A temperature measurement method for magnetic nanoparticles based on electron paramagnetic resonance
An electron paramagnetic resonance and magnetic nanoparticle technology, which is applied in the directions of thermometers, thermometers, and heat measurement using electrical/magnetic components that are directly sensitive to heat, to achieve the effect of broadening application scenarios and improving temperature measurement accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
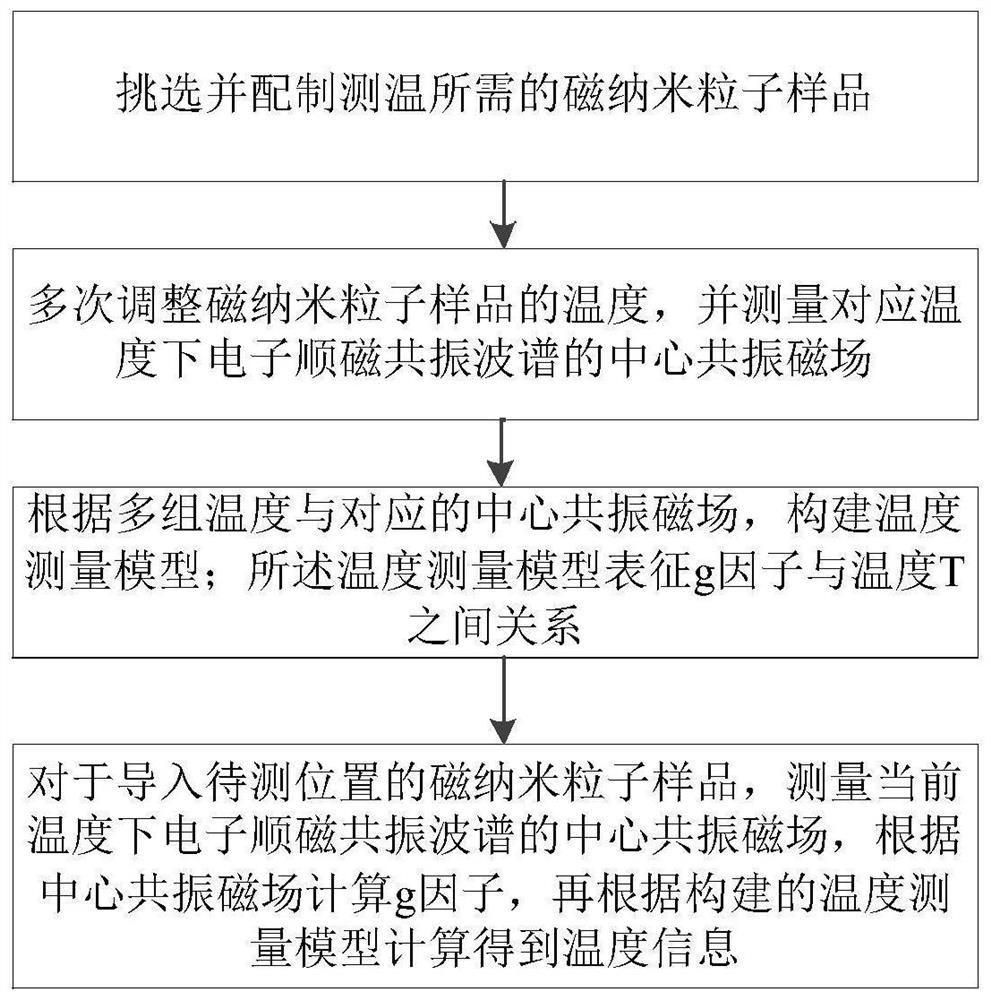
Image
Examples
example
[0051] 1. Simulation model and test description:
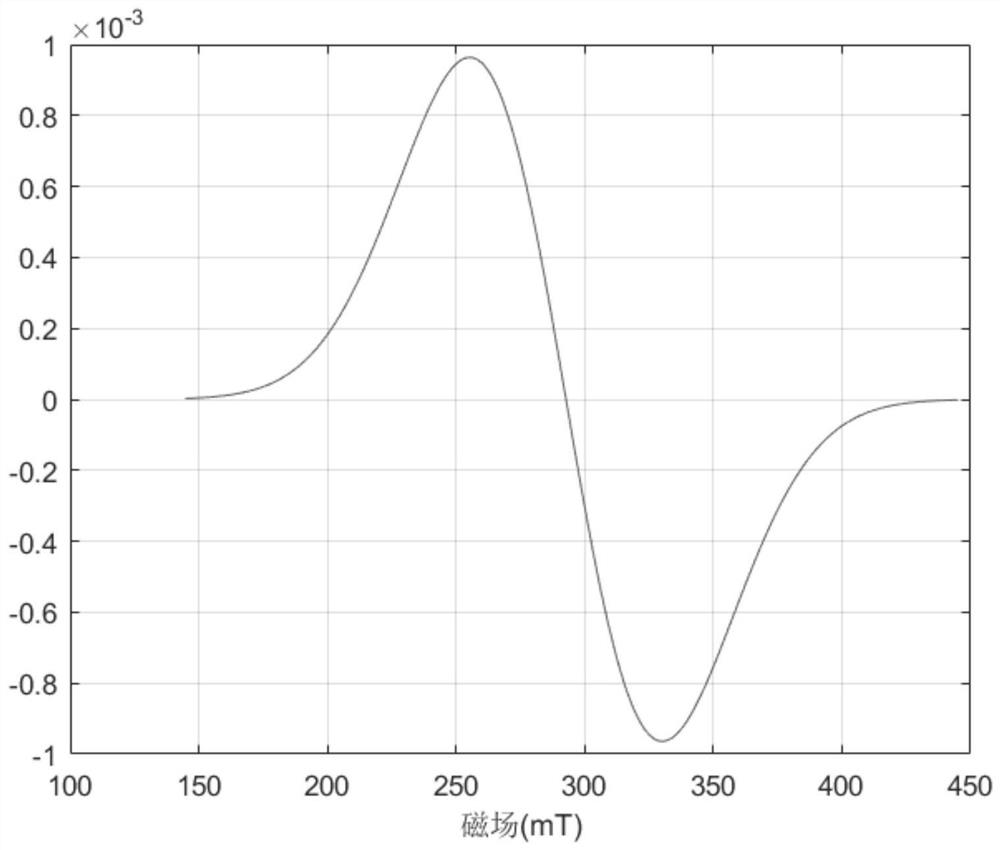
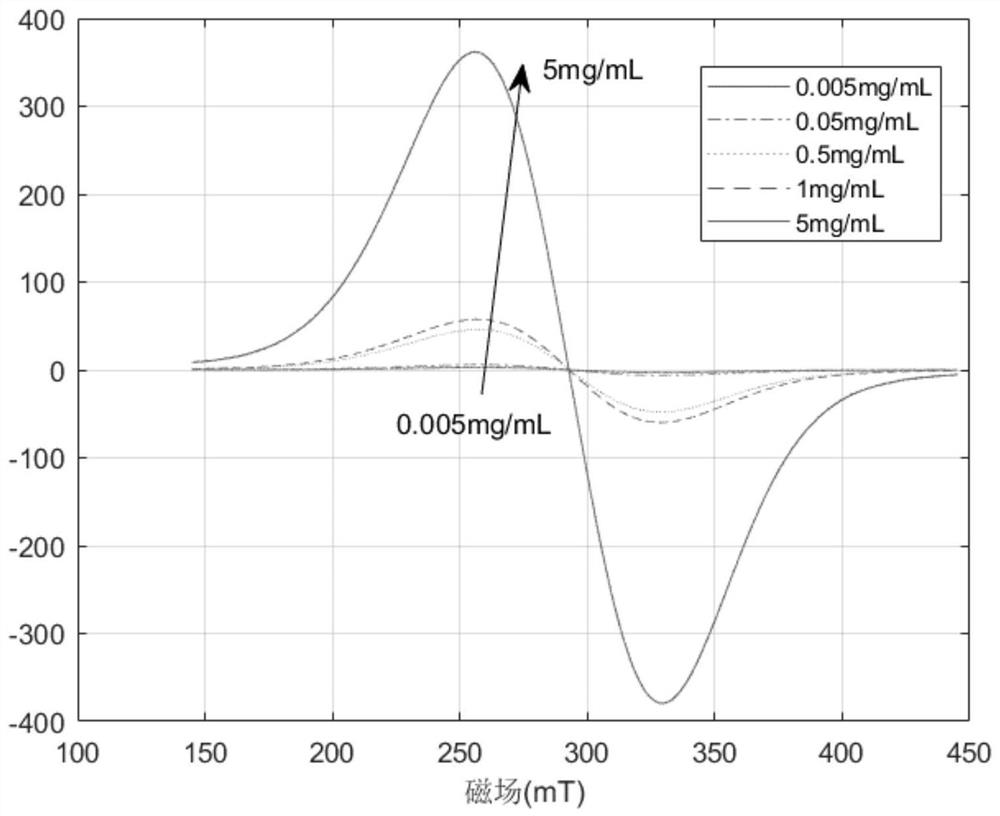
[0052] In order to study the feasibility of the temperature measurement method of magnetic nanoparticles based on electron paramagnetic resonance, this example simulates the electron paramagnetic resonance signal of magnetic nanoparticles. The simulation parameters are: particle size D=10nm, spin quantum number S=5 / 2, nuclear spin quantum number I=1 / 2, main magnetic field scanning range is 145-445mT, microwave frequency v=9.141GHz, simulation temperature 10 ℃.
[0053] 2. Simulation test results:
[0054] figure 2 Reflects the electron paramagnetic resonance spectrum of magnetic nanoparticles with a particle size of 10 nm. It can be seen from the figure that the spectrum has only one large envelope peak with a g factor of 2.2316.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com