Implant for maxillofacial bone defect repair, and preparation method of implant
An implant and maxillofacial bone technology, which is applied in the field of biomedical engineering, can solve the problems of skin nerve tissue damage, stress shielding effect, and bone tissue appearance damage, so as to improve ingrowth and vascularization, and reduce weight and stress shielding. , the effect of reducing material cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
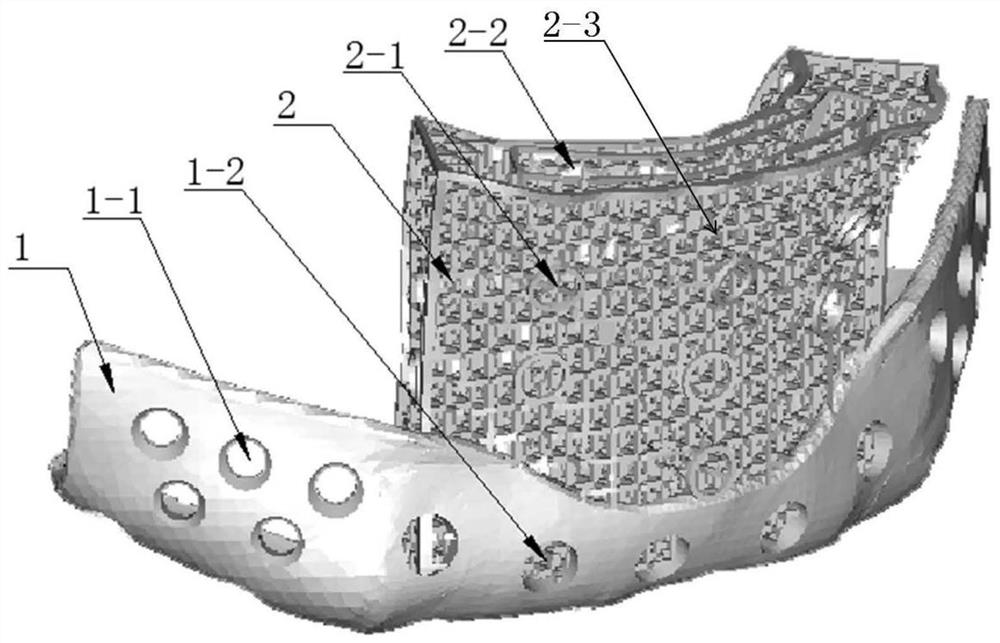
[0047] like figure 1 The shown implant for the repair of maxillofacial and chin defects, the implant structure includes a fixation unit 1, a porous structure part 2 integrally and smoothly connected with the fixation unit 1, and only one end of the porous structure part 2 is connected with the fixation unit 1 connect;
[0048] The fixation unit 1 includes a screw hole 1-1 and a first through hole 1-2, the fixation unit 1 matches the shape of the healthy residual bone, and the fixation unit 1 realizes the connection with the healthy residual bone through the screw and the screw hole 1-1.
[0049] The thickness T of the fixing unit 1 is 1.5 mm. Screw holes 1-1 are customized according to different screw types, such as selecting countersunk holes, tapered holes, countersunk holes or threaded holes ( Figure 6-9 Shown), what screw hole 1-1 adopted in the present embodiment is tapered hole (as Figure 7 shown). The hole diameter D1 of the screw hole 1-1=2.4mm. The hole diamete...
Embodiment 2
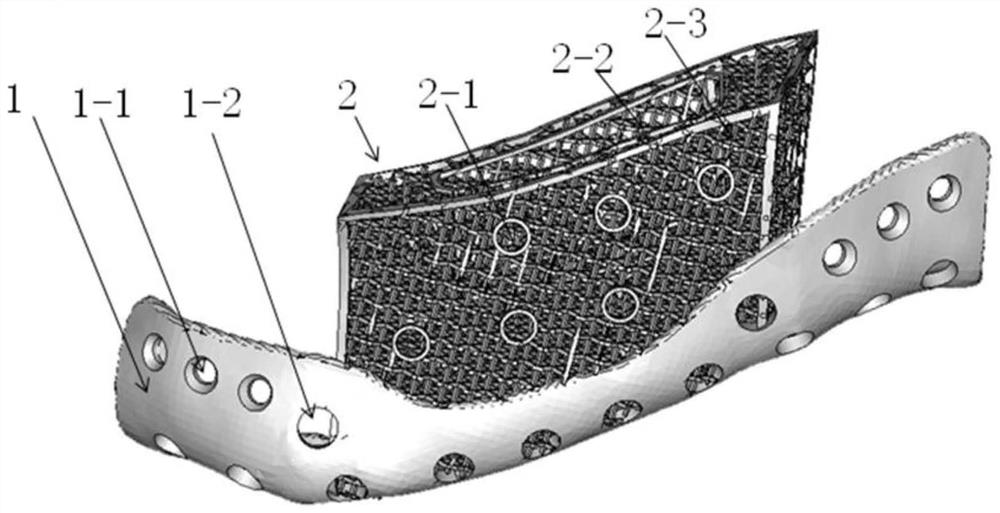
[0057] like figure 2 The implant used for maxillofacial body defect repair shown, it differs from embodiment 1 in that:
[0058] The distance H between the reserved groove for implantation and the healthy remaining bone on both sides was 7.7 mm, the width u of the groove was 9.4 mm, the length w was 30.1 mm, and the depth v was 15 mm.
[0059] The preparation method of the implant for repairing maxillofacial body defects provided in this example is the same as that in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0061] like image 3 The difference between the shown implant for maxillofacial hemiside defect repair and Example 1 is:
[0062] There are two planting reserved grooves 2-2 on the upper part of the porous structure part, and the distance H between the two planting reserved grooves and the healthy remaining bone on both sides is 5.9mm. Among them, the reserved width u of the reserved groove for planting on the right side and the edge of the porous structure is 4.3mm, the length w is 27.4mm, and the depth v is 11mm; the reserved width u of the reserved groove for planting on the left side and the edge of the porous structure is 9.4mm , the length w is 30.1mm, and the depth v is 15mm.
[0063] The preparation method of the implant for repairing the hemimaxillofacial defect provided in this example is the same as that in Example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Hole diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Rib length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com