Method for recycling valuable metals from waste lithium ion batteries
A lithium-ion battery and valuable metal technology, which is applied in the field of waste battery recycling, can solve the problems of large consumption of chemical reagents, complex process, low metal recovery rate, etc., and achieves the effects of low cost, simple process, and reduction of the addition of chemical reagents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
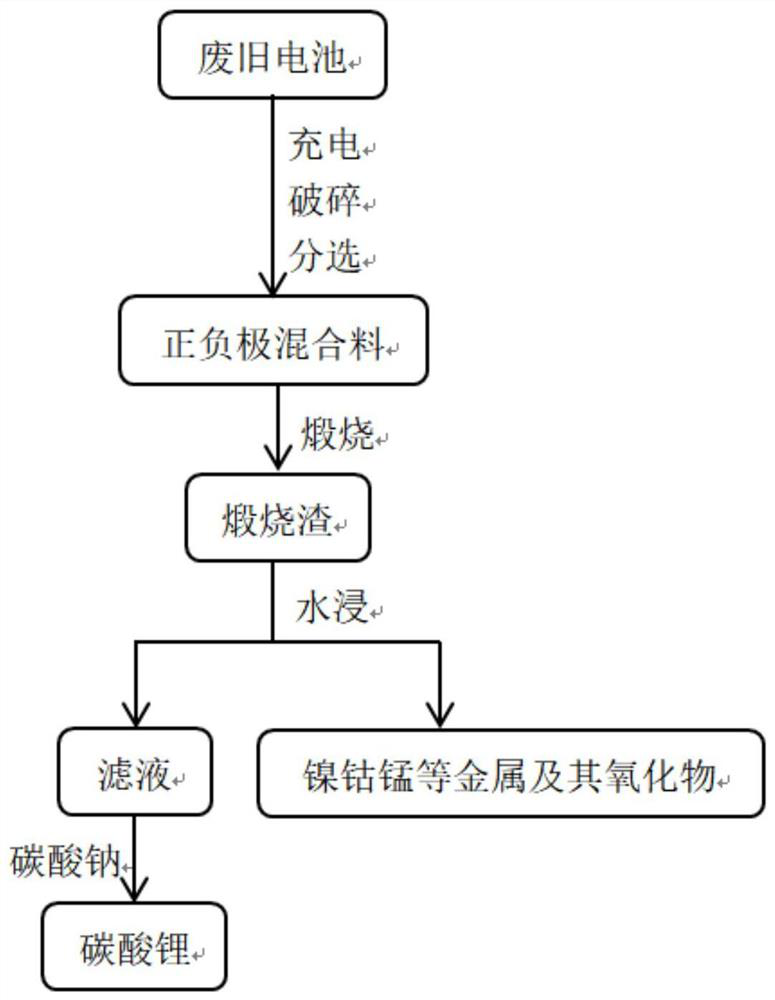
[0048] The waste lithium cobalt oxide battery was charged at a constant current of 0.2C to a battery voltage of 4.2V, and then crushed and sorted in a closed environment filled with nitrogen to obtain a mixture of positive and negative electrodes. Calcinate the mixture at 800°C for 5h, then take out the calcined slag, add deionized water according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:5, stir in a water bath at 20°C for 2h, separate the leachate from solid to liquid, add sodium carbonate to the filtrate to obtain lithium carbonate Precipitation, the filter residue is metallic cobalt and its oxides. The recovery rate of lithium and other metals obtained is above 95%, and the purity is high.
Embodiment 2
[0050] Charge the waste lithium manganese oxide battery with a constant current at a rate of 0.1C until the battery voltage is 3.5V, and then place it in a closed environment filled with nitrogen for crushing and sorting to obtain a mixture of positive and negative electrodes. Calcinate the mixture at 700°C for 10 hours, then take out the calcined slag, add deionized water according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:8, stir in a water bath at 60°C for 3 hours, separate the leachate from solid to liquid, and add sodium carbonate to the filtrate to obtain lithium carbonate Precipitation, the filter residue is metal manganese and its oxides. The recovery rate of lithium and other metals obtained is above 95%, and the purity is high.
Embodiment 3
[0052] The waste nickel-cobalt lithium manganese oxide battery is charged at a constant current of 0.5C to a battery voltage of 4.5V, and then crushed and sorted in a closed environment filled with nitrogen to obtain a mixture of positive and negative electrodes. Calcinate the mixture at 900°C for 2 hours, then take out the calcined slag, add deionized water according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:10, stir in a water bath at 80°C for 1 hour, separate the leachate from solid to liquid, add sodium carbonate to the filtrate to obtain lithium carbonate Precipitation, the filter residue is metal nickel, cobalt, manganese and its oxides. The recovery rate of lithium and other metals obtained is above 95%, and the purity is high.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com