Establishment and application of melon transient expression system
A technology of transient expression, melon, applied in the field of cell engineering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] Embodiment 1 provides a kind of method for preparing the muskmelon transient expression system, comprising:
[0076] (1) Material cultivation: seeds of the melon variety M7 were placed in a 30° C. incubator and soaked in the dark for 24 hours. Select well-germinated seeds and cultivate them for about 2 weeks in a culture room with a relative air humidity of 60% and a photoperiod of 16h light / 8h dark.
[0077] (2) Sampling: under the condition of good growth, the fully stretched cotyledon or the first true leaf is clipped to prepare protoplasts. Use a blade to cut the leaves into thin strips about 1 mm wide in the direction perpendicular to the midrib, and immediately put them into the enzymatic hydrolysis solution [comprising: 1.5% (w / v) cellulase R-10, 0.4% (w / v) dissociating enzyme R-10, 20mM 2-morpholinoethanesulfonic acid (MES) and 0.4M mannitol] (add 0.5g true leaf or cotyledon per 10mL enzymolysis solution).
[0078] (3) Dark enzymolysis: Vacuumize the enzymolys...
Embodiment 2
[0088] Usually young plant tissue is used for isolating protoplasts. With reference to the steps shown in above-mentioned embodiment 1, the sampling site has been changed, and embodiment 2 has compared the impact of different sampling sites on the obtained melon protoplast, and its research content is as follows:
[0089] In this example, the cotyledon of about 1 week and the first true leaf of about 2 weeks are used to compare the influence of the sampling site on the protoplast.
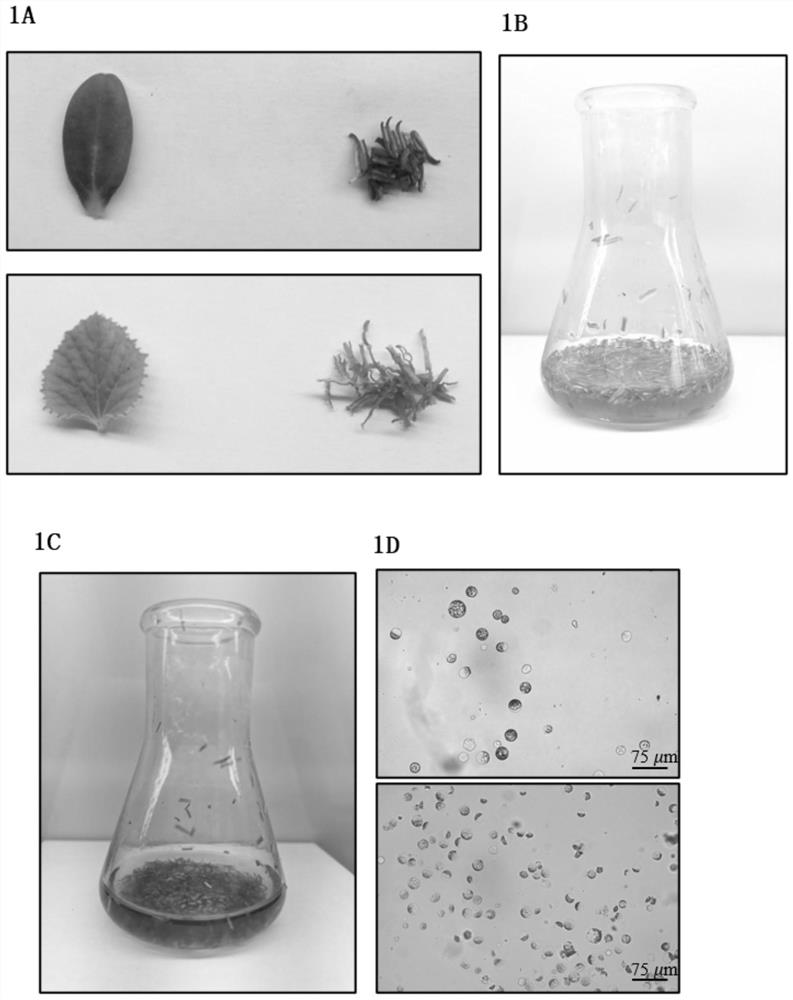
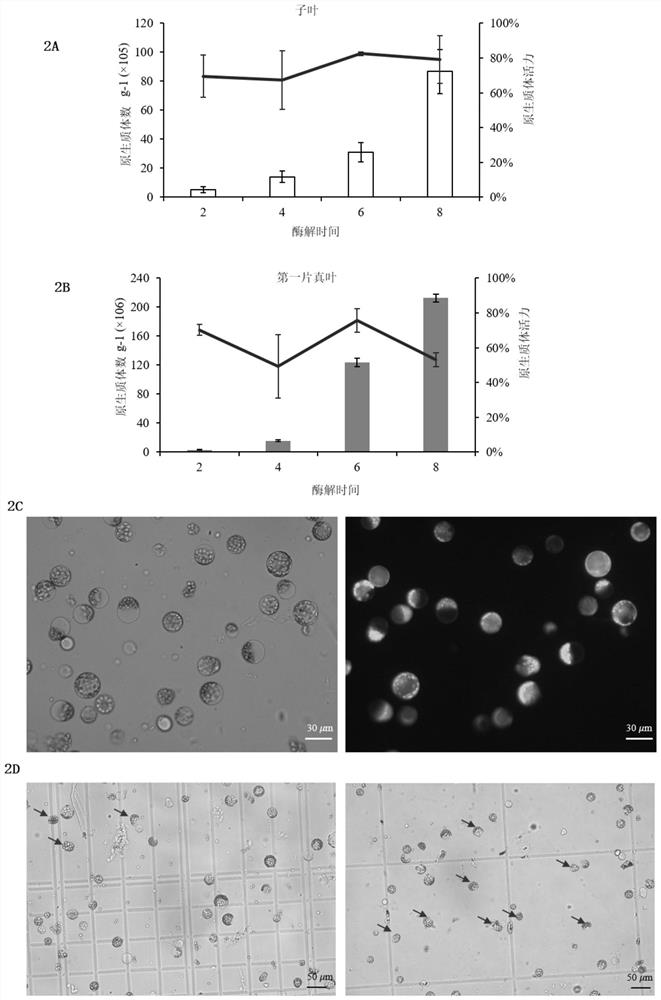
[0090] Such as figure 1 as shown, figure 1 A is the cotyledon and first true leaf of melon M7 on the left and right, respectively. The cotyledons and first true leaves were harvested using the same razor blade shredding method and immediately digested in an enzymatic solution. First, after 30 minutes of vacuuming in the dark, and then through low-speed constant temperature enzymatic hydrolysis (28 ° C, 40 r min -1 ). in figure 1 B and figure 1 C shows the enzymolysis solution after vacuum in...
Embodiment 3
[0092] With reference to the steps and conditions shown in the above-mentioned Example 1, the enzymatic hydrolysis time was changed, and Example 3 compared the impact of different enzymatic hydrolysis times on protoplasts.
[0093] To optimize the enzymatic hydrolysis time, the protoplast yield and vigor of the cotyledon and first true leaf were analyzed at 2 h, 4 h, 6 h and 8 h, respectively.
[0094] The result is as figure 2 2A is the graph showing the effect of enzymolysis time on cotyledon protoplast yield and vigor, and 2B is the graph showing the effect of enzymolysis time on the protoplast yield and vigor of the first true leaf. figure 2 A and figure 2 The abscissa in B is hour, figure 2 A and figure 2 The histogram in B represents the result graph of protoplast yield, and the line graph represents the result graph of protoplast viability. The results showed that the protoplast yield of cotyledon and true leaf increased with the increase of enzymatic hydrolysi...
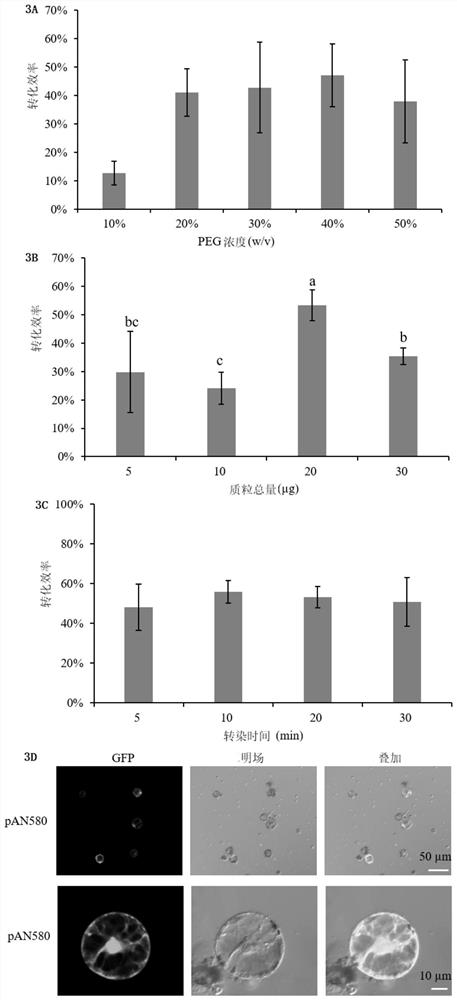
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| conversion efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com