Group of chimeric antigen receptors (CARS)
A chimeric antigen receptor, antigen technology, applied in the direction of antibody medical components, antibody mimics/scaffolds, receptors/cell surface antigens/cell surface determinants, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0396] Example 1: Generation of rcSso7d-based low affinity single domain binding moieties for CAR panels according to the invention
[0397] In a first example, a strategy for generating low-affinity antigen-binding moieties suitable for use as antigen-binding moieties of a CAR panel according to the present invention is shown. Charge-reduced Sso7d (rcSso7d) is a charge-reduced version of a small (~7 kDa) DNA-binding protein from the archaea Sulfolobus solfataricus. The charge reduction minimizes nonspecific binding due to reduced electrostatic interactions. rcSso7d is a single domain protein antigen binding moiety with high thermostability and monomeric behavior, and is therefore an example suitable for binding to scaffolds. Starting from the well-characterized antigen-binding moiety rcSso7d E11.4.1, which binds to human EGFR with a K of 19 nM d combined (Traxlmayr et al., JBiol Chem. 2016;291(43):22496-22508), by performing an alanine scan, in which we replaced all amino a...
Embodiment 2
[0412] Example 2: Cysteines forming extracellular disulfide bonds prevent full exploitation of the avidity effects that reversibly control CAR function
[0413] Cysteines that form extracellular disulfide bonds in the extracellular hinge region, eg CD8α, can prevent utilization of the affinity effect according to the present invention. This is demonstrated in Example 2, wherein a low affinity mutant of the binding moiety "E11.4.1G32A" of Example 1 is fused to a CAR signaling backbone in which two extracellular cysteine residues in the hinge region of CD8α (UniProt ID P01732, positions C164 and C181) were substituted or unsubstituted with serine residues, respectively. In response to target cells, however, cysteine-containing CAR variants ("Cys") effectively triggered T-cell activation, but serine-containing variants ("Ser") did not or only weakly. Thus, this example illustrates the importance of preventing disulfide bond formation when generating CAR molecules suitable for ...
Embodiment 3
[0428] Example 3: Single-chain variable fragments (scFvs) can trigger CAR aggregation in cell membranes, preventing exploitation of avidity effects that reversibly control CAR function
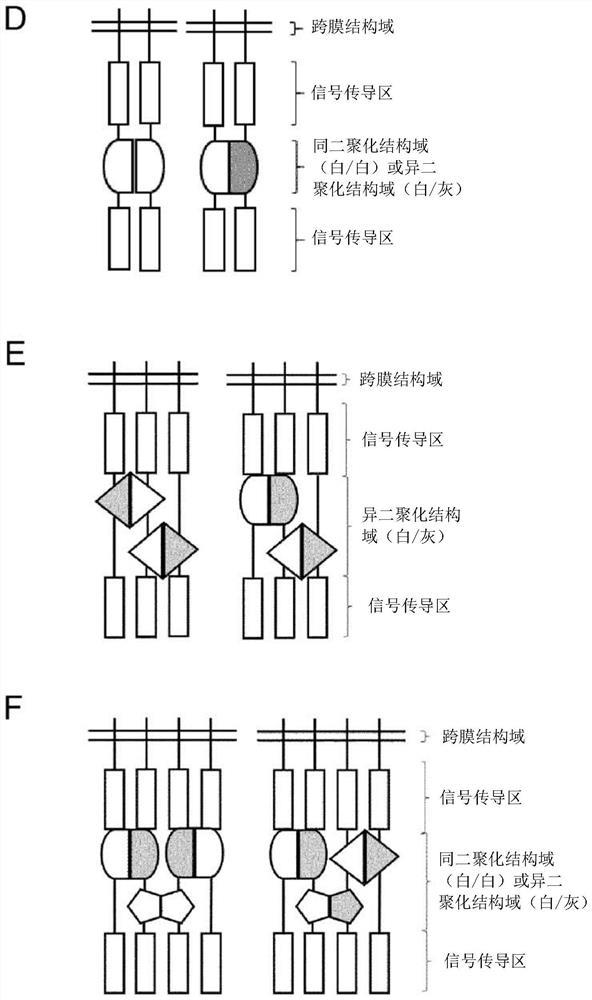
[0429] The third example shows that the integration of scFv-based binding moieties into CAR molecules can prevent avidity effects that exploit combinations of specific recognition antigens. Figure 4 A schematic diagram of the CAR construct shown in A shows the CAR variants tested (4D5-5-8cys-BB-3z, 4D5-5-8ser-BB-3z, 4D5-5(split)-8ser-BB-FKBP(36V )-3z) design. In the example shown, scFv 4D5-5 against HER2 was used as the antigen binding moiety and integrated into a monomeric ("Ser") or dimerized ("Cys") CAR signaling backbone. Figure 4 B shows CAR expression in primary T cells. The potent binding affinity of scFv 4D5-5 was reported as 1.1 μM (Liu et al., Cancer Res. 2015;75(17):3596-3607), which was comparable to that of E11.4.1-G32A. Jurkat T cells expressing a truncated form of HER2 (tHE...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com