Method for removing endotoxin in phage preparation and application of method
A bacteriophage and endotoxin technology, applied in the direction of bacteriophage, virus/bacteriophage, microorganism-based method, etc., can solve the problems of limitation, different molecular size, density, sedimentation coefficient, etc., to achieve simple equipment, good removal effect, and wide market. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
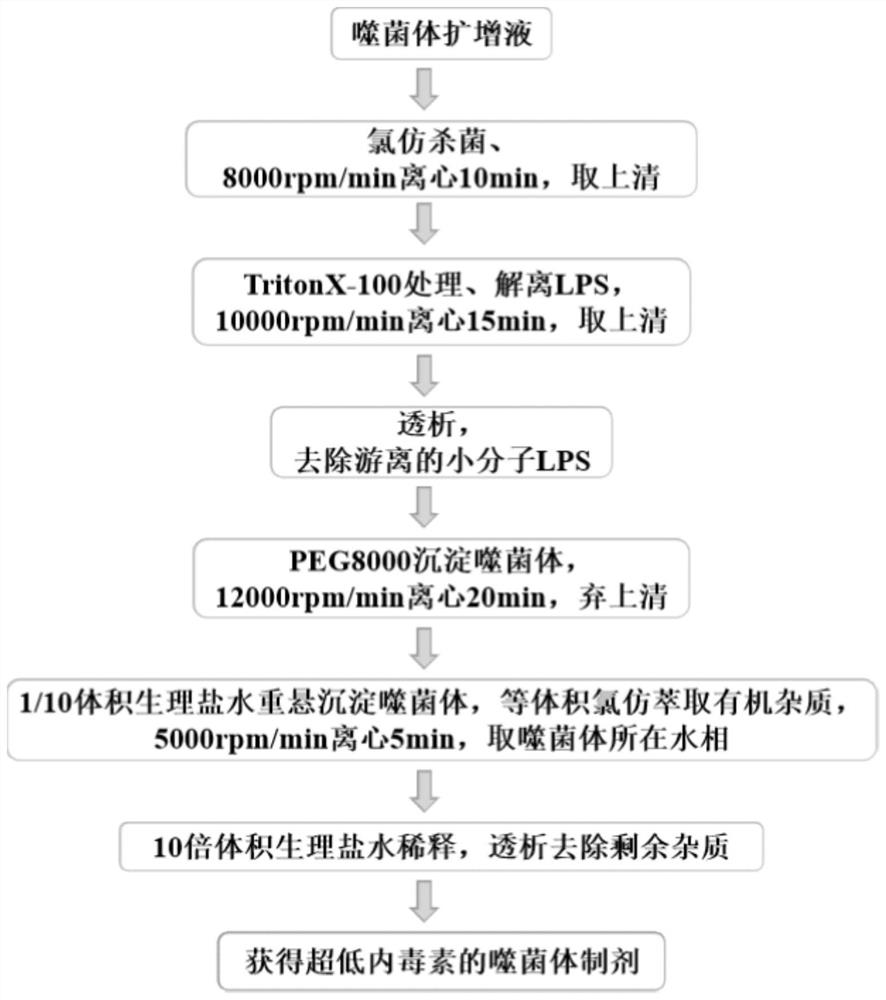
[0080] Example 1 Removal of free and small molecule LPS in the solution
[0081] 1. Phage amplification
[0082] Streak the host bacteria on the LB solid medium, place it in a constant temperature incubator at 37°C and cultivate it for about 12 hours, pick a single colony that conforms to the shape of the bacteria, place it in 5ml LB liquid medium, and culture it with shaking at 37°C and 220rpm About 8 hours. Transplantation was carried out at a ratio of 1%, and the host bacteria were cultivated to the logarithmic growth phase.
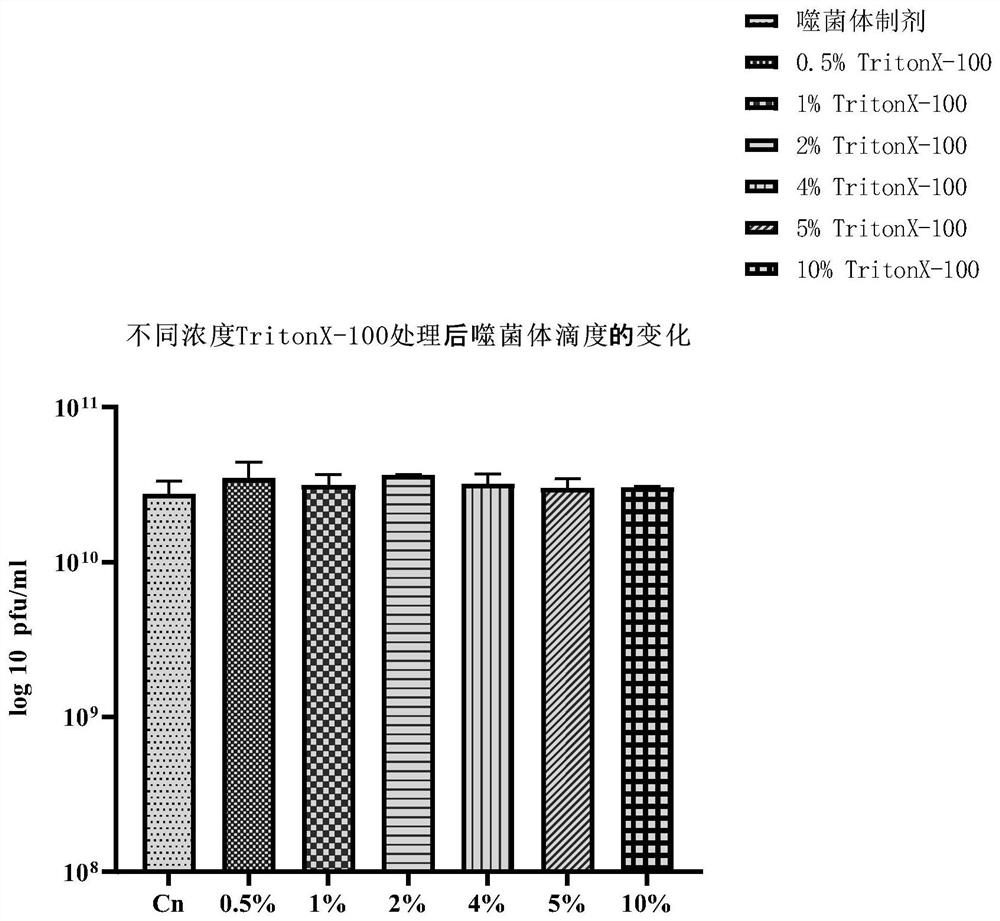
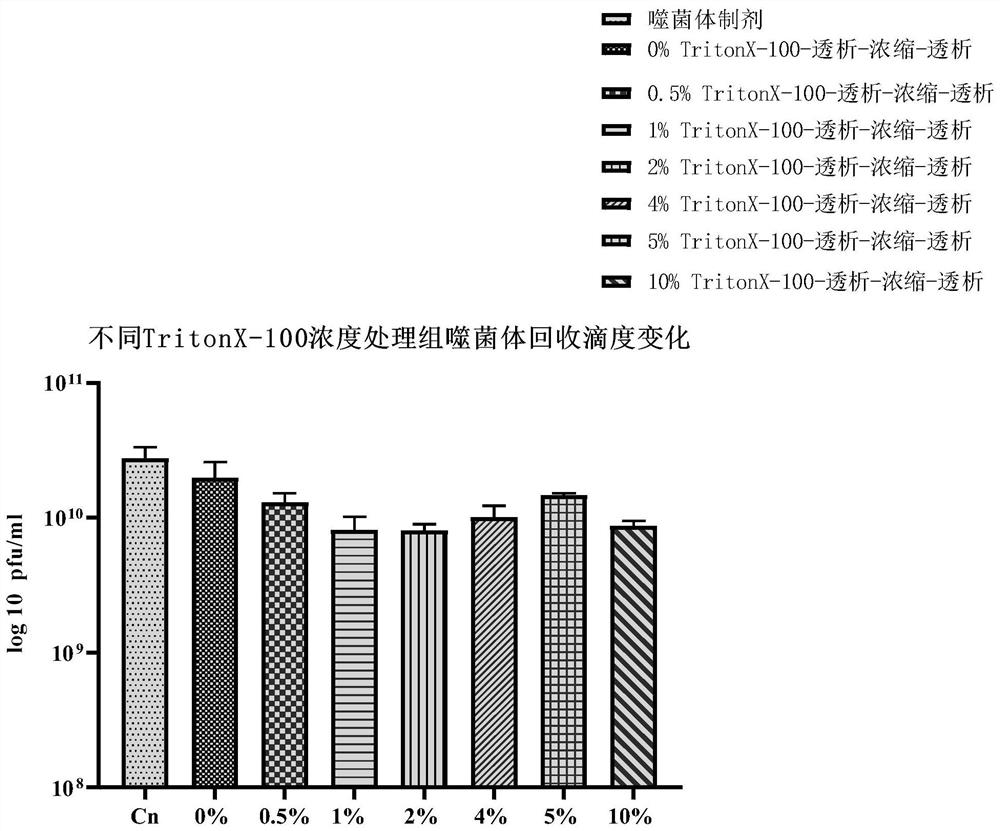
[0083] The host bacteria in the logarithmic growth phase were transferred according to the ratio of 1%, and an equal proportion of the target phage was added at the same time, and then placed at 37° C. and 220 rpm for shaking culture for about 2 hours. In addition, two groups of control experiments were set up, one group was only inoculated with bacteria, and the other group was neither inoculated with host bacteria nor added with phage. Comparing ...
Embodiment 2
[0099] Embodiment 2 removes macromolecule LPS and improves the titer of bacteriophage
[0100] 5. PEG concentration
[0101] Put the dialyzed solution in Step 4 of Example 1 into a suitable centrifuge tube (15ml or 50ml), add solid NaCl at 5.84g / 100ml, and fully dissolve. Then add PEG8000 according to the ratio of 10% (W / V) to dissolve it, so that the solution becomes a homogeneous solution. Then place it at 4°C overnight or for more than 8 hours, then centrifuge at 12000 rpm / min for 20 minutes, discard the supernatant after centrifugation, and invert the centrifuge tube for 2-3 minutes to remove the supernatant solution as much as possible. According to 10% of the original solution, add washing solution (0.9% physiological saline or PBS solution or SM buffer, etc.) for resuspension, and fully wash the tube wall. The resulting liquid is the phage concentrate.
[0102] Purpose of this step:
[0103] (1) Removal of macromolecular LPS in phage preparations.
[0104] (2) Remo...
Embodiment 3
[0106] Embodiment 3 removes the residue of organic reagent
[0107] 6. Chloroform extraction
[0108] Add the solution resuspended in Step 5 of Example 2 to the chloroform solution at a ratio of 1:1, vortex for 1 min, mix thoroughly, and then centrifuge at 5000 rpm / min for 5 min, the solution has obvious layers, take the supernatant and repeat the extraction once.
[0109] Purpose of this step:
[0110] (1) Further remove residual TritonX-100 reagent.
[0111] (2) Remove PEG8000 and other impurities in the solution.
[0112] 7. Dialysis
[0113] Dilute the solution obtained in step 6 according to clinical needs in an appropriate ratio, transfer it into the dialysis membrane of BiotechCE Tubing MWCO:1000kD and place it in 100 times the volume of normal saline for dialysis, and dialyze twice to remove the chloroform in the solution solution.
[0114] Purpose of this step:
[0115] (1) The main function is to remove various reagents introduced in the solution.
[0116] (2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com