Maize gene zmravl1 and functional site and its use
A corn and purpose technology, applied in genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the level of preliminary positioning of corn leaf angle research, and the genetic and molecular regulatory network of corn leaf angle is far from being elucidated, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of broadening the source, shortening the selection process, and broadening the genetic basis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0091] Example 1 Initial and fine mapping of ZmRAVL1 gene
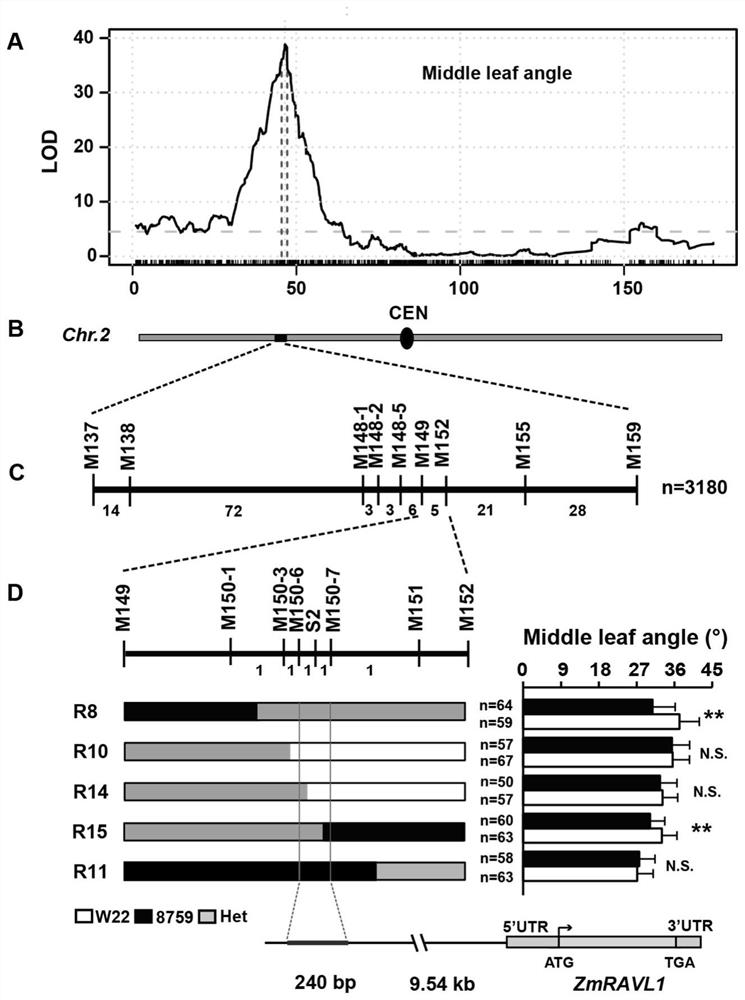
[0092] A set of RIL populations constructed by backcrossing and selfing of the maize inbred line W22 and the ancestor species CIMMYT 8759 (referred to as 8759 in this paper) were used to initially map the leaf angle QTL. The phenotypic value of the angle between the angle and the flag leaf was blurred as the phenotypic input value for QTL mapping, combined with 19,378 high-density, high-quality molecular markers, using the multi-QTL model in R / qtl, using the R software (Version 3.1. 0) Perform QTL positioning. After 1000 times of permutation test (significance P=0.01), the QTL significance thresholds of the angle between the upper leaves of the panicle and the angle of the flag leaves were determined to be LOD=5.
[0093] For the upper leaf angle of maize ears, a total of 10 QTLs were mapped, among which UPA2 (Compact Plant Architecture 2) located on chromosome 2 had the greatest effect, which could explain 12.1% of ...
Embodiment 2
[0124] Example 2 Nucleic acid molecule information of ZmRAVL1
[0125] The nucleic acid molecular sequence of ZmRAVL1 was obtained on maizeGDB (https: / / www.maizegdb.org / ) (since the genome of the maize inbred line B73 and the genome sequences of many other maize inbred lines have been obtained, only the nucleic acid sequence In general, the sequences of most genes are known, and the sequences of all genes including this gene can be obtained from multiple websites such as maizeGDB; although the function of this gene can be predicted on websites such as maizeGDB, but The function of this gene regulating corn leaf angle was discovered by the present inventor for the first time. The materials used in the present invention are corn inbred line W22 and corn wild species Rumba 8759, W22 has completed sequencing, and the genome sequence has also been released; The sequence of this gene in Dagucao 8759 was obtained by referring to the W22 and B73 genome clones. The detailed information...
Embodiment 3
[0129] Example 3 Protein molecular information of ZmRAVL1
[0130] (1) Sequence encoding the protein
[0131] ( https: / / www.maizegdb.org / gene_center / gene / GRMZM2G102059 )
[0132] MEFASSSSRFSREEDEEEEQEEEEEEEEASPREIPFMTAAATADTGAAASSSSPSAAASSGPAAAPRSSDGAGASGSGGGGSDDVQVIEKEHMFDKVVTPSDVGKLNRLVIPKQHAEKYFPLDAAANEKGQLLSFEDRAGKLWRFRYSYWNSSQSYVMTKGWSRFVKEKRLDAGDTVSFCRGAGDTARDRLFIDWKRRADSRDPHRMPRLPLPMAPVASPYGPWGGGGGGGAGGFFMPPAPPATLYEHHRFRQALDFRNINAAAAPARQLLFFGSAGMPPRASMPQQQQPPPPPHPPLHSIMLVQPSPAPPTASVPMLLDSVPLVNSPTAASKRVRLFGVNLDNPQPGTSAESSQDANALSLRTPGWQRPGPLRFFESPQRGAESSAASSPSSSSSSKREAHSSLDLDL
[0133] (SEQ ID No: 27) (see image 3 )
[0134] (2) Domains that encode proteins
[0135] (http: / / smart.embl-heidelberg.de / smart / show_motifs.pl)
[0136] Domain prediction of the amino acid sequence encoded by the gene on the Smart website shows that the amino acid sequence encoded by the gene contains a B3 domain ( image 3 amino acid sequence marked in red). In the gramene website, the g...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com