A non-pathogenic R. solanacearum strain transfected with phage trp574 gene and its preparation method and application
A non-pathogenic, bacteriophage technology, applied in the field of bacterial wilt control, can solve the problems of pathogenic bacteria resistance environment, pollution, and the need to improve the control effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1 Preparation of bacterial wilt engineered bacteria transfected with bacteriophage trp574 gene
[0036] 1. Construction of recombinant plasmids
[0037] In the early stage, the inventors discovered a transcriptional regulator orf30 by sequencing the genome of the lytic phage P574, and further designed amplification primers for the target gene orf30 according to the P574 genome information. The purpose fragment of about 688bp was increased, and the purpose fragment was sequenced, and it was found that the orf30 sequence was 555bp, and its nucleotide sequence was as shown in SEQ ID NO:1, and its encoded amino acid sequence was as shown in SEQ ID NO:2; BALST alignment search found that orf30 only had 82% homology with Ralstonia phage GP4. The protein search results showed that orf30 has a conserved sequence of transcriptional regulator, and the highest amino acid sequence homology is less than 70%. Therefore, rf30 was named trp574 gene, where T stands for Transcri...
Embodiment 2
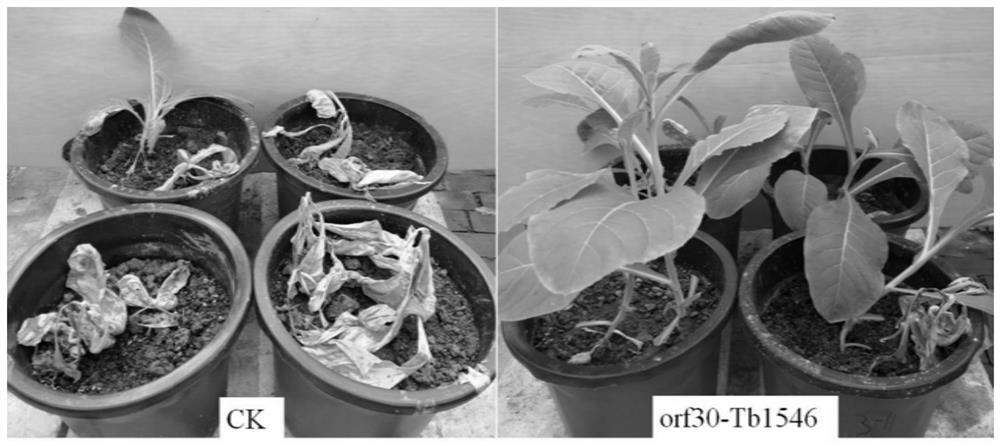
[0060] Embodiment 2 Tobacco bacterial wilt control pot experiment
[0061] 1. Method
[0062] R. solanacearum culture: activate Tb1546 stored at -80°C with TTC medium, cultivate at 30°C for 48h to obtain bacterial colonies of R. solanacearum, pick a single colony and cultivate in LB liquid medium for 24h for use. Similarly, the activated orf30-Tb1546 strain was cultured in LB liquid for 24-48 h, and set aside. Potted plant inoculation: The time was on June 26, 2019 in the Bacteria Research Room of South China Agricultural University. Each pot is filled with 15kg of soil, and 2 tobacco seedlings with 6 leaf ages are planted, and the number of each treated tobacco is 48, with a total of 24 pots. First inoculate the orf30-Tb1546 strain of engineering bacteria, and inoculate 200 mL of engineering bacteria solution per pot with a concentration of 2 × 10 6 CFU / mL. The next day, the concentration of 5 × 10 6 Ralstonia solanacearum Tb1546 of CFU / mL was sprayed on the rhizosphere...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com