Analysis method for determining content of palladium in waste residues
An analysis method and waste residue technology, which is applied in the analysis field of determining palladium content in waste residue, can solve the problems of high cost of detection equipment, poor adaptability of palladium, failure to meet the detection requirements of palladium content, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
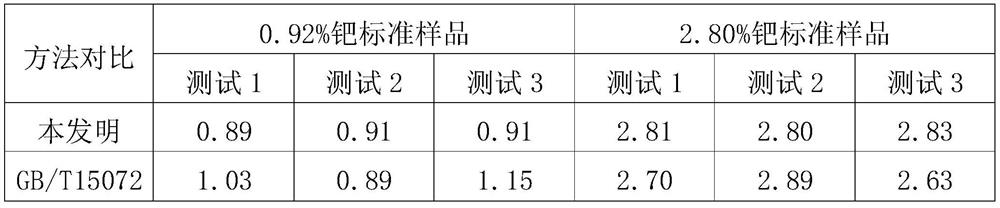
[0011] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments.
[0012] An analytical method for measuring palladium content in waste residue, the specific steps include:
[0013] 1. Sample pretreatment
[0014] 1. Weigh 20g of the waste residue sample with an accuracy of 0.0001g, place it in a ceramic crucible, and calcinate it in a muffle furnace at 850°C for 5h.
[0015] 2. Take out the ceramic crucible and cool it down to room temperature, add 5ml of a mixed solution of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid with a volume ratio of 3:1, heat at low temperature to slightly boil, add 0.1g of sodium chloride, 20ml of 10% hydrochloric acid, fully dissolve and transfer to a 100ml volumetric flask , diluted to the mark with distilled water.
[0016] 2. Make a standard regression curve
[0017] 3. Accurately weigh 0.1666g of palladium chloride, add 20ml of 10% hydrochloric acid solution to fully dissolve, transfer to a 100ml volumetr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com