Bioelectrochemical device for synchronously degrading chlorophenol in water phase by cathode and anode
A bio-electrochemical, water-phase technology, applied in the fields of electrochemical-biological combined treatment, water pollutants, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of water temperature difficult to meet requirements, difficult to apply directly, high cost, and achieve green environmental protection. Environmental benefits, achieve pollution remediation, avoid costly effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
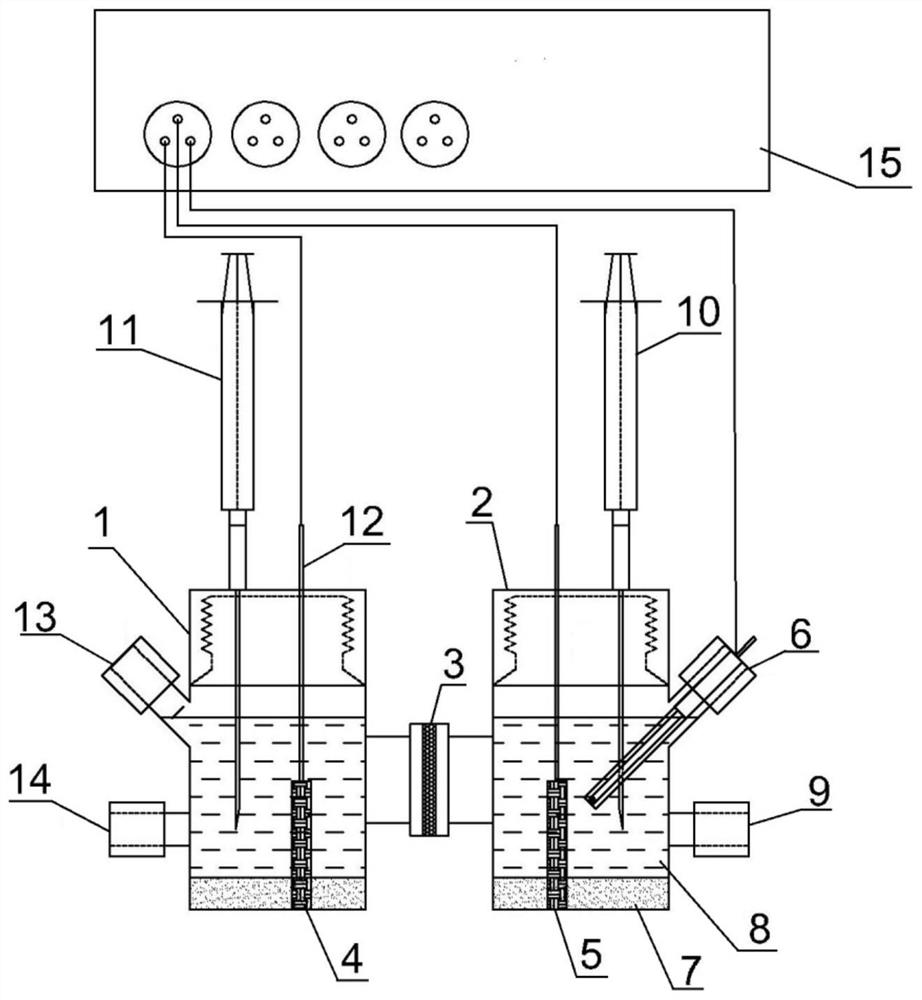
[0034] This embodiment provides a simple bioelectrochemical device for synchronously degrading chlorophenols in the water phase with the cathode and anode, such as figure 1 As shown, the main body of the device includes an anode chamber 1 and a cathode chamber 2, wherein the anode chamber 1 and the cathode chamber 2 are separated by a proton exchange membrane 3, an auxiliary electrode 4 is arranged in the anode chamber 1, and the cathode chamber 2 A working electrode 5 and a reference electrode 6 are arranged inside; a cathode drainage port 9 is arranged on one side of the cathode chamber 2, a cathode charging / sampling port 10 is arranged on the upper part of the cathode chamber 2, and an anode charging port is arranged on the upper part of the anode chamber 1. / Sampling port 11, the auxiliary electrode 4 and the working electrode 5 are respectively pierced with titanium wires 12, through which the titanium wires 12 are connected with an external multi-channel potentiostat 15 t...
Embodiment 2
[0045] A simple bioelectrochemical device for synchronously degrading chlorophenol in the water phase with the cathode and anode of this embodiment, compared with Example 1, the difference is that the electrode potential is not applied to the working electrode through a multi-channel potentiostat, and the circuit system is in an open circuit State, all the other conditions are consistent with embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0047] A simple bioelectrochemical device in which the cathode and the anode can jointly degrade chlorophenols in the water phase in this example is compared with Example 2. The difference is that the homogeneous sediment needs to be sterilized at 121°C for 20 minutes, and the continuous sterilization is 3 day, all the other conditions were consistent with Example 2.
[0048] Examples 2 and 3 use the same main body of the device as in Example 1, with only differences in the open circuit of the circuit system and the sterilization of the inoculated sediment, which are used for the comparison and description of Example 1.
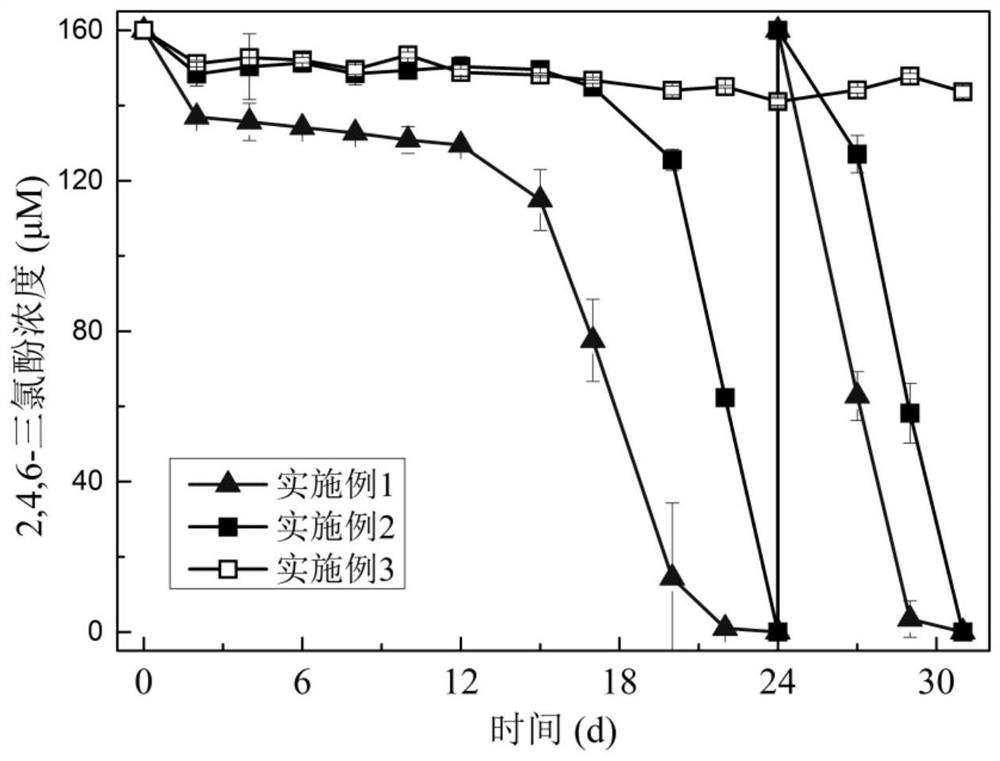
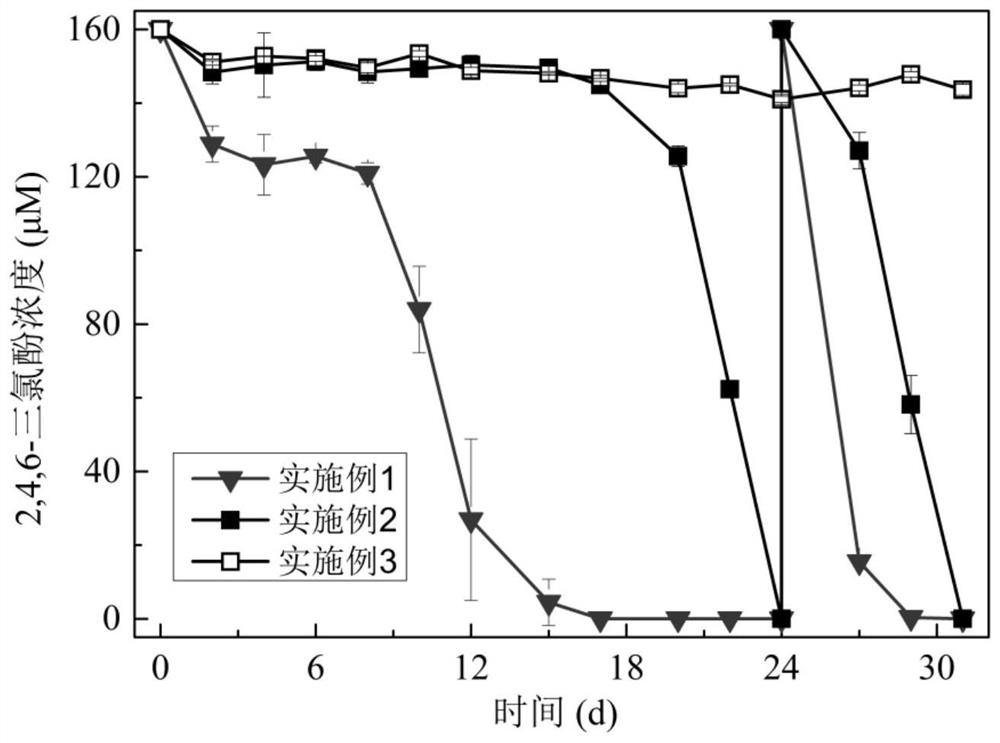
[0049] The degradation diagram of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol in the cathode chamber during the operation of the device in Example 1-3 is as follows figure 2 shown. The concentration of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol in Example 3 remained unchanged. In Example 2, 2,4,6-trichlorophenol was degraded on the 17th day, and the degradation was complete after the 24th day. Comp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com