Preparation method of diiodomethane
A technology of diiodomethane and dichloromethane, which is applied in the field of preparation of halogenated fine chemicals, can solve the problems of high production cost, large amount of high-concentration salt-containing waste water, unreusable catalysts, etc. The effect of production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
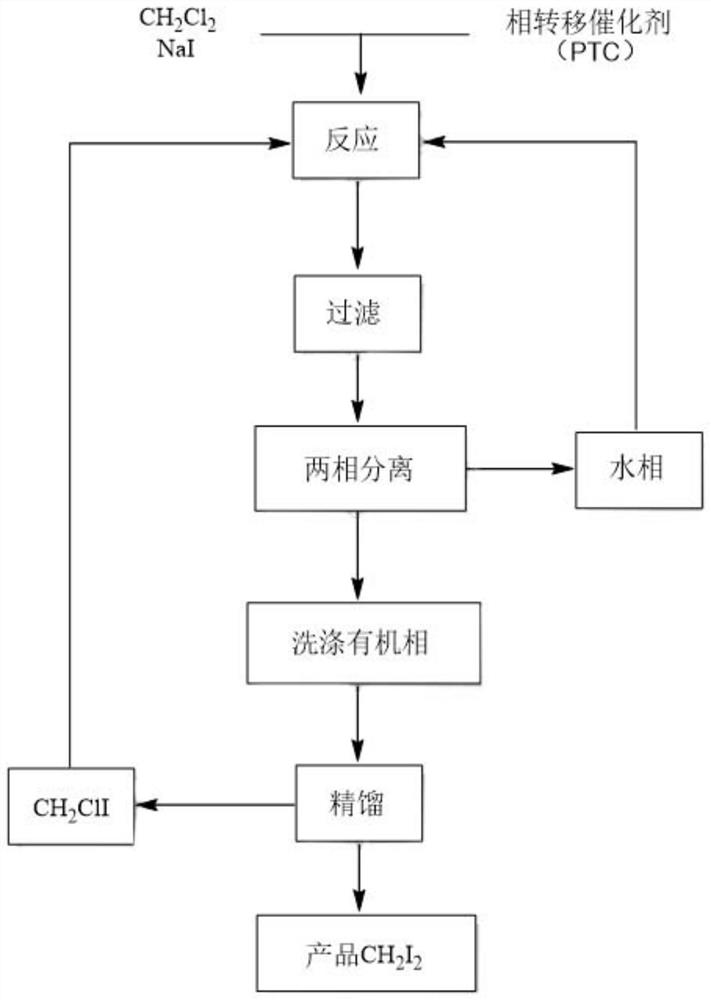
[0024] Example 1: 250 g of dichloromethane, 3.9 g of triethylbenzyl ammonium chloride and 300 g of distilled water were successively added into a reactor with stirring, 1080 g of sodium iodide was added in batches under stirring, and the temperature was raised to 105-110°C , maintain the reaction for 12 hours, after gas chromatographic analysis of the sample, cool down to about 50°C, and suction filter the precipitated sodium chloride solid. The filtrate was left to stand for stratification, and the lower organic layer was separated, and the upper aqueous layer was reserved for the next application. The organic layer was washed with 250ml of 5% sodium thiosulfate solution, washed once with 200ml of water, and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The obtained light yellow oil was subjected to vacuum fractionation, the vacuum degree was controlled at 20-30 mm Hg, and the bath temperature was not more than 90° C. to obtain 585.1 g of diiodomethane product with a yield of 74.2% an...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Embodiment 2: above-mentioned water layer (containing unreacted sodium iodide 63.0g and triethylbenzyl ammonium chloride 3.9g) directly drops into next batch reaction, adds dichloromethane 250g, adds sodium iodide 1017g, heats up Keep the reaction at 105-110°C for 12 hours. After sample gas chromatographic analysis, cool down to about 50°C, and suction filter the precipitated sodium chloride solid. The filtrate was left to stand for stratification, and the lower organic layer was separated, and the upper aqueous layer was reserved for the next application. The organic layer was washed with 250ml of 5% sodium thiosulfate solution, washed once with 200ml of water, and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The light yellow oil was subjected to fractional distillation under reduced pressure to obtain 564.5 g of diiodomethane product with a yield of 71.7% and a purity of 99.1% (GC).
Embodiment 3
[0026] Example 3: Add 250 g of dichloromethane, 3.9 g of triethylbenzyl ammonium chloride and 200 g of distilled water successively into a reactor with stirring, add 1080 g of sodium iodide in batches under stirring, and heat up to 105-110°C , maintain the reaction for 12 hours, after gas chromatographic analysis of the sample, cool down to about 50°C, and suction filter the precipitated sodium chloride solid. The filtrate was left to stand for stratification, and the lower organic layer was separated, and the upper aqueous layer was reserved for the next application. The organic layer was washed with 250ml of 5% sodium thiosulfate solution, washed once with 200ml of water, and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The obtained light yellow oil was fractionated under reduced pressure, the vacuum degree was controlled at 20-30 mm Hg, and the bath temperature was not more than 90° C. to obtain 602.5 g of diiodomethane product with a yield of 76.5% and a purity of 99.5% (GC).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com