Memory allocation method and device in user mode protocol stack
A memory allocation and protocol stack technology, applied in resource allocation, multi-program device, program control design, etc., can solve problems such as increasing CPU consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
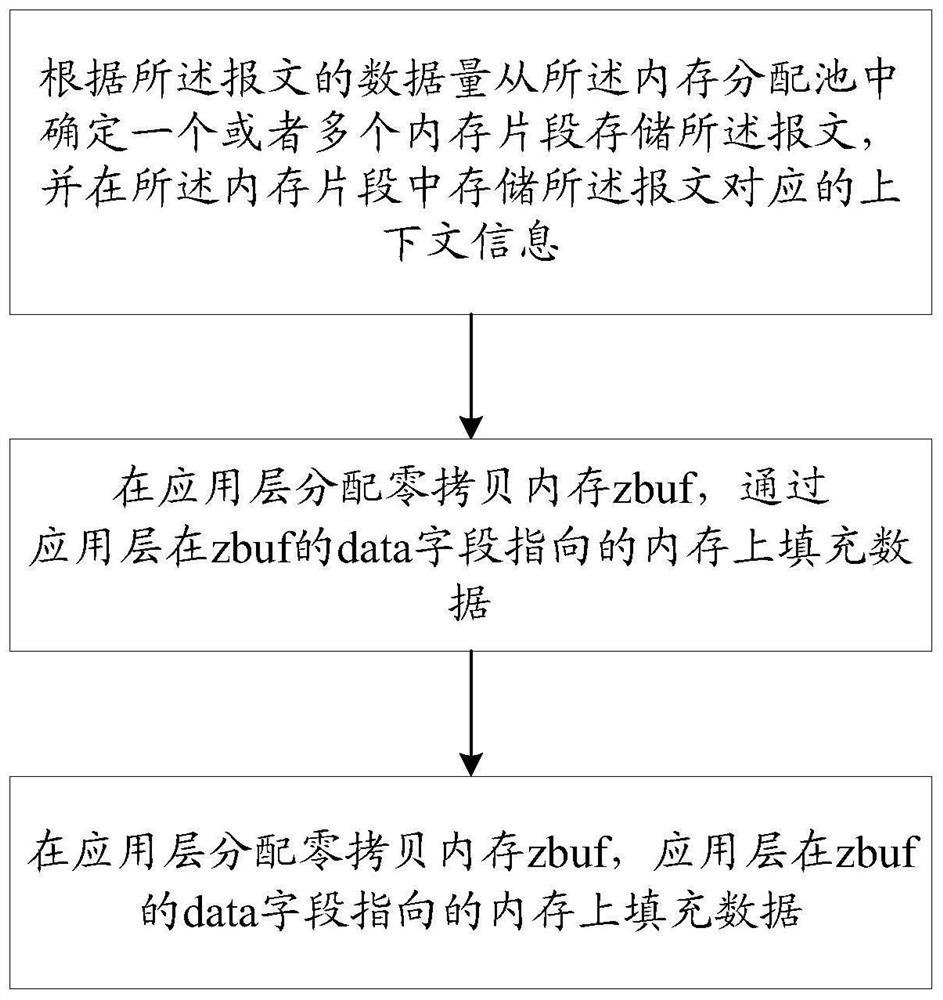
[0076] combine image 3 Describe the memory allocation process of this embodiment:
[0077] In the embodiment of the present invention, a large and continuous space is used as a memory allocation pool (menpool), and the space is divided into multiple fixed-length and aligned segments, and the sizes can be designed as 4K, 8K, 16K, 32K, 64K, 128K etc., the specific size depends on the application scenario. like image 3 The working flow chart of the memory allocator in the example of the present invention is given. Each memory segment reserves fixed-length bytes in its header to store the corresponding context information, including memory size, reference count, and memory first address. The allocation principle of the memory allocator: Since the fragments in the memory allocation pool are prepared in advance, zbuf of any size is allocated, and the fragment with the most suitable size is selected first. If the fragment of the current length has been allocated, use the followi...
Embodiment 2
[0079] combine image 3 Describe the memory allocation process of this embodiment:
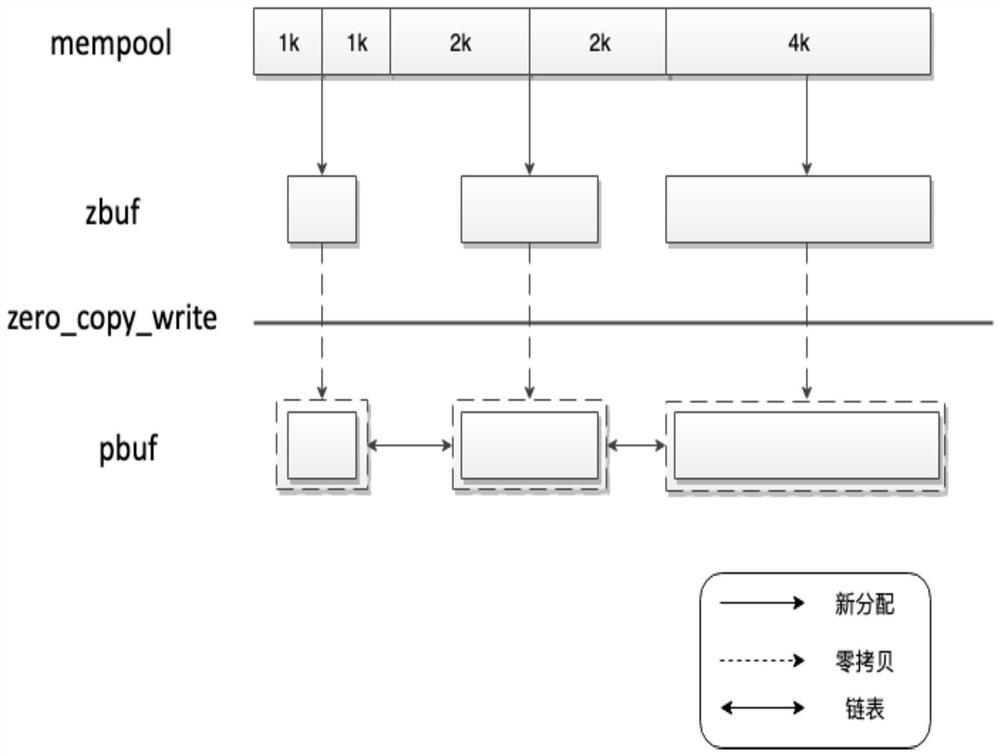
[0080] like image 3 In the memory allocation pool (menpool), multiple 1K, 2K, and 4K memory segments are pre-allocated. The application layer allocates 1K, 2K, and 4K zbuf from the memory allocation pool, and initializes the reference count of zbuf to 1. The application layer Fill data in the memory pointed to by the data field of zbuf, and finally call the write interface to pass the address of data to the protocol stack. Note that the address of zbuf is not passed here. Different from the writing interface of the traditional protocol stack, the copy mode is used to copy from the application layer to the memory space of the protocol stack. The zbuf allocated in the example of the present invention transfers the application layer data space to the user mode protocol stack through DMA mode, and the protocol stack uses additional The memory holds the address and length of the data space, i.e....
Embodiment 3
[0082] Figure 4 The middle is the scenario where the application layer requests to allocate a zbuf, retries 2 times in a row, and writes the zbuf to the protocol stack three times. After the first zbuf is written to the protocol stack, the protocol stack has sent the first half of the data, and the remaining half is in the pbuf queue. When the application layer retries, due to the window limitation of the protocol stack, the first half is written first, the protocol stack uses the new pbuf to save the memory space, and the reference count for zbuf is incremented by one; If the space is continuous, the data length of the directly updated pbuf is the sum of the two, without updating the reference count; when retrying for the second time, use the new pbuf to save, and the reference count is incremented by one. The protocol stack sends the data of the pbuf queue sequentially, and when it receives the response packet of each pbuf, the reference count is decremented by one in turn...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com