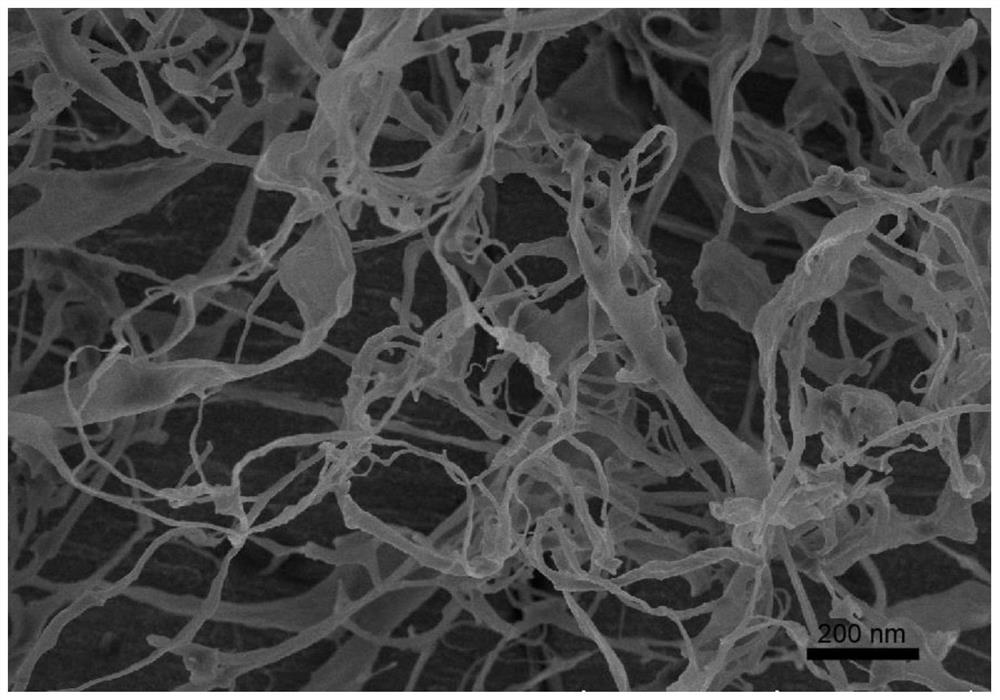
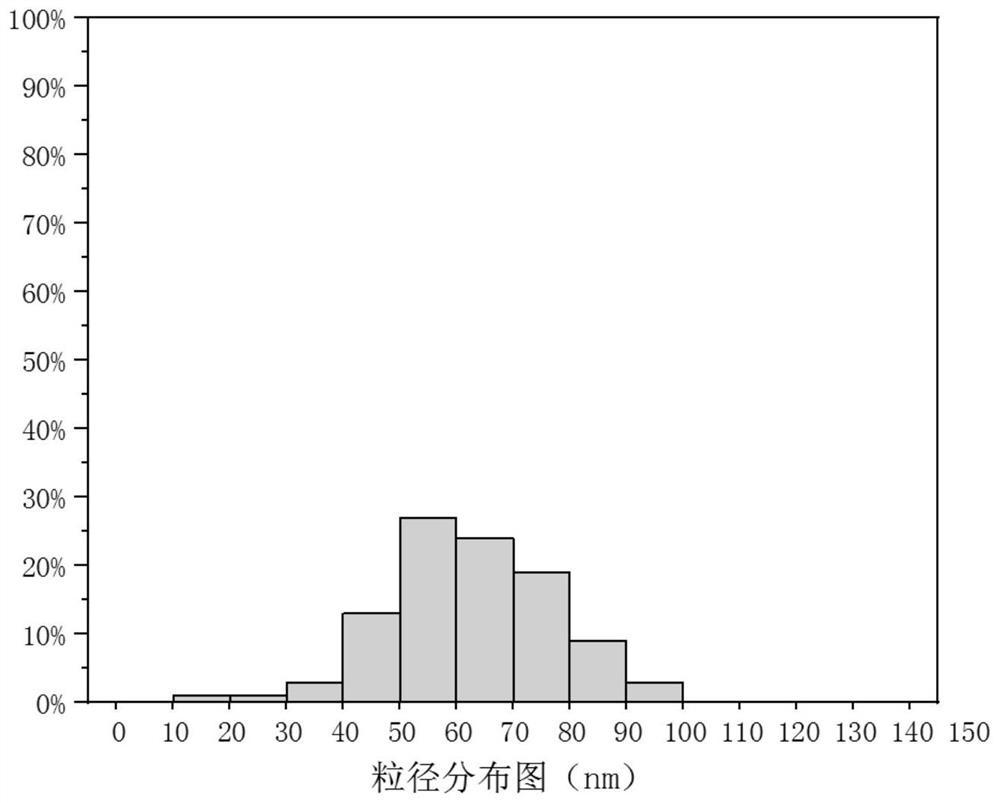
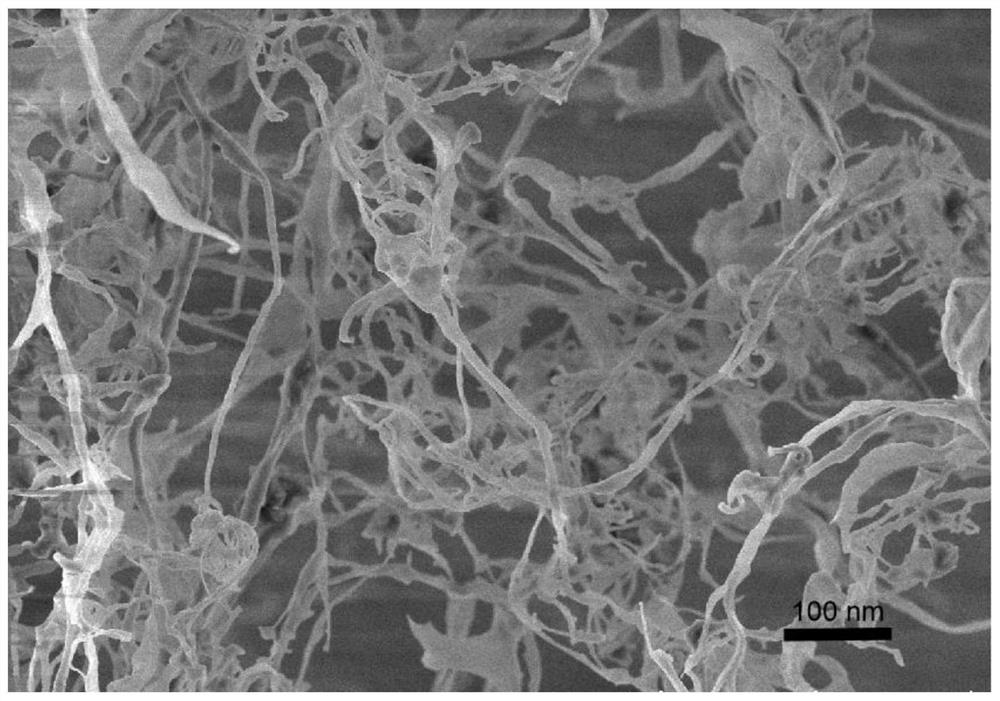
Preparation method of nanocellulose
A nano-cellulose and fiber technology, applied in the field of fiber materials, can solve problems such as lack of equipment, environmental impact, and application restrictions, and achieve the effects of easy removal, easy removal of impurities, and high solid content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0073] The embodiment of the present invention provides the first nanocellulose, and the specific preparation steps are as follows:
[0074] (1) Weigh 50g of wood powder that has passed through a 80-mesh sieve, add the wood powder to 1000ml of dilute sulfuric acid solution (the mass percent of dilute sulfuric acid solution is 1.5%), then place it in a water bath at 130°C and stir for 120min, and the reaction ends After that, suction filtration, washing to neutrality and drying are carried out successively to obtain the preliminary fiber product;
[0075] (2) 40g of the preliminary fiber product prepared in step (1) is weighed, added to 800ml of deionized water, and dispersed by magnetic stirring, then 6g of sodium chlorite is added to form a reaction solution, and the temperature of the water bath is set The temperature is 80°C, and the reaction is carried out by adding 6g of sodium chlorite every 30 minutes for a total of 120 minutes (that is, a total of 4 times of sodium chl...
Embodiment 2
[0080] The embodiment of the present invention provides the second nanocellulose, and the specific preparation steps are as follows:
[0081] (1) Weigh 50g of wood powder that has passed through a 80-mesh sieve, add the wood powder to 1000ml of dilute sulfuric acid solution (the mass percent of dilute sulfuric acid solution is 1.5%), then place it in a water bath at 130°C and stir for 120min, and the reaction ends After that, suction filtration, washing to neutrality and drying are carried out successively to obtain the preliminary fiber product;
[0082] (2) 40g of the preliminary fiber product prepared in step (1) is weighed, added to 800ml of deionized water, and dispersed by magnetic stirring, then 6g of sodium chlorite is added to form a reaction solution, and the temperature of the water bath is set The temperature is 80°C, and the reaction is carried out by adding 6g of sodium chlorite every 30 minutes for a total of 120 minutes (that is, a total of 4 times of sodium ch...
Embodiment 3
[0087] The embodiment of the present invention provides the third nanocellulose, and the specific preparation steps are as follows:
[0088] (1) Weigh 50g of wood powder that has passed through a 80-mesh sieve, add the wood powder to 1000ml of dilute sulfuric acid solution (the mass percent of dilute sulfuric acid solution is 1.5%), then place it in a water bath at 130°C and stir for 120min, and the reaction ends After that, suction filtration, washing to neutrality and drying are carried out successively to obtain the preliminary fiber product;
[0089] (2) 40g of the preliminary fiber product prepared in step (1) is weighed, added to 800ml of deionized water, and dispersed by magnetic stirring, then 6g of sodium chlorite is added to form a reaction solution, and the temperature of the water bath is set The temperature is 80°C, and the reaction is carried out by adding 6g of sodium chlorite every 30 minutes for a total of 120 minutes (that is, a total of 4 times of sodium chl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com