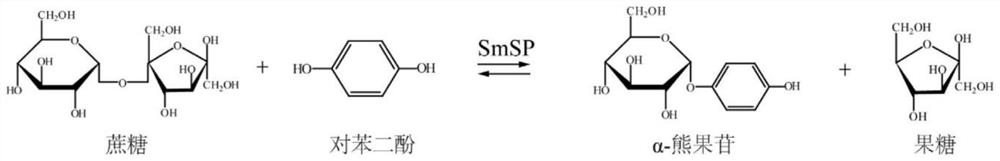
Genetic engineering strain for synthesizing alpha-arbutin as well as construction method and application of genetic engineering strain
A genetically engineered strain, arbutin technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of unfavorable industrial production and low yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1: Catalytic synthesis of α-arbutin by whole cells
[0031] The recombinant Bacillus subtilis to be fermented was activated by streaking on the LB solid medium containing the corresponding resistance, and cultivated overnight at 37°C. A single colony was transferred to LB liquid medium (20 mL) supplemented with corresponding resistance, and cultured on a shaker at 37° C. for 10 h to obtain a seed liquid. The seed solution was transferred to 30 mL TB medium supplemented with corresponding resistance at an inoculum amount of 1% (v / v), and cultured at 37° C. for 12 hours to obtain a fermentation solution. The fermentation broth was centrifuged (8,000 rpm, 10 min, 4° C.) to collect the cells, and washed twice with 20 mmol / L PB buffer (pH 7.0). The whole-cell catalytic system contains 310.9g / L sucrose, 50g / L HQ, 20mmol / L PB, and the amount of cell addition is OD 600 =20. The whole-cell catalytic reaction was carried out in a 50mL airtight container, and placed in ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Embodiment 2: Construction of genetic engineering strain BS-HT-SmSP
[0033] Table 1
[0034]
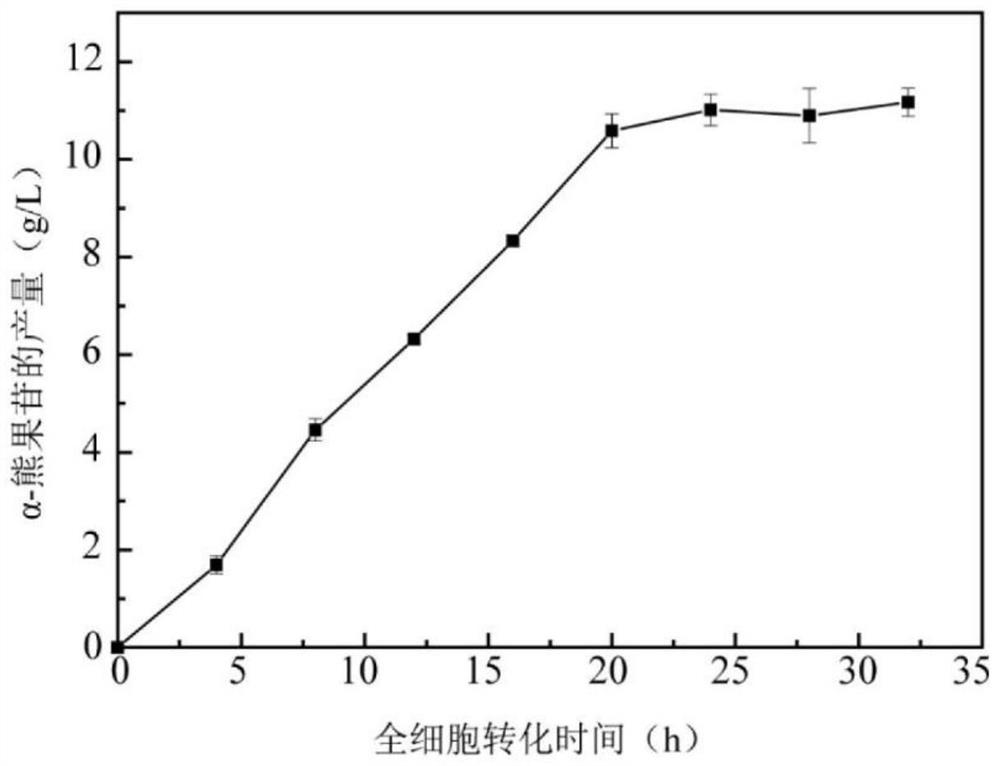
[0035] According to the codon preference of Bacillus subtilis, the gtfA gene derived from S. mutans UA159 was artificially synthesized, and the gene sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. Using gtfA-F (BamH I) and gtfA-R (Sma I) as primers, the gtfA gene was amplified by PCR to obtain the gtfA gene with restriction sites at both ends. The E. coli-Bacillus subtilis shuttle vector pHT01-Pgrac100 was selected as the expression vector, and the gtfA gene was cloned into the restriction site BamH I and Sma I by restriction enzyme ligation to obtain the recombinant plasmid pHT01-Pgrac100-gtfA , transforming the plasmid into Bacillus subtilis B. subtilis WB600 to obtain a genetic engineering strain BS-HT-SmSP capable of catalyzing the synthesis of α-arbutin. The result is as figure 2 As shown, using the whole cell catalyzed method for synthesizing α-arbutin in Example 1, the output...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Embodiment 3: Optimization of sucrose phosphorylase (SmSP) expression vector
[0037] Table 2
[0038]
[0039] Note: The underline indicates the restriction site, and the italic letters indicate the homology arm sequence
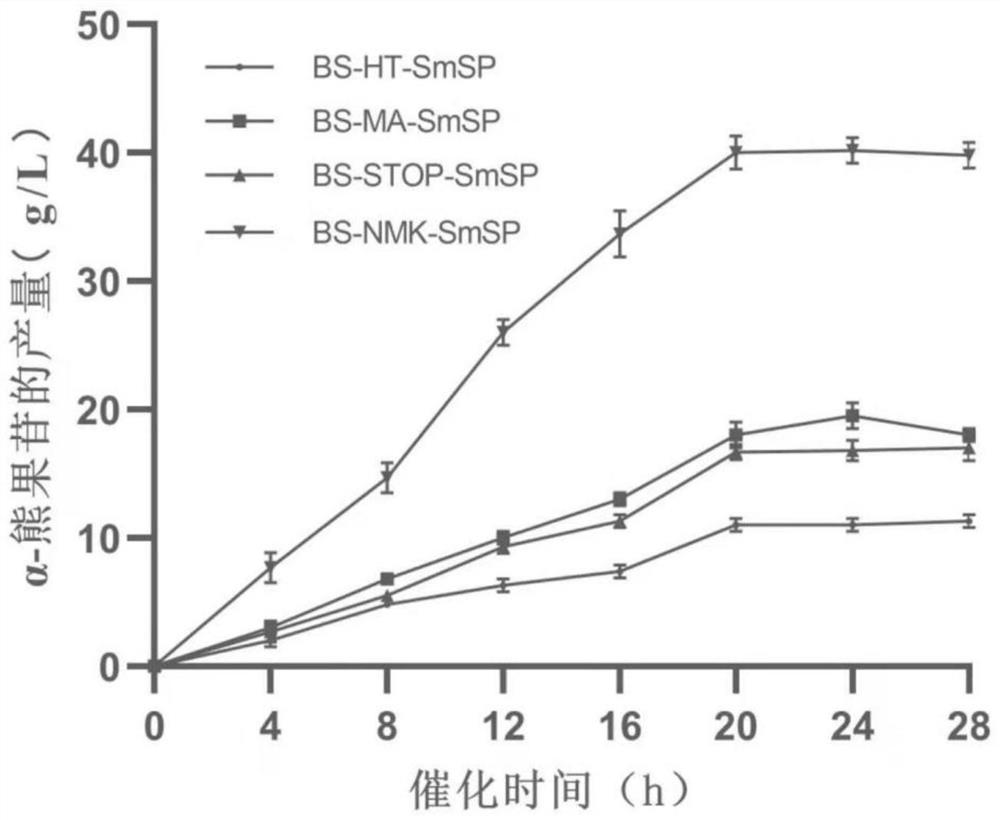
[0040] Three recombinant expression vectors pSTOP1622-PxylA-gtfA, pMA0911.1-PHpaII-gtfA and pP43NMK were obtained by one-step cloning and ligation of gtfA gene to pSTOP1622-PxylA and pP43NMK-P43 plasmids, and restriction restriction to pMA0911.1-PHpaII plasmid -P43-gtfA. The above three plasmids were respectively transferred into B.subtilisWB600 to obtain three recombinant strains of BS-STOP-SmSP, BS-MA-SmSP and BS-NMK-SmSP, and the whole cells in Example 1 were used to catalyze the synthesis of α-ursi Glycoside method, the three recombinant strains and the BS-HT-SmSP strain were catalytically verified, and the results were as follows image 3 As shown, the yield of α-arbutin catalyzed by BS-NMK-SmSP was higher than that of the other three recomb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com