L-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase and application thereof
An aspartic acid and decarboxylase technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of large amount of enzyme, reduced amount of enzyme, lower cost, etc., and achieves the effect of less amount of enzyme, rapid reaction and overcoming large amount of enzyme.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0044]Preparation method of derivatizer: Take 0.0343g o-phthalaldehyde and 0.1472g N-acetyl-L-cysteine, add 5mL absolute ethanol, and then dilute to 25mL with 0.1M sodium borate (pH=9.5).
[0045] Derivatization reaction: take 300 μL of the sample to be tested, add 200 μL of sodium borate buffer (0.1M pH=9.5), then add 200 μL of derivatizing agent, mix by inverting repeatedly for 6-8 times, derivatize in the dark for 2 minutes, and then inject the sample.
[0046] HPLC system: Agilent 1100; Chromatographic column: Welch Ultimate® AQ-C18 (4.6×250mm, 5μm);
[0047] Mobile phase: 50mmol / L sodium acetate aqueous solution:methanol=45:55 (volume ratio).
[0048] Flow rate: 0.8mL / min;
[0049] Column temperature: 35°C;
[0050] Detection wavelength: 334nm.
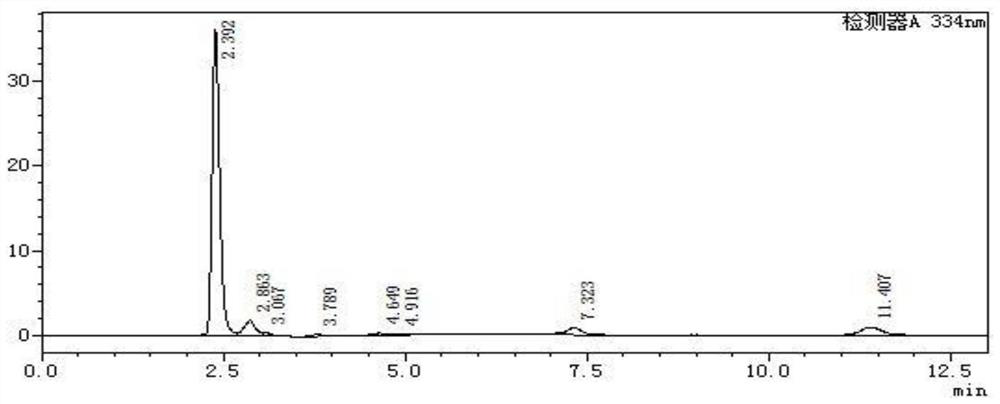
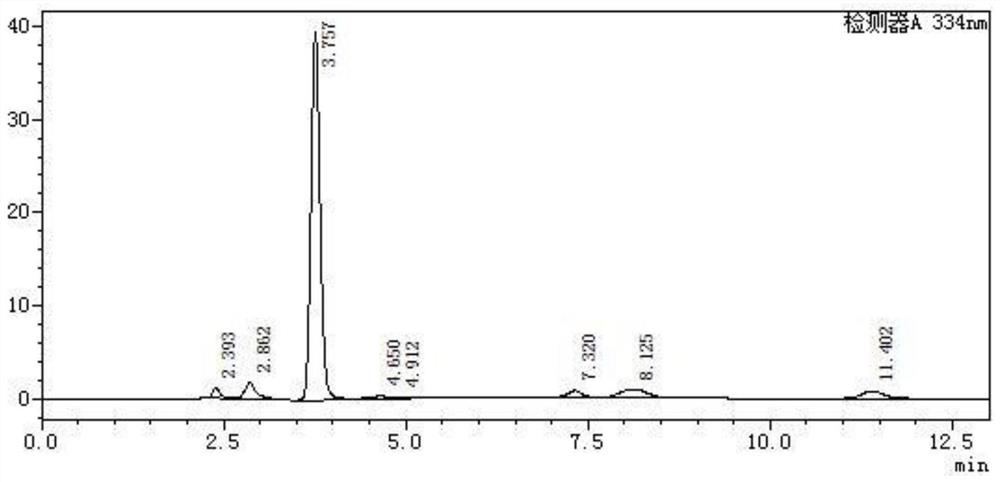
[0051] Among them, the L-aspartic acid detection picture is as follows figure 1 Shown, L-aspartic acid elution time is 2.392min.
[0052] β-alanine liquid phase detection pictures such as figure 2 Shown, β-alanine peak ti...
Embodiment 1
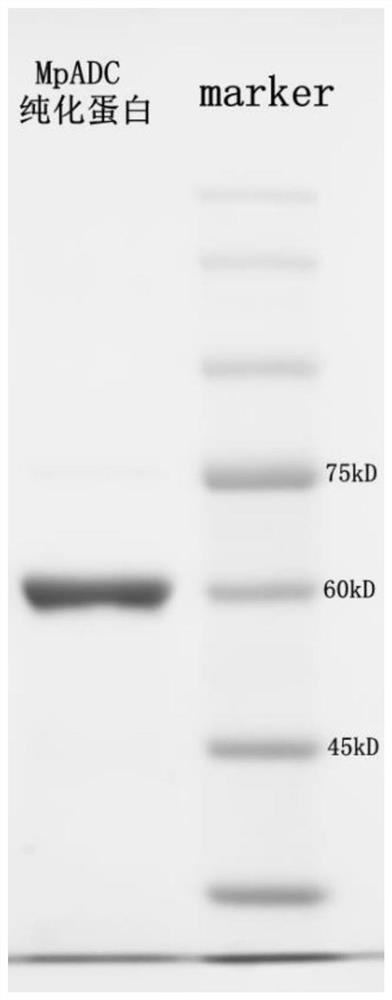
[0054] Construction of High Expression Engineering Bacteria
[0055] (1) The peach aphid obtained from the NCBI database ( Myzus persica ) The protein sequence XP_022171514 of cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase, codon optimized to SEQ ID NO.3, was synthesized by Nanjing GenScript Biotechnology Co., Ltd., using Nde I and Bam The HI restriction site was cloned into the pET28a(+) vector to obtain the pET28a(+)-MpADC recombinant plasmid.
[0056] (2) Transform the resulting recombinant vector into Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) competent cells.
[0057] (3) In a sterile environment, take 100 μL of the cells and evenly spread the cells on the LB solid medium plate (Kan resistance) with a coating stick. 12-14h).
[0058] (4) Streak the LB plate (Kan resistance) and incubate at 37°C for 12 hours, then connect to a 5mL LB test tube (Kan resistance) and culture overnight.
[0059] (5) Inoculate TB medium containing 45 μg / mL of kanamycin with 2% inoculum, incubate at 37°C for 4...
Embodiment 2
[0061] The rest of the steps in Example 2 are the same as those in Example 1, the difference lies in step (5), which is as follows: Inoculate 1% engineered bacteria into TB medium containing 30 μg / mL of kanamycin, culture at 30°C for 5 hours, and then add The inducer IPTG was used to a final concentration of 0.2mmol / L, and the temperature was lowered to 20°C to induce the expression of the target protein. The culture was continued for 25 hours, and the fermentation was terminated. The bacteria were collected for later use.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com