Metabolic enzyme-induced biodegradation method of micro-nanoplastic particles and its product analysis method
A technology for plastic particles and biodegradation, applied in the field of biodegradation and its analysis, can solve the problems of chemical inertness and difficult biodegradation of micro-nano plastics, achieve rapid and high-throughput mass spectrometry detection, promote degradation, and reduce costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
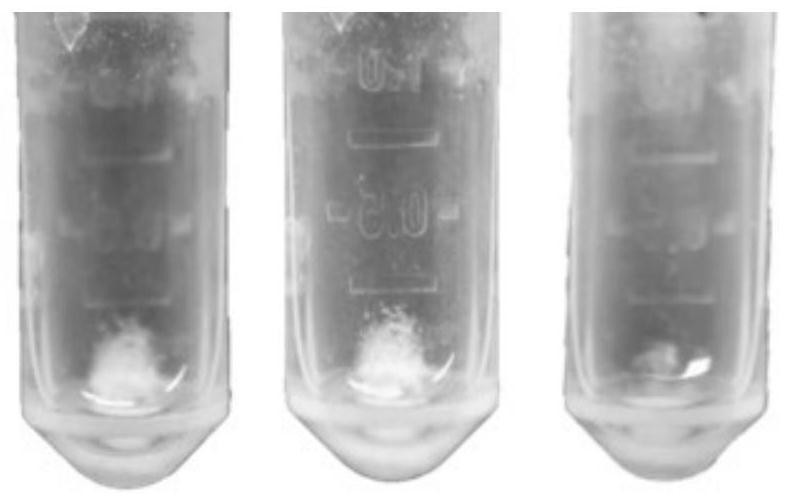
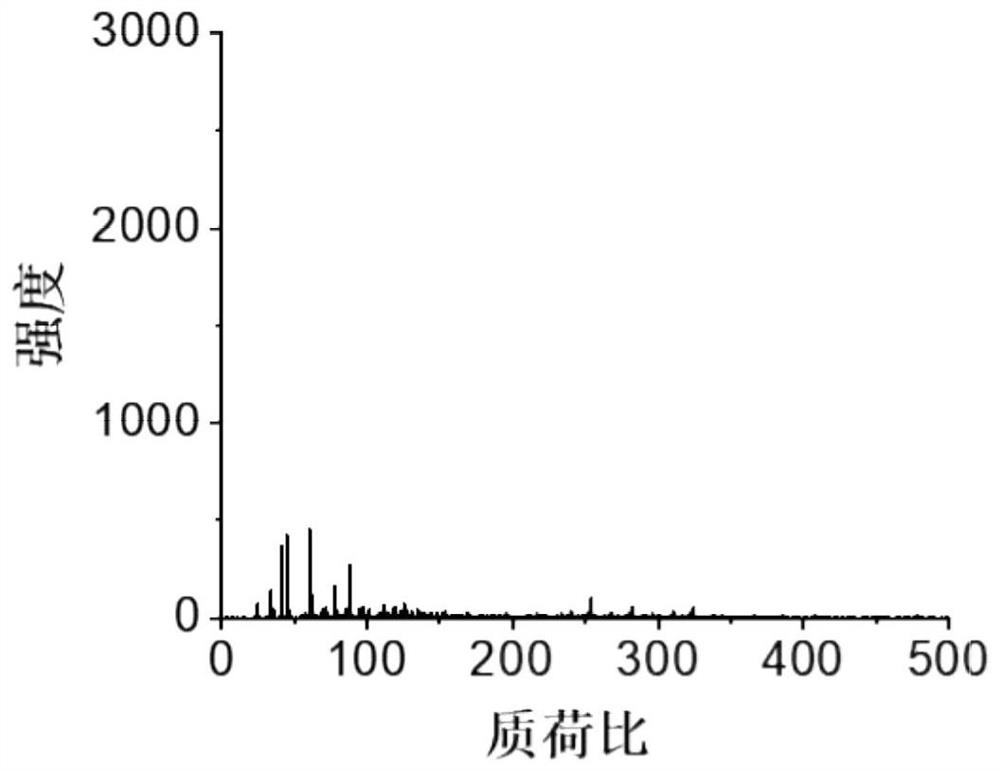
[0074] Take an appropriate amount of PET plastic products, cut them into small pieces, place them in a ball mill jar, and vacuum grind them in a ball mill. The ground plastic sample is dispersed with water and a dispersion liquid of a certain concentration is prepared, then the micro-nano plastic dispersion liquid and the metabolic enzyme solution are mixed, placed in a vortex shaker to mix, and the mixed liquid is incubated in a water-proof incubator. After incubating for a period of time, pipette 1 μL of the mixture and drop it on a commercial MTP 384 stainless steel non-polished target plate without adding additional matrix, and place it in a fume hood for natural volatilization. After the sample is dried, the target plate is placed on the target holder of the matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometer (MALDI-TOF MS), and the micro-nanoplastic sample is directly detected by mass spectrometry by MALDI-TOF MS . The instrument model used is a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com