Method for treating wastewater after ore leaching and ore closing of ionic rare earth ore
An ionic rare earth ore and wastewater treatment technology, which is applied in metallurgical wastewater treatment, water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc. It can solve the problems of large amount of wastewater, waste of resources, hidden danger of pollution, etc. , to achieve the effect of recycling, low environmental impact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] This embodiment provides a method for treating wastewater after leaching and closure of ionic rare earth ore, comprising the following steps:
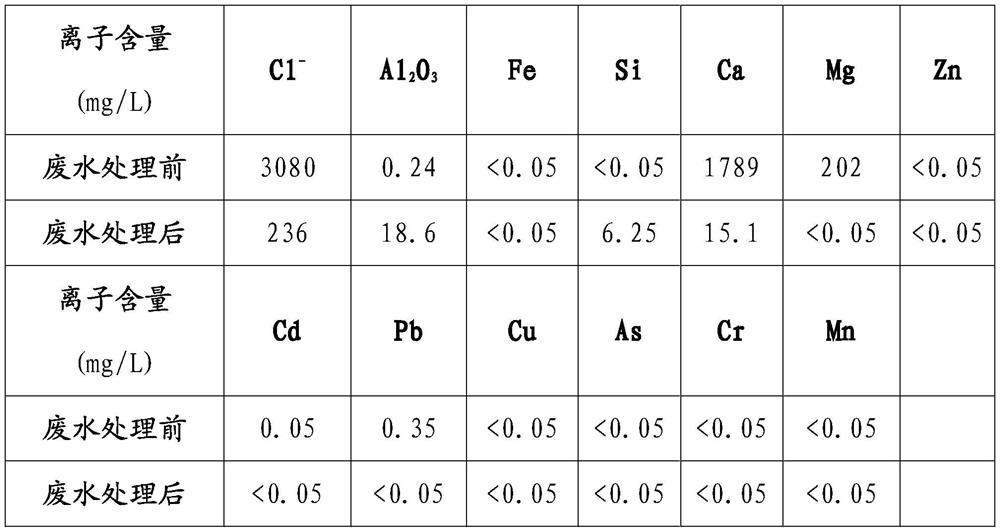
[0018] (1) With the precipitation supernatant produced in the leaching process as raw material, a total of 0.85L, the concentrations of rare earth ions, chloride ions, calcium ions, aluminum ions and other non-rare earth ions and heavy metal ions in the wastewater are measured as shown in Table 1. Show.
[0019] (2) Add 78g of lime and 32g of sodium metaaluminate to the waste water until Ca in the waste water 2+ :Al 3+ :Cl - The mass ratio is 12: 2: 1, stirring and reacting, filtering; the concentration of rare earth ions, chloride ions, calcium ions, aluminum ions and other non-rare earth ions and heavy metal ions in the filtrate is as shown in Table 1. In the waste water, Ca, The contents of Mg and Cl ions are greatly reduced, and the contents of heavy metal ions such as Zn, Cd, Pb, Cu, As, Cr, and Mn are all <0.05mg / L, mee...
Embodiment 2
[0024] This embodiment provides a method for treating wastewater after leaching and closure of ionic rare earth ore, comprising the following steps:
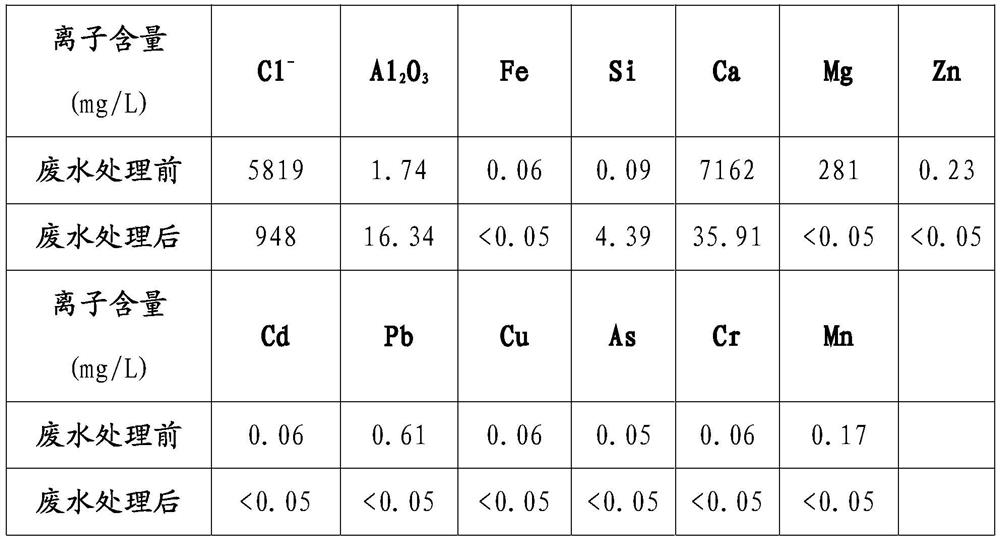
[0025] (1) Using the comprehensive wastewater mixed with the leaching tailing liquid, precipitation supernatant, and product washing liquid produced in the leaching process as raw material, a total of 1.5L, to measure the concentration of rare earth ions, chloride ions, calcium ions, and aluminum ions in the wastewater And the concentrations of other non-rare earth ions and heavy metal ions are shown in Table 2.
[0026] (2) Add 54.5g of lime and 21g of sodium metaaluminate to the wastewater until Ca in the wastewater 2+ :Al 3+ :Cl - The mass ratio is 9: 1.5: 1, stirring and reacting, filtering; the concentration of rare earth ions, chloride ions, calcium ions, aluminum ions and other non-rare earth ions and heavy metal ions in the filtrate is as shown in Table 2. In the waste water, Ca, The contents of Mg and Cl ions are gre...
Embodiment 3
[0031] This embodiment provides a method for treating wastewater after leaching and closure of ionic rare earth ore, comprising the following steps:
[0032] (1) With the precipitated supernatant produced in the ore leaching process as raw material, a total of 0.8L, the concentrations of rare earth ions, chloride ions, calcium ions, aluminum ions and other non-rare earth ions and heavy metal ions in the wastewater are measured as shown in Table 3. Show.
[0033] (2) Add 57g of lime and 28g of sodium metaaluminate to the wastewater until Ca in the wastewater 2+ :Al 3+ :Cl - The mass ratio is 10: 2: 1, stirring and reacting, filtering; the filtrate measures the concentration of rare earth ion, chloride ion, calcium ion, aluminum ion concentration and other non-rare earth ion and heavy metal ion concentration as shown in table 3, in the waste water, Ca, The contents of Mg and Cl ions are greatly reduced, and the contents of heavy metal ions such as Zn, Cd, Pb, Cu, As, Cr, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com