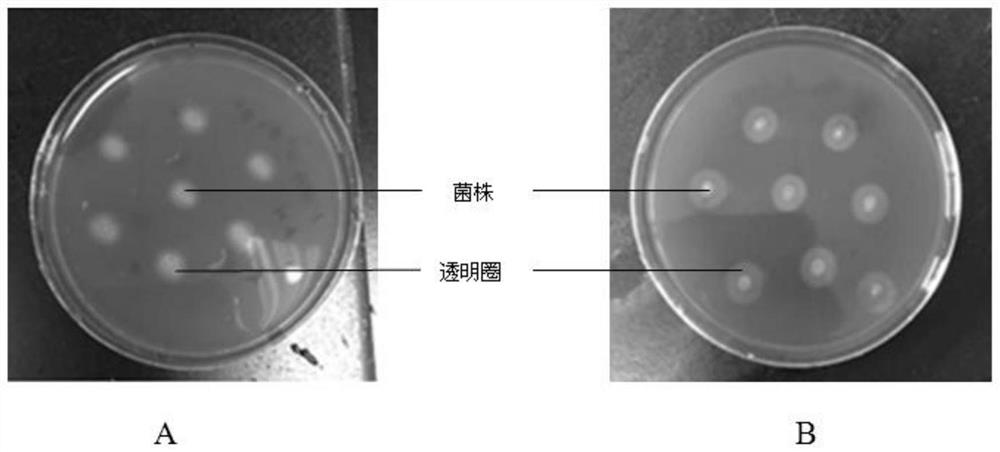
A cellulosic-degrading biocontrol bacillus and its application and preparation
A technology for degrading cellulose and Bacillus, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problem of inseparable from high-efficiency cellulose-degrading strains, etc., and achieve the effects of good industrial production prospects, rapid degradation, and shortening the decomposition cycle.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Isolation and Screening of Cellulose Degrading Bacteria
[0022] 1. The source of soil samples
[0023] Fresh soil samples were taken from the straw returning soil of the Caoxinzhuang Experimental Farm, Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, Yangling District, Shaanxi Province. After air-drying, the weeds in the soil were screened out, and then the weighed soil was put into a tissue culture bottle. Appropriate amount of water for a week of culture until the microorganisms in the soil recover. After the microorganisms in the soil were recovered, wheat and corn stalks were added to tissue culture flasks at 28°C for 50 days of enrichment culture. Soil samples were collected at 1, 14 and 40 days to isolate cellulose-degrading bacteria.
[0024] 2. Culture medium formula
[0025] (1) Enrichment medium: 5 g of cellulose (straw), 5 g of peptone, 5 g of sodium chloride, 0.5 g of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 0.5 g of magnesium sulfate, and 1000 ml of distilled water...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Identification of cellulose degrading strains
[0036] After culturing the strain in liquid medium at 140 rpm shaker for 2 days, DNA was extracted and 16s rDNA sequencing was performed. The sequence result is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1;
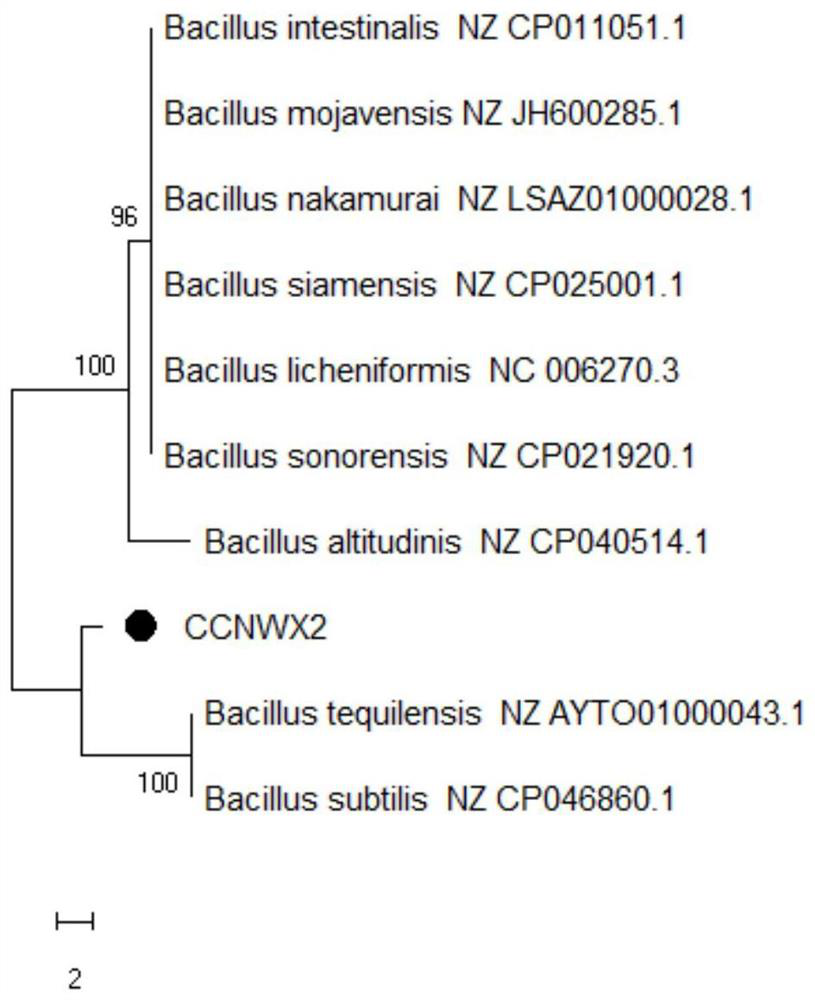
[0037] BLAST alignment was performed on NCBI to construct a phylogenetic tree. The result is as image 3 As shown, the similarity between this strain and Bacillus tequilensis is 98%, which belongs to the genus Bacillus (Bacillus sp.) and is named Bacillus sp. CCNWX2.
[0038] The strain was deposited in the General Microbiology Center (CGMCC) of the China Microorganism Culture Collection and Management Committee on June 1, 2020, and the deposit number is CGMCC No: 19895. The deposit address is: Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, No. 3, No. 1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing.
Embodiment 3
[0040] Determination of cellulase activity
[0041] 1. Drawing of glucose standard curve
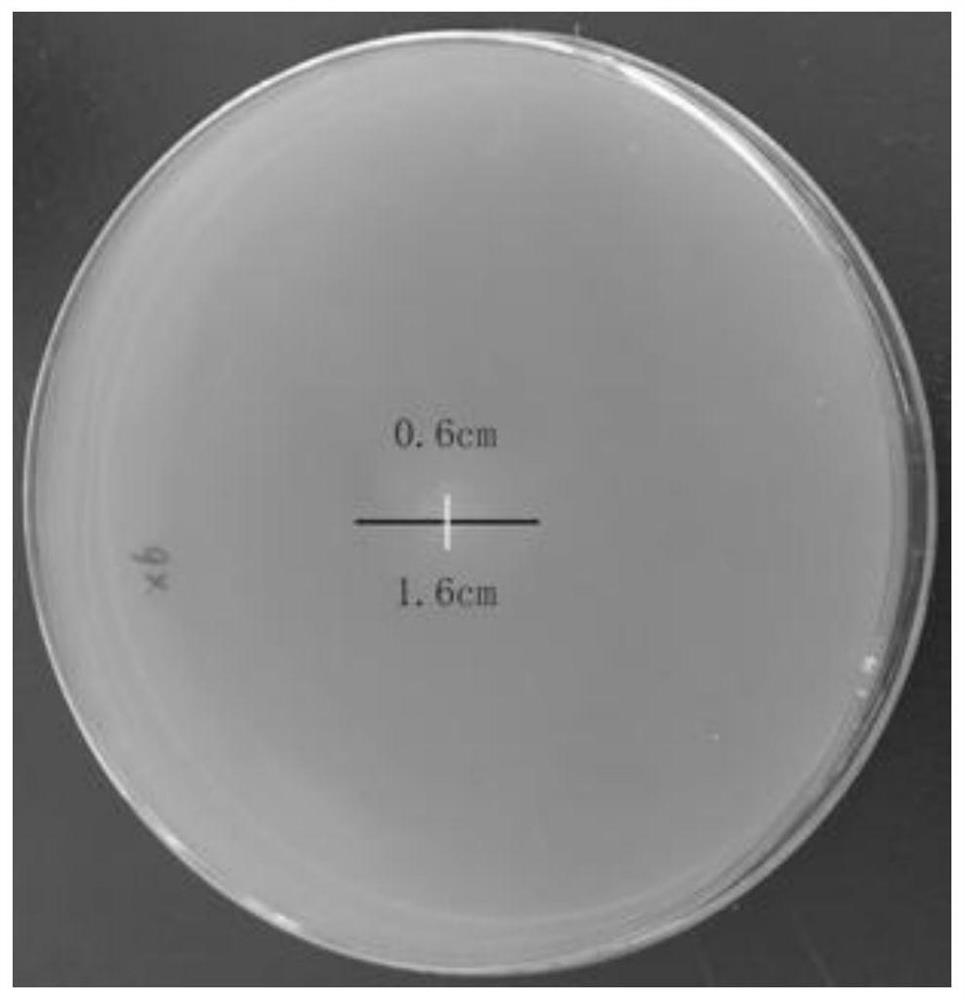
[0042] Add 0mL, 0.2mL, 0.4mL, 0.6mL, 0.8mL, 1mL of 1mg / mL standard glucose solution to 18 15ml tubes in 3 tubes (3 replicates) respectively, and make up to 1.5ml with distilled water, add 1.5mL DNS solution, shake well, place it in a boiling water bath and continue to heat for 10min, take it out and cool it immediately, fill it up to 15mL with distilled water, shake well, measure its absorbance at a wavelength of 540nm, take the glucose content (mg / mL) as the abscissa, the corresponding The absorbance is the ordinate, and the glucose standard curve is drawn as Figure 4 .
[0043] 2. Determination of cellulase activity
[0044]After the crude enzyme solution was centrifuged at 12,000 r / min, 0.5 mL of the supernatant was added to a colorimetric tube with a stopper that was dried to constant weight in advance, and 1 mL of 1% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose solution was added accurately. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com