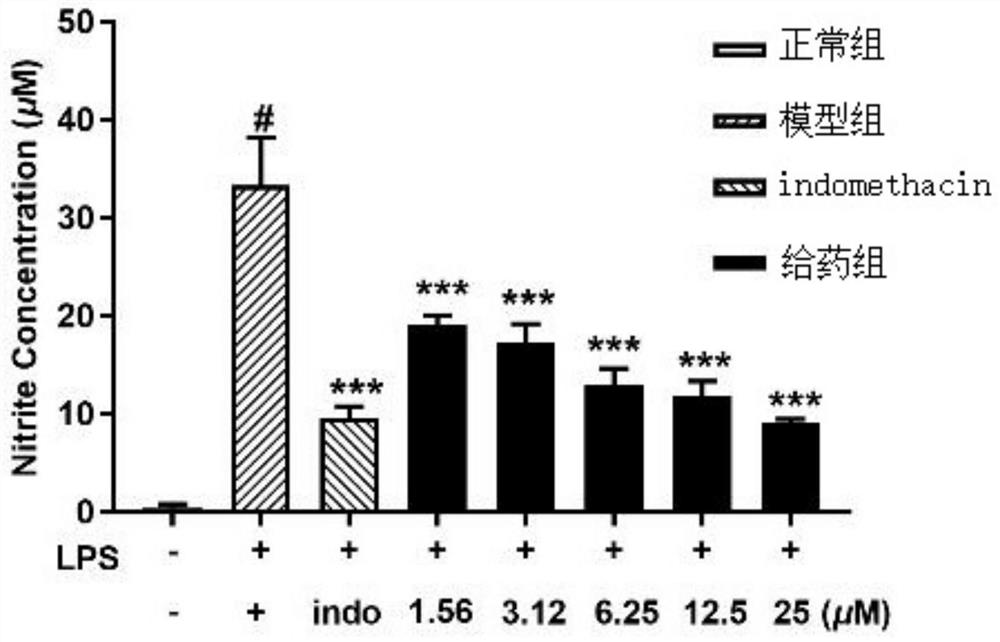
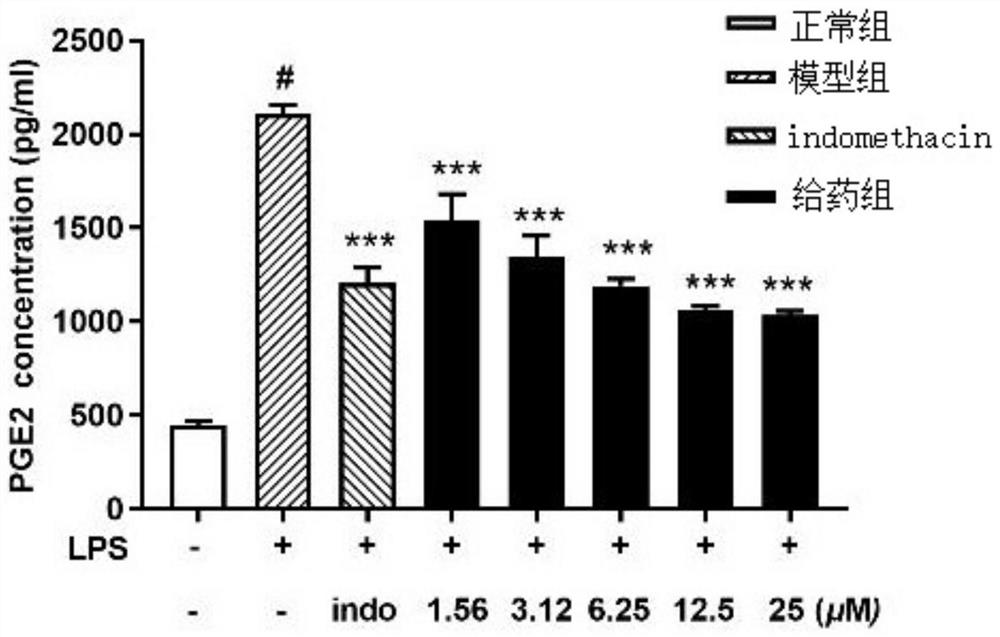
Sea anemone co-epiphytic fungus SYSU-MS5127, fermentation compound and application of sea anemone co-epiphytic fungus and compound
A technology of SYSU-MS5127 and compounds, applied in the field of sea anemone symbiotic fungus SYSU-MS5127 and its fermented compounds and applications, can solve the decline of body defense function, human substance metabolism and water and sodium metabolism disorders, gastrointestinal side effects, etc. problems, achieving significant anti-inflammatory activity, no cytotoxicity, and high safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1 Isolation of sea anemone symbiotic fungus Fusarium graminearum SYSU-MS5127
[0045]1. Experimental sample: sea anemone from Laishizhou, Shenzhen.
[0046] 2. Experimental method:
[0047] Disinfect the surface of the fresh sea anemone, dry it slightly, grind the sea anemone, inoculate it into PDA medium under aseptic conditions, and culture it below 28°C for 5-7 days to obtain a single strain SYSU-MS5127; the obtained strain SYSU -MS5127 was stored at 4°C on the slant of PDA medium.
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2 Identification of the symbiotic fungus SYSU-MS5127 in sea anemones
[0049] 1. Morphological and physiological and biochemical identification:
[0050] When the bacterial strain SYSU-MS5127 obtained in Example 1 was cultured at a constant temperature of 28°C in PDA medium, the surface of the colony was white and orange-red hairy hyphae, the back was dark red, and orange-red spores were produced; the center of the mycelium protruded to form a sclerotia , grow to the four sides in a group; the initial stage of growth is white mycelium, the color of the mycelium becomes darker in the later stage, and the color of the mycelia becomes orange-red, with pink powdery things attached to the mycelia, and the plate is relatively moist.
[0051] 2. Molecular identification:
[0052] Using the CTAB method to extract the purely cultured DNA of the sea anemone symbiotic fungus SYSU-MS5127, using a pair of primers ITS1F and ITS4 in the ITS spacer region to amplify the ITS-rR...
Embodiment 3
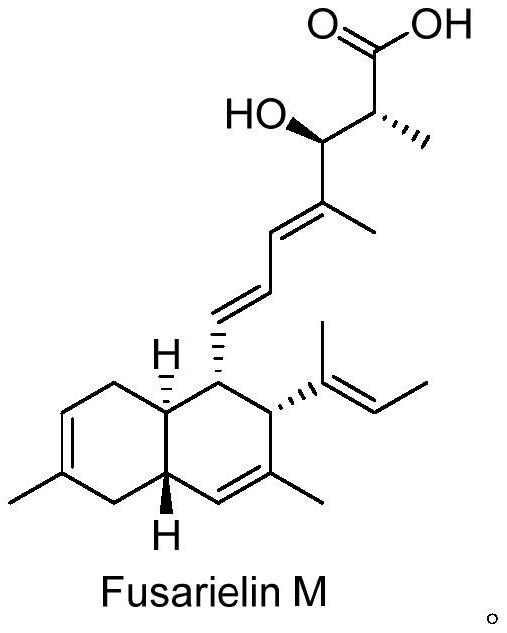
[0053] The separation and identification of embodiment 3 compound Fusarielin M
[0054] 1. The separation of the compound Fusarielin M specifically comprises the following steps:
[0055] S1. Expanded cultivation of sea anemone symbiotic fungi: insert sea anemone symbiotic fungi into the seed medium with an inoculum size of 5 mL, culture at 28° C. and 180 rpm on a shaker for 72 hours to obtain seed culture solution; inoculate the seed culture solution to In the fermentation medium, the inoculum size is 15ml, cultured at 25°C for 28 days, filtered, and the filter residue is the sea anemone symbiotic fungal cell;
[0056] Soak the sea anemone symbiotic fungus thallus obtained from the expanded culture with methanol, filter and concentrate to obtain the extract, and the extract is sequentially mixed with 2L ethyl acetate at a volume ratio of 20%, 30%, 40%, 50%, 60%, 70% %, 80%, 90%, and 100% ethyl acetate-petroleum ether solutions were separated by gradient elution of silica gel...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com