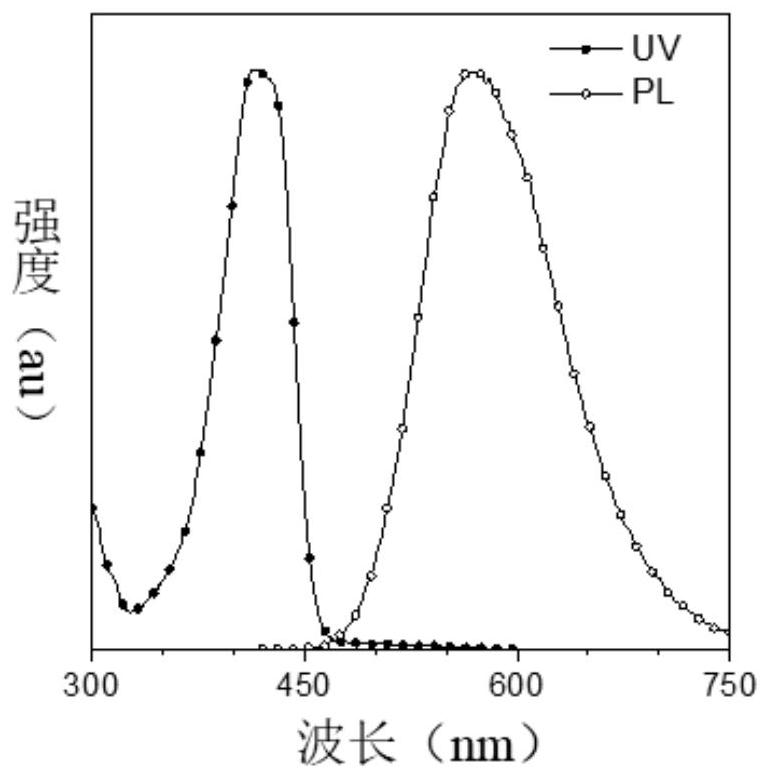
[0105] (1) Research on optical properties
[0106] The ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) absorption spectrum and photoluminescence (PL) spectrum of DMA-AB-F and F-AB-DMA in tetrahydrofuran (THF) solution are respectively as follows figure 2 and 3 shown. The maximum absorption wavelengths of the two products in THF solution are both at 415nm, but the emission wavelengths are at 473 and 555nm respectively, and the Stokes shifts are 58 and 140nm respectively. The main reason is that F-AB-DMA has a larger ground state and This is caused by the difference in the dipole mome...
Embodiment 3
[0115] Embodiment 3: product is in the treatment of multi-drug resistant bacteria infection
[0116] (1) Bacterial culture, staining and imaging
[0117] Multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli (MDR E.coli) and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) were cultured in LB medium under the conditions of 37° C. and 220 rpm. Bacteria were harvested by centrifugation at 3500 rpm for 10 minutes and washed twice. will contain 1×10 9 Bacterial colony forming units (CFU mL -1) in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) solution (10 μM, 100 μL) was transferred to a 1.5-mL microcentrifuge tube. After vortexing, the bacteria were incubated at 37 °C for 1 hour at a shaking speed of 220 rpm. To take fluorescent images, transfer 10 µL of the stained bacteria solution to a glass slide, which is then covered with a coverslip. Such as Figure 15 and Figure 16 As shown, the DMA-AB-F photosensitizer successfully infects multidrug-resistant bacteria using a confocal laser scanning microscop...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com