Method for advanced reduction degradation of azo dye by using ultraviolet/magnesium process desulfurization slag
A magnesium desulfurization and azo dye technology, applied in the field of solid waste resource utilization, can solve the problems of high infrastructure investment and operation costs, and reduced desulfurization costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
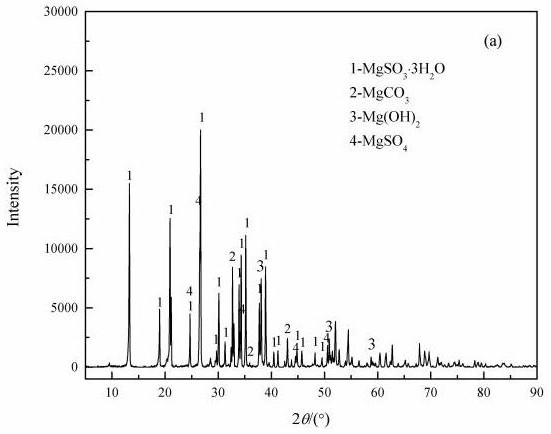
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] A method of using ultraviolet / magnesium desulfurization slag in this embodiment for advanced reduction and degradation of azo dyes is carried out according to the following steps:
[0018] (1) Dry the waste (desulfurization residue) from the wet magnesium flue gas desulfurization system in stable operation at 80°C, grind it through an 80-mesh sieve, and take the powder under the sieve and bag it for use;
[0019] (2) Take 150 mL of methyl orange wastewater with a concentration of 200 mg / L in the reaction tank, add 0.9 g of pretreated desulfurization residue, and adjust the reaction pH of the solution to 3.5. Continue to stir, and irradiate the reaction solution with a 20W ultraviolet lamp for 3.0 h;
[0020] (3) Adjust the pH of the treated wastewater to 6.0, and after standing for a period of time, filter the water.
[0021] After treatment, the removal rate of methyl orange in wastewater can reach more than 85%.
Embodiment 2
[0023] A method of using ultraviolet / magnesium desulfurization slag in this embodiment for advanced reduction and degradation of azo dyes is carried out according to the following steps:
[0024] (1) Dry the waste (desulfurization residue) from the wet magnesium flue gas desulfurization system in stable operation at 80°C, grind it through an 80-mesh sieve, and take the powder under the sieve and bag it for use;
[0025] (2) Take 200 mL of methyl orange wastewater with a concentration of 100 mg / L in the reaction tank, add 0.8 g of pretreated desulfurization residue, and adjust the reaction pH of the solution to 3.0. Continue to stir, and irradiate the reaction solution with an 80W ultraviolet lamp for 2.0 h;
[0026] (3) Adjust the pH of the treated wastewater to 7.0, and after standing for a period of time, filter the water.
[0027] After treatment, the removal rate of methyl orange in wastewater can reach more than 85%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com