Voltage balancing circuit for semiconductor device
A voltage balance and semiconductor technology, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, electronic switches, output power conversion devices, etc., can solve problems such as voltage imbalance, and achieve the effect of high-precision voltage balance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
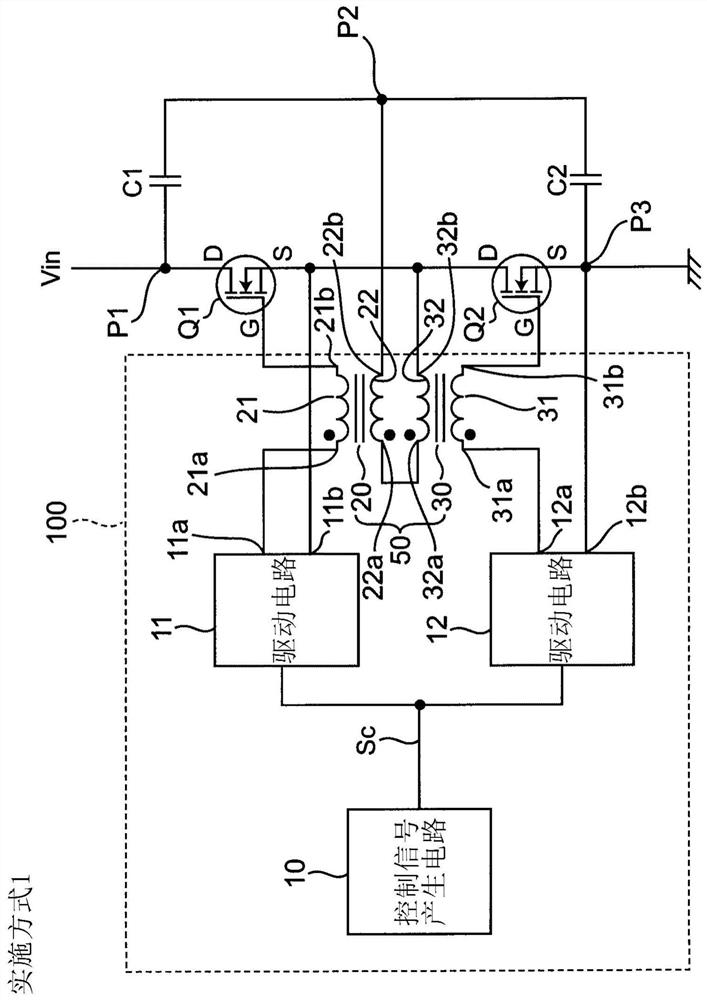
[0040] figure 1 It is a circuit diagram showing a configuration example of the switching circuit 100 and its peripheral circuits in the first embodiment. exist figure 1 Among them, the switching circuit 100 includes a control signal generating circuit 10 , a pair of driving circuits 11 and 12 , and a pair of transformers 20 and 30 . Here, a pair of transformers 20, 30 constitutes a voltage balance circuit 50 for obtaining a voltage balance of the semiconductor device Q1 when a switching control signal is applied to each gate (control terminal) of the pair of semiconductor devices Q1, Q2. , The voltage balance of the voltage (output voltage) between the drain (first element terminal) and source (second element terminal) of Q2.
[0041] exist figure 1 Among them, the semiconductor devices Q1 and Q2 are, for example, N-channel MOS field effect transistors, and are connected in series with each other. That is, the input voltage Vin is applied to the drain of the semiconductor ...
Embodiment approach 2
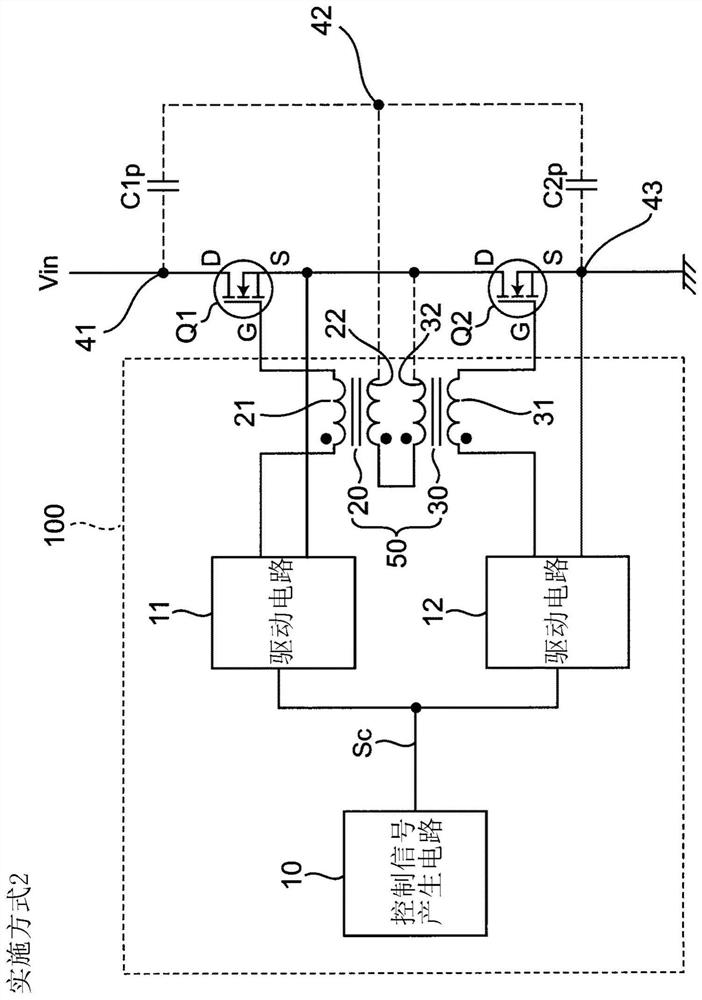
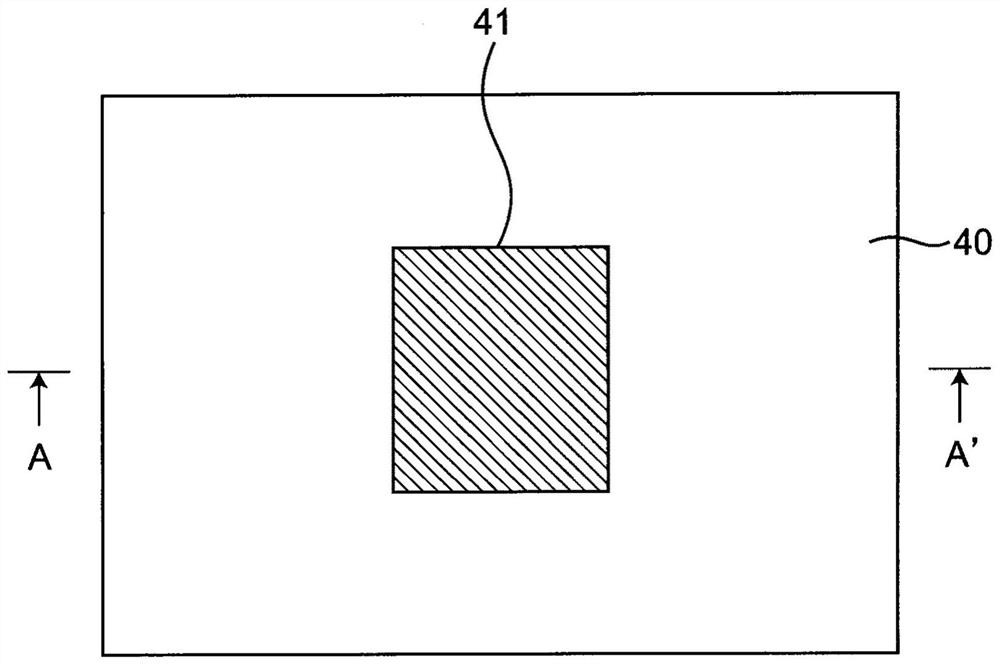
[0048] figure 2 It is a circuit diagram showing a configuration example of the switching circuit 100 and its peripheral circuits according to the second embodiment. also, Figure 3A yes figure 2 A top view of the electrode 41 portion, Figure 3B its about Figure 3A A longitudinal sectional view of line A-A'. figure 2 The peripheral circuit of the switching circuit 100 with figure 1 Compared with the peripheral circuit of the present invention, it is characterized in that the capacitors C1 and C2 are replaced by the parasitic capacitors C1p and C2p, respectively.
[0049] Specifically, as Figure 3A and Figure 3B As shown, the parasitic capacitance C1p is parasiticly formed between a pair of electrodes 41, 42 sandwiching the dielectric substrate 40 on which the semiconductor devices Q1, Q2 are mounted and the electrodes are opposed to each other, and the parasitic capacitance C2p Similar to the parasitic capacitance C1p, it is parasiticly formed between a pair of e...
Embodiment approach 3
[0054] Figure 5 It is a circuit diagram showing a configuration example of a power conversion device according to Embodiment 3. Figure 5 The power conversion device is used with figure 1 The switching circuit 100 of the voltage balancing circuit 50 is an asynchronous rectification type boost chopper circuit.
[0055] exist Figure 5 In the above, the input voltage Vin from the DC voltage source 1 is applied to the series circuit of the semiconductor devices Q1, Q2 via the reactor Lr. The drain of the semiconductor device Q1 is connected to the smoothing electrolytic capacitor Cb and the load resistor 2 via the rectifier diode D1.
[0056] In the power conversion device configured as above, the input voltage Vin can be boosted by asynchronous rectification and output to the load resistor 2 . In addition, the operation and effect of the voltage balance circuit 50 are the same as those of the first and second embodiments.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com