Method for calculating water consumption of plant covered with degradable mulching film
A technology for degrading mulch and calculation methods, which is applied to calculations using numerical representations, calculations using non-contact manufacturing equipment, and complex mathematical operations. It can solve problems such as low precision and large calculation errors, and improve accuracy. , reduce errors, and reduce the effect of calculation errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
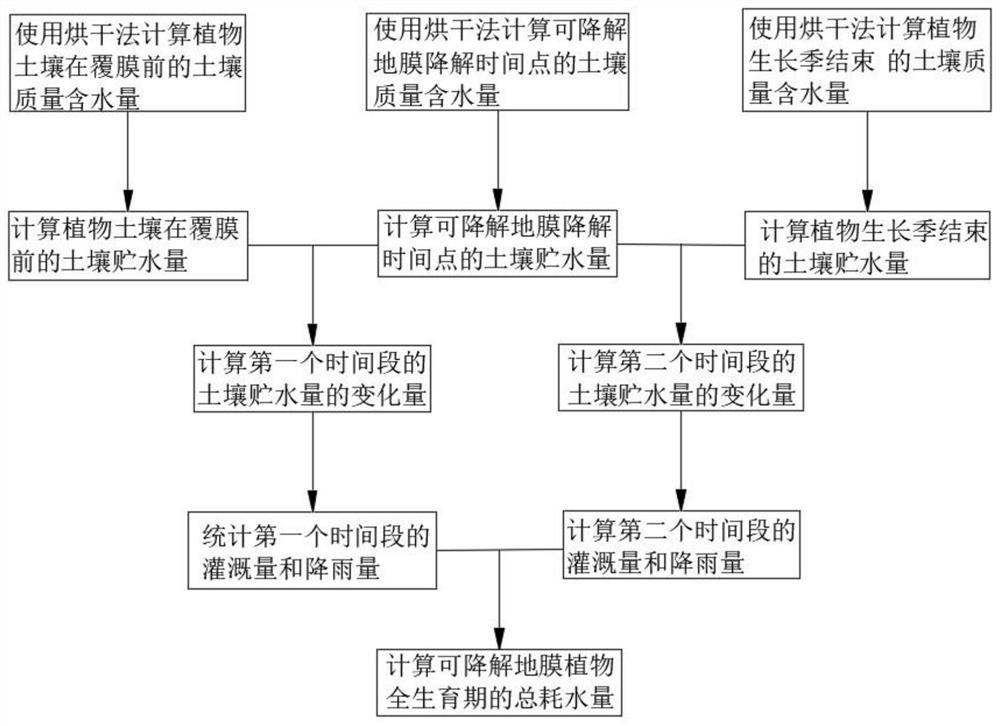
[0051] see figure 1 , Figure 4-8 , a method for calculating the water consumption of plants covered with degradable plastic films, the method for calculating the water consumption of plants covered with degradable plastic films includes the following steps:
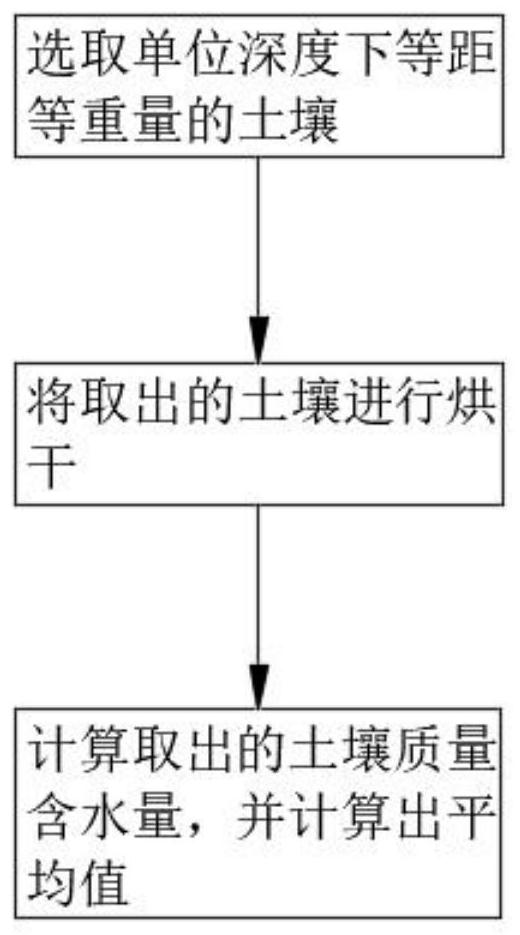
[0052] S1. Use the drying method to calculate the soil quality and water content of the plant soil on the day before the mulching, the degradation time of the degradable mulch film, and the end of the plant growth season; the end of the plant growth season refers to the time when the plants are harvested or harvested.
[0053] S2. Calculate the soil water storage in the first time period from the plant soil mulching to the degradable mulch degradation time point;
[0054] S3. count the irrigation amount and rainfall in the first time period;
[0055] S4. Calculate the soil water storage at the time point of degradation of the degradable plastic film and the second time period at the end of the plant growth season;
[...
Embodiment 2
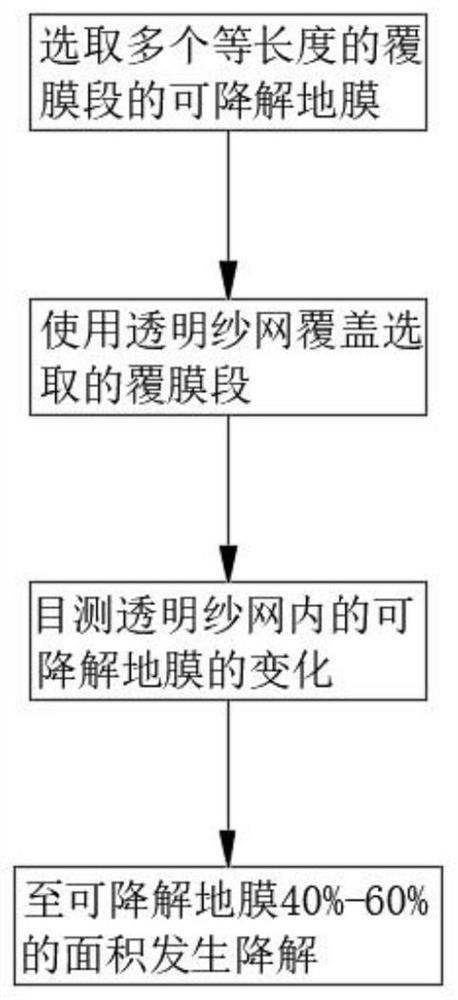
[0064] see figure 1 with figure 2 , where the same or corresponding components as those in Embodiment 1 use the corresponding reference numerals as in Embodiment 1, and for the sake of simplicity, only the differences from Embodiment 1 will be described below. The difference between this embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is: please refer to figure 2 , the method for confirming the degradation time point of the degradable plastic film includes the following steps:
[0065] S1. Between the soil of the film-covered plants, select a plurality of degradable plastic films of equal length film-covered sections;
[0066] S2. Use a transparent gauze to cover the upper end of the degradable mulch film of the selected mulch section;
[0067] S3. Observe the changes of the degradable plastic film in the area covered by the transparent gauze by visual inspection;
[0068] S4. When 40%-60% of the degradable plastic film in the area covered by the transparent gauze is degraded, it is the t...
Embodiment 3
[0070] see figure 1 with figure 2 , wherein the same or corresponding components as those in Embodiment 2 use the corresponding reference numerals as in Embodiment 2, and for the sake of simplicity, only the differences from Embodiment 2 are described below. The difference between this embodiment 3 and embodiment 2 is: please refer to figure 2 , in step S1 of the method for confirming the degradation time point of the degradable plastic film, the number of selected film sections is 2-5, and the selected length of the film sections is 0.8m-1.3m. Selecting multiple film sections is convenient for determining the degradable film on behalf of the entire film area, effectively improving the accuracy of determining the degradation time point of the degradable film, and selecting an appropriate length of film section is convenient for manual visual observation to determine the degradation of the degradable film Condition.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com