Building capable of avoiding cross infection through indoor foul air control
A technology for buildings and trachea, applied in special buildings, building structures, buildings, etc., can solve the problems of air turbulence, easy to blow from one person to the next, and high thermal conductivity of surface materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
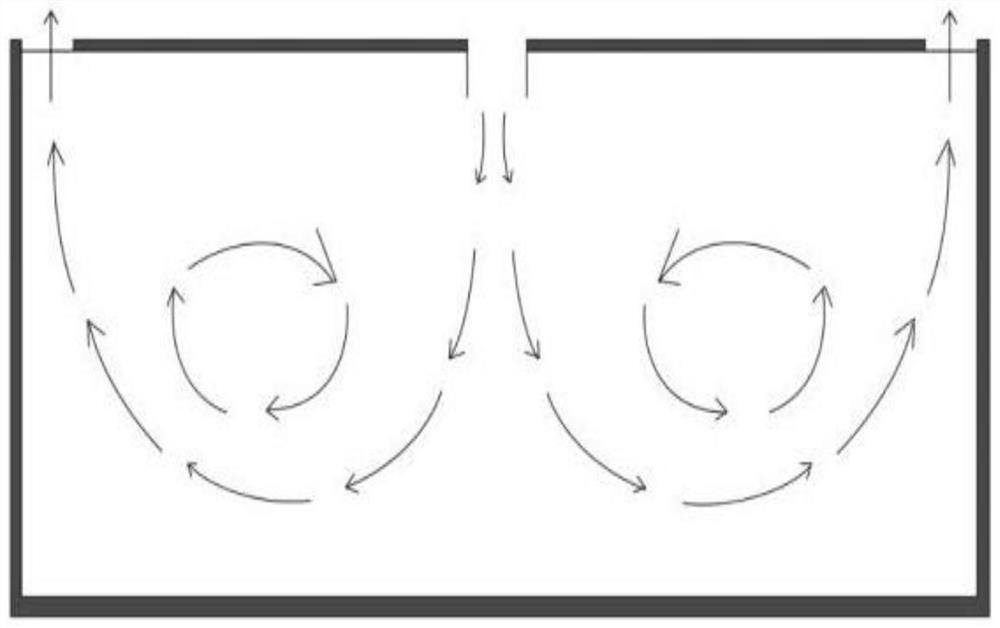
[0055] see Figure 5 to Figure 6 , as shown in the legend, a building that avoids cross-infection through indoor turbidity control, including:
[0056] A sealed heat preservation room body 10, one or more personnel gathering belts are arranged in the sealed heat preservation room body 10;
[0057] The air supply system 20, the air supply system 20 inputs fresh air to the inside of the sealed and heat-insulated room body 10, and the air-supplied system 20 includes a fresh air delivery end 21 communicated with the inside of the sealed and insulated room body 10;
[0058] Exhaust system 30, the exhaust system 30 discharges the air containing dirty air inside the sealed and heat-insulating room body 10, and the exhaust system 30 includes a dirty air receiving end 31 communicating with the inside of the sealed and heat-insulated room body 10;
[0059] Ventilation heat recovery system 40, ventilation heat recovery system 40 includes air supply conveying device 41 communicated with ...
Embodiment 2
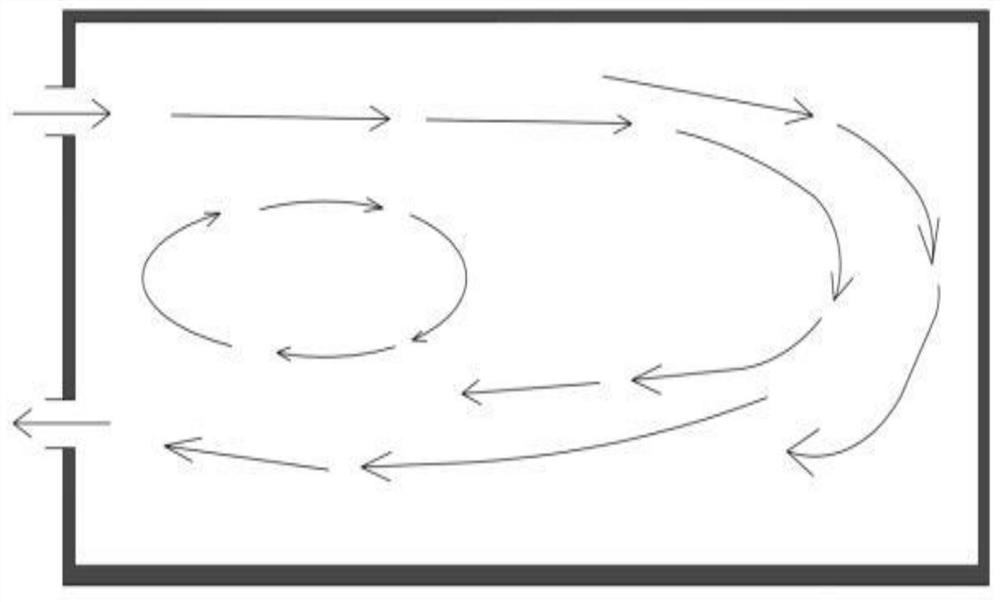
[0081] see Figure 7 , as shown in the legend therein, the rest are the same as the first embodiment, the difference is that a heat source accumulation zone is distributed in the sealed and heat-insulated room, the fresh air sending end 21 is arranged on the wall of the sealed and insulated room body, and the dirty air receiving end 31 is set On the wall of the sealed and insulated room.
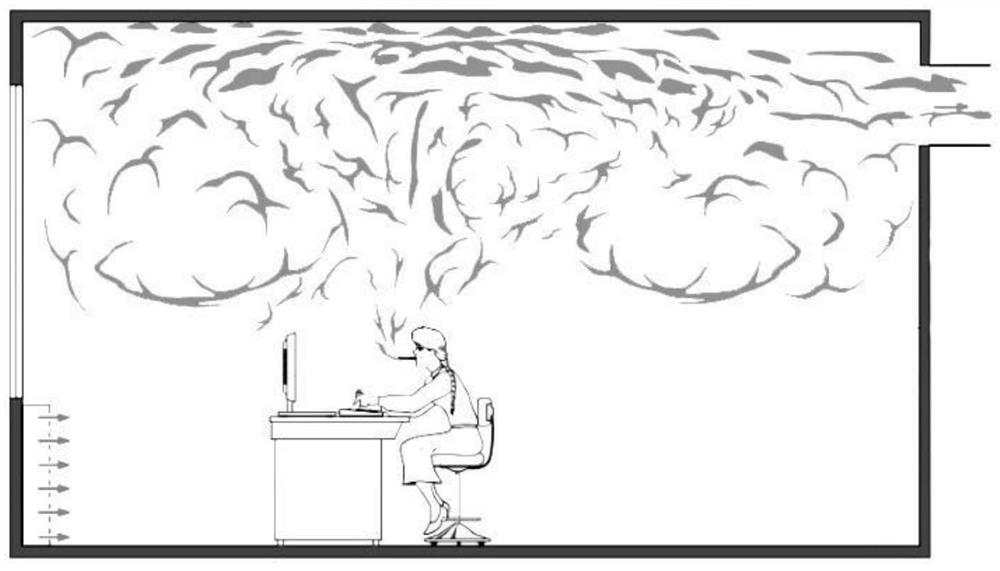
[0082] In this embodiment, in a small office / room, cool air with a speed of less than 0.2m / s is sent from the bottom of one side of the room, through the heat radiation at the bottom, and the heat provided by the heat source of the human body in the room. The hot and dirty air together reaches the top area of the ceiling and then exits the room over the other side. There is almost no polluting gas in the work area, avoiding indoor cross-infection and improving the health of the indoor environment, which can effectively reduce the demand for fresh air volume and reduce energy consumption. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com