Yarrowia lipolytica genetically engineered bacterium for producing limonene and application of yarrowia lipolytica genetically engineered bacterium
A technology of Yarrowia lipolytica and genetically engineered bacteria, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as inability to meet, and achieve the effects of reducing production costs, increasing yield, and reducing waste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
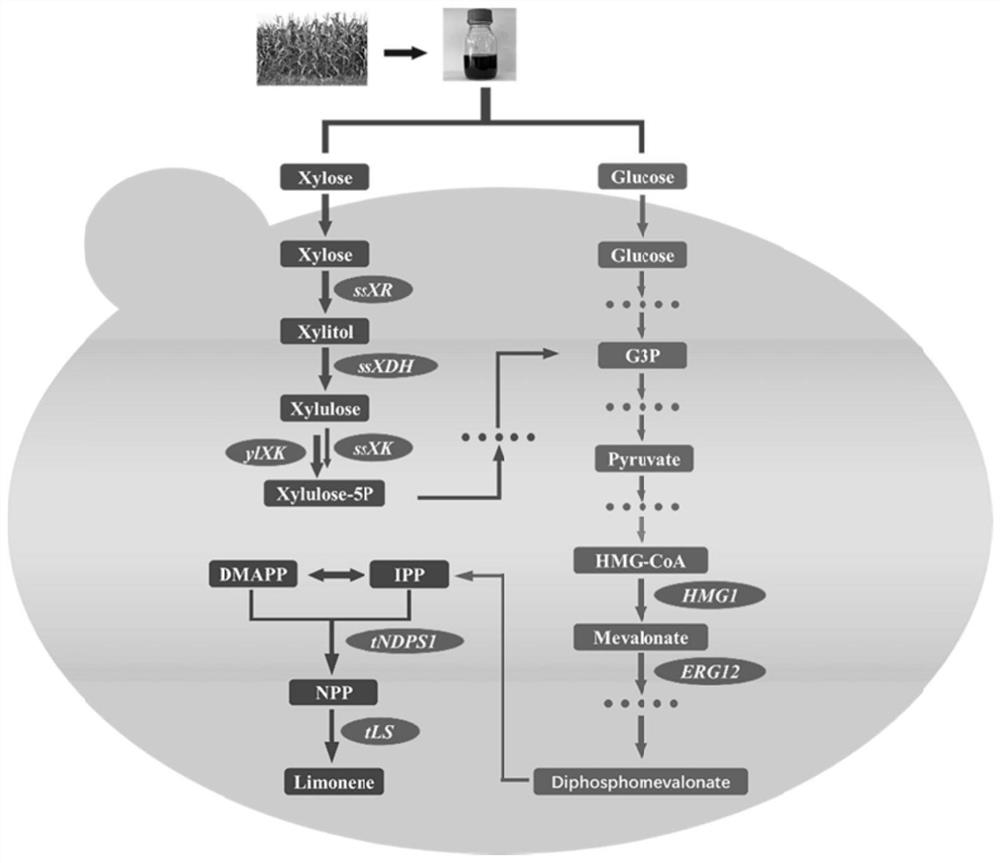
[0056]Example 1: Construction of xylose utilization metabolic pathway in Yarrowia lipolytica
[0057] (1) Since Yarrowia lipolytica itself can only metabolize a small amount of xylose, in order to use xylose to synthesize limonene, this example introduces the optimized xylose reductase gene XR and xylitol dehydrogenase gene XDH derived from Scheffersomyces stipites , and overexpressed the xylose assimilating enzyme gene XK from Yarrowia lipolytica.
[0058] (2) The optimized xylose reductase gene XR derived from Scheffersomyces stipites was constructed into the plasmid pHR_AXP_hrGFP through double restriction sites PteI and NheI to obtain the plasmid pHR_AXP_XR. The optimized xylitol dehydrogenase gene XDH derived from Scheffersomyces stipites was constructed into plasmid pHR_XPR2_hrGFP through double restriction sites PteI and NheI to obtain plasmid pHR_XPR2_XDH. The xylose assimilating enzyme gene XK from Yarrowia lipolytica was constructed into the plasmid pHR_A08_hrGFP th...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Example 2: Construction of limonene synthesis pathway in Yarrowia lipolytica
[0065] (1) The optimized sequence of the gene LS derived from Agastache rugosa and the optimized sequence of the gene NDPS1 derived from tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) were respectively constructed into plasmid pINA1312 through restriction site PmlI to obtain plasmids pINA1312-LS and pINA1312-NDPS1.
[0066] (2) The expression cassette of the LS gene in the plasmid pINA1312-LS obtained in step (1) was connected to the plasmid pINA1312-NDPS1 obtained in step (1) through the restriction site StuI to obtain the plasmid pINA1312LN containing the genes LS and NDPS1.
[0067] (3) The expression cassette of the LS gene in the plasmid pINA1312-LS obtained in step (1) is connected to the plasmid pINA1312LN obtained in step (2) through the restriction site ClaI to obtain two copies of the gene LS and one copy of the gene LS. Plasmid pINA1312LLN of the gene NDPS1.
[0068] (4) The plasmid pINA1312LLN o...
Embodiment 3
[0071] Example 3: Mevalonate (MVA) Pathway Optimization in Yarrowia lipolytica
[0072] (1) The plasmid pINA1269-HMG1-ERG12 was linearized and then transformed into the strain YBX07 obtained in Example 2 by homologous recombination to obtain strain YBX08.
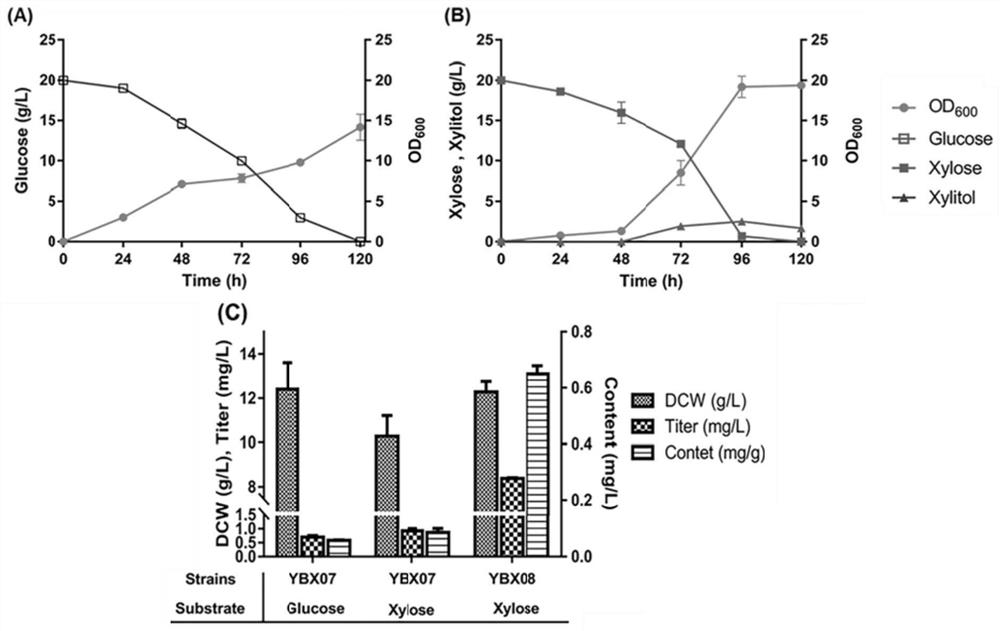
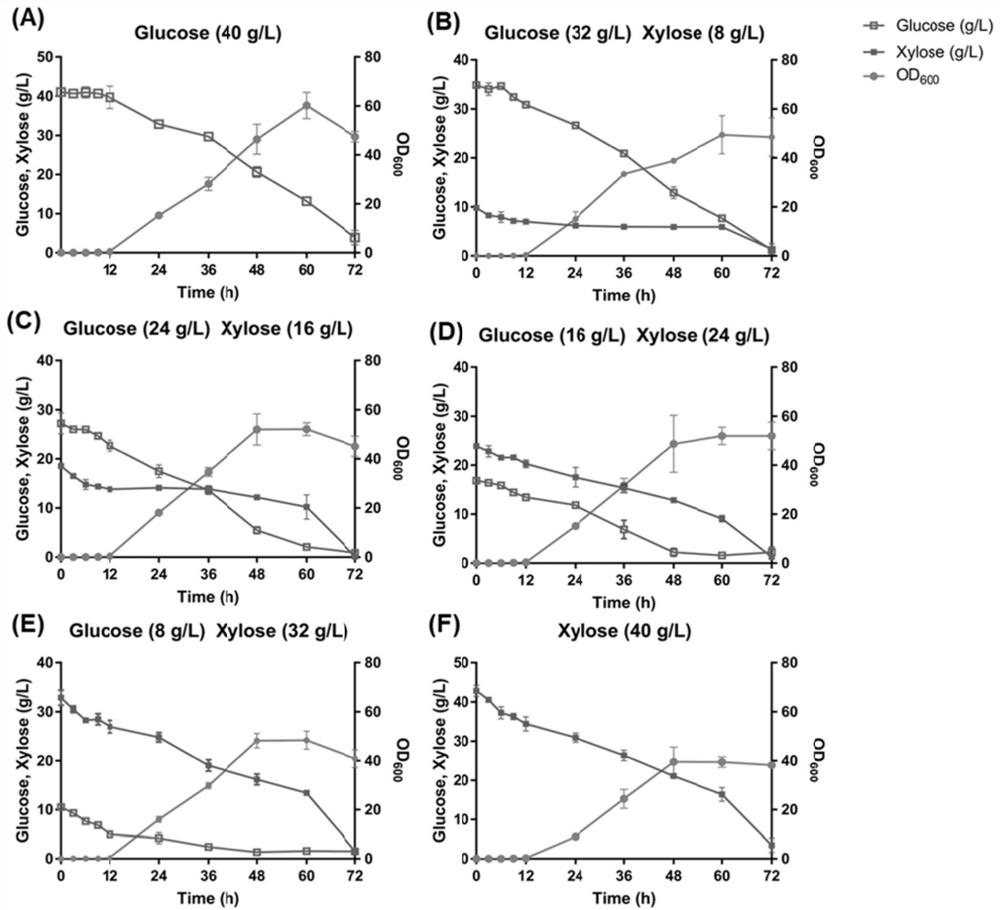
[0073] (2) The obtained recombinant strain YBX08 was subjected to shake-flask fermentation, and the specific shake-flask fermentation method was the same as the fermentation method of strain YBX07 in YPX medium in Example 2. After the fermentation, the limonene production, dry cell weight (DCW) and limonene yield of the strain YBX08 were measured respectively according to the standard limonene assay method. The results are shown in figure 2 c.
[0074] From figure 2 It can be seen in C that strain YBX08 can use xylose as a carbon source to synthesize limonene, and the limonene production is higher than that of strain YBX07 in YPX medium.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com