Targeting kit with splice switching oligonucleotides to induce apoptosis of mast cells
A nucleotide and polynucleotide technology, applied in the application field of selectively targeting mast cells and Kit-related tumor diseases, can solve problems such as loss of STOP codon function
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
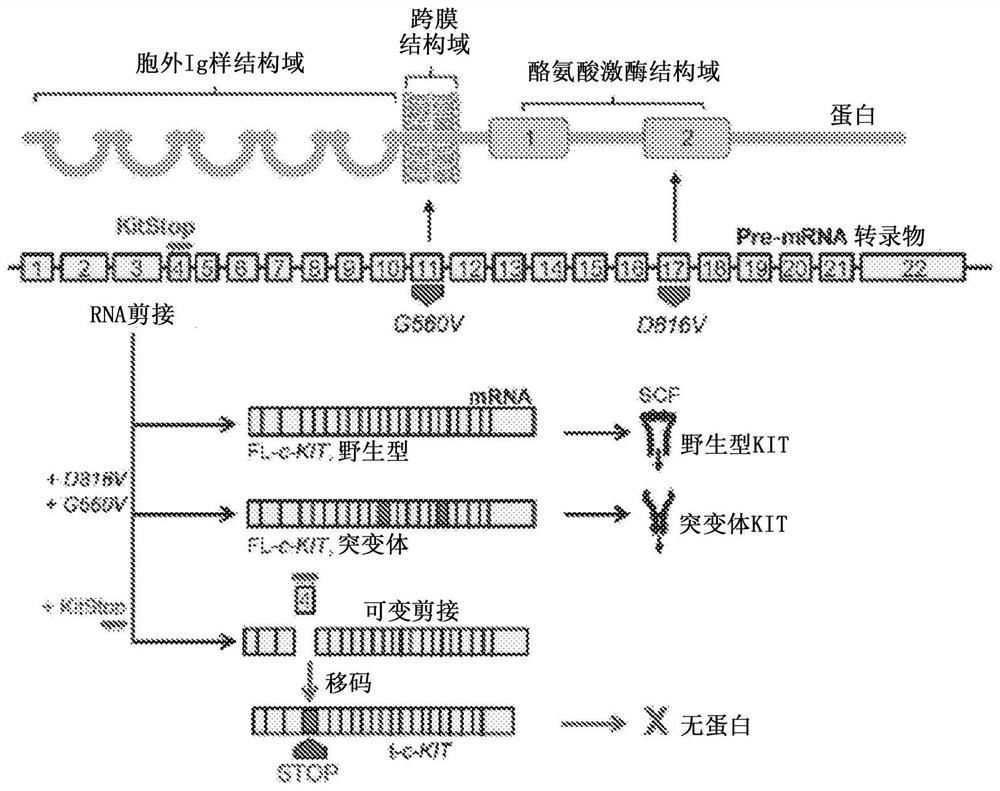
[0160] Skipping wild-type and mutant c-Kit exon 4 in ESO-treated MCs
[0161] Transfection efficiencies of ESO in human and mouse MCs reached greater than 95% without evidence of cytotoxicity as determined by propidium iodide and LIVE / DEAD staining (Cruse et al., 2016). Analyzing the sequence of human c-KIT pre-mRNA, it was predicted that ESO-induced skipping of exon 4 would introduce a frameshift into the mature mRNA open reading frame. Predicted protein translation from mRNA contains precocious STOP codons. Therefore, frameshifting with ESO induces premature termination of translation of c-Kit mRNA, resulting in severe truncation of the protein, or nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD; Figure 1A ). Both results should abolish Kit receptor expression. The stable 25-mer morpholino ESO was designed to target the donor splice site of exon 4 in c-Kit pre-mRNA called KitStop. Since the splice site is located early in the mRNA transcript, if a truncated protein is produced, the...
Embodiment 2
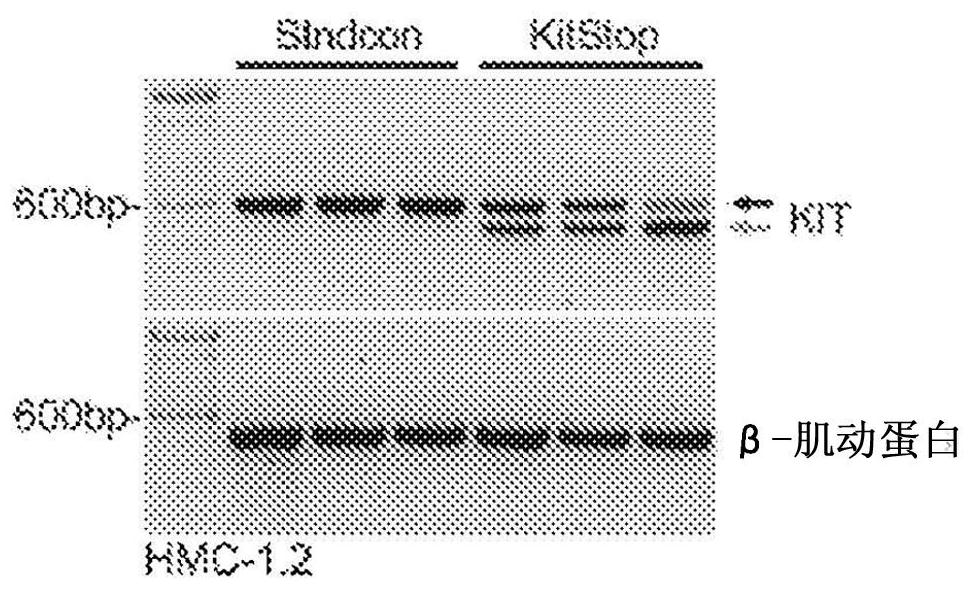
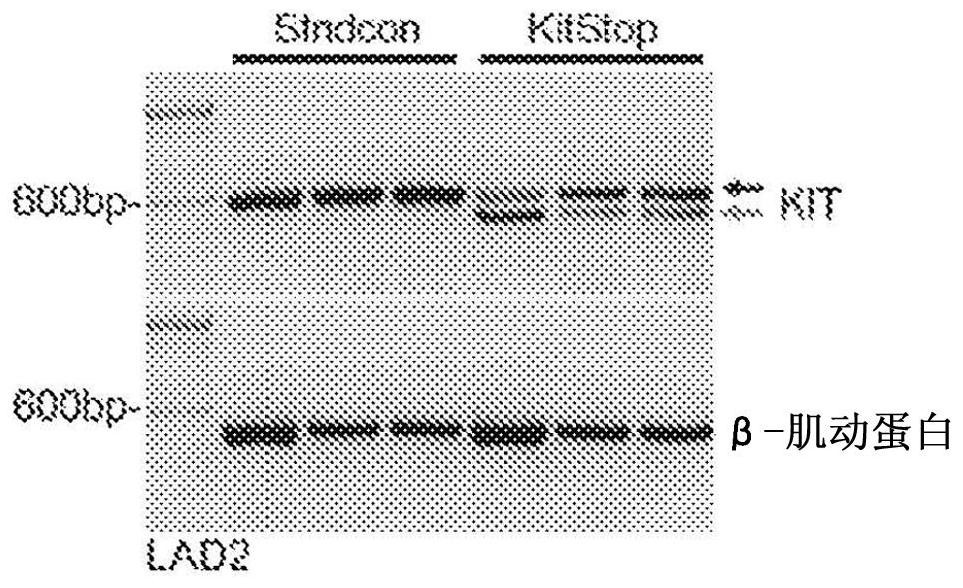
[0163] Loss of Kit expression employing c-Kit exon skipping
[0164] To test whether introducing a frameshift into wild-type or mutant c-Kit mRNA would prevent Kit protein expression, flow cytometry was used to measure Kit expression in LAD2 and HMC-1.2 cells (gating strategies, see Figure 2E and Figure 2F ). MCs express wild-type Kit on their cell surface, but Kit is rapidly internalized upon activation by its ligand, SCF. After endocytosis, Kit signals in the intracellular compartment before being degraded (Wiley & Burke, 2001). Therefore, two surfaces ( Figure 2A and 2C ) and the Kit total expression ( Figure 2B and 2D ). KitStop reduced surface Kit expression by 94.5±1.4% after 48 hours and 99.0±0.6% after 7 days ( Figure 2C ). In the same cells, total Kit expression decreased by 93.5 ± 0.9% after 48 hours and 95.6 ± 1.8% after 7 days ( Figure 2D ). These data demonstrate an almost complete loss of surface and wild-type Kit expression in KitStop-treated ...
Embodiment 3
[0167] Reduction of constitutive KIT signaling in HMC-1.2 cells with KitStop
[0168] The KIT D816V mutation confers constitutive KIT signaling. As further evidence that the effect of KitStop on HMC-1.2 cell viability and proliferation is through KIT-dependent signaling, phosphorylation of KIT and the downstream kinase ERK were examined. ERK was chosen because it is a downstream kinase in the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK pathway with a well-established role both downstream of KIT signaling and in cell proliferation. In HMC-1.2 cells, both KIT and ERK are constitutively phosphorylated ( Figure 4A ). Transfection of KitStopESO will KIT ( Figure 4B ) and ERK ( Figure 4C ) phosphorylation was reduced by a considerable level. Because KitStop effectively reduces the expression of functional KIT protein rather than inhibiting phosphorylation of KIT, this reduction in KIT phosphorylation may be a direct result of the reduced expression of constitutively active KIT protein. However, comp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com