Method for replacing endogenous gene segment in non-homologous end connection manner
An endogenous gene and non-homologous technology, which is applied in the field of replacing endogenous gene fragments by means of non-homologous end joining, can solve the problems of long production cycle and low success efficiency, and achieve the goal of improving production efficiency and high efficiency Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
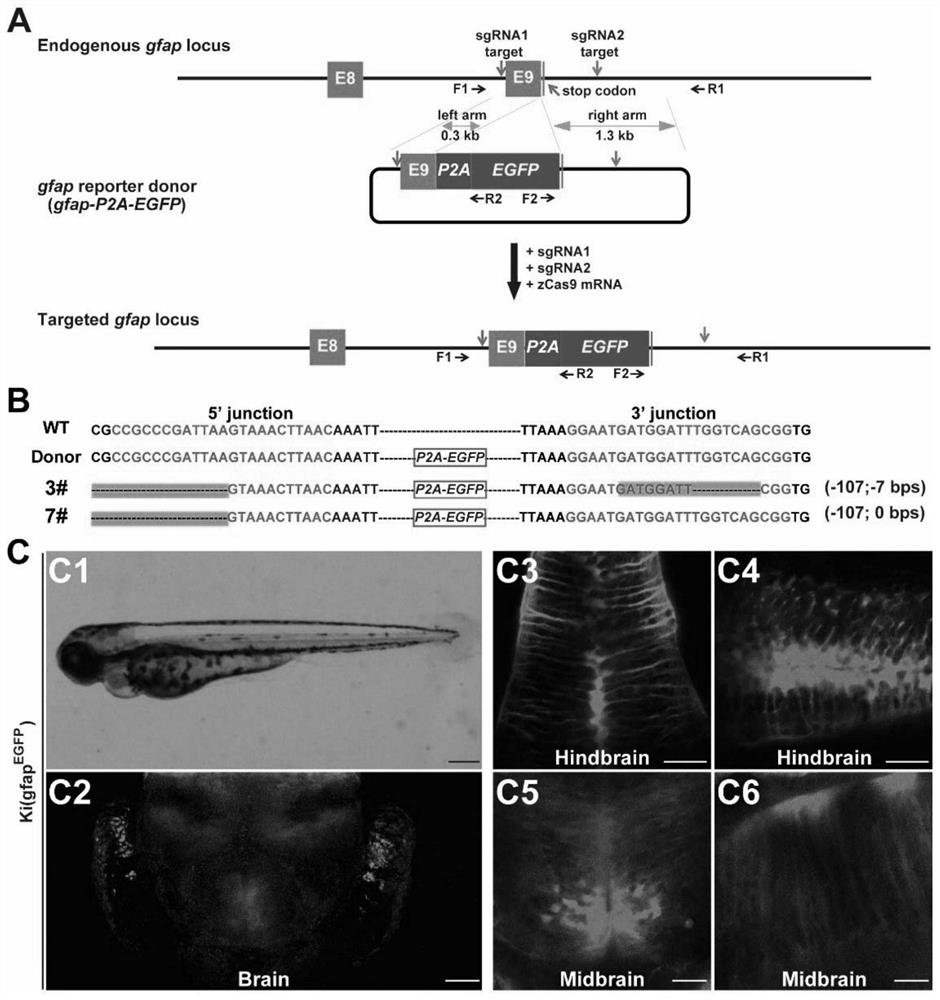
[0061] A method of replacing endogenous gfap gene fragments in a non-homologous end-joining mode of the present invention, comprising the steps of:
[0062] (1) Take the intron and UTR of the untranslated segment of the gfap gene in the genome as the target segment, and determine a guide RNA target sequence (two in total) on both sides of the target segment; determine the intron in the genome for the target segment A left homology arm sequence and a right homology arm sequence, each of which includes a respective guide RNA target sequence;
[0063] (2) Prepare a replacement donor plasmid or a donor DNA fragment, which includes the following sequentially connected elements: left homology arm sequence, middle exogenous replacement sequence, and right homology arm sequence;
[0064] (3) co-introduce the donor plasmid or donor DNA fragment, 2 guide RNAs or DNA that can form the 2 guide RNAs, Cas9 protein or mRNA or DNA that can form Cas9 protein into the target cell to obtain exog...
Embodiment 2
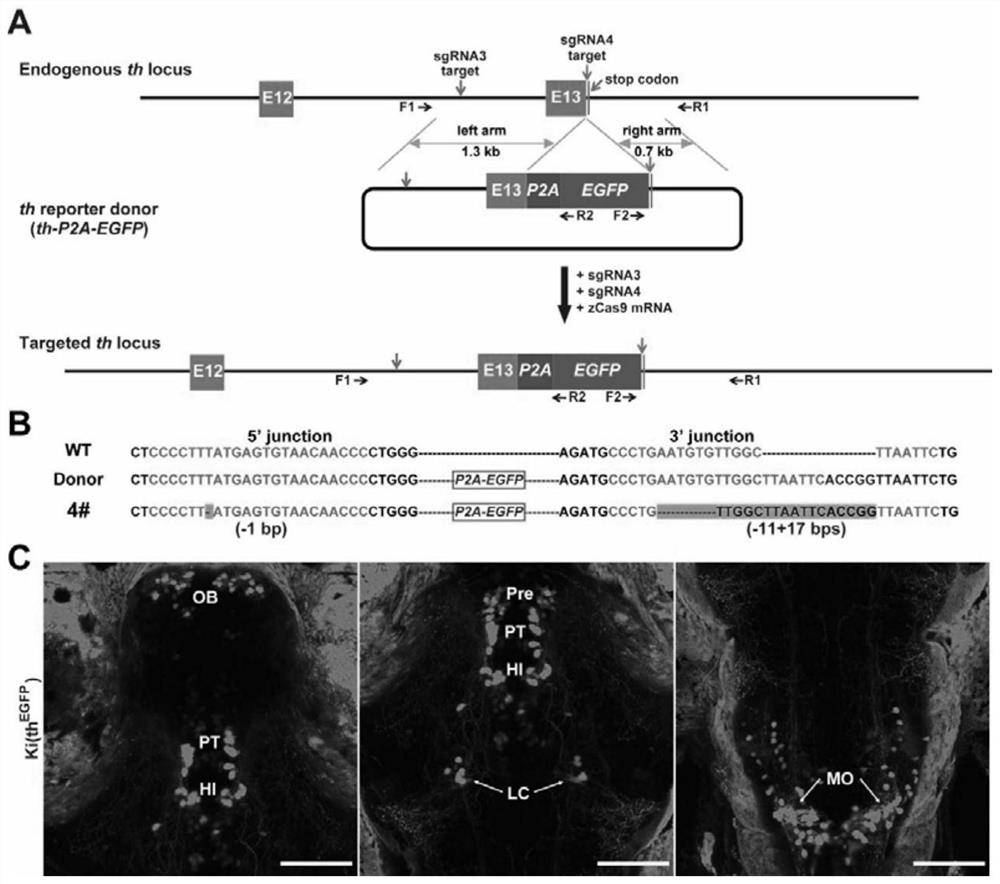
[0078] A method of replacing endogenous th gene fragments in a non-homologous end joining method of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0079] (1) Take the intron of the untranslated segment and the exon of the translated segment of the target gene in the genome as the target segment, and determine a guide RNA target sequence (two in total) on both sides of the target segment; The segment determines the left homology arm sequence and the right homology arm sequence in the genome, and both the left homology arm sequence and the right homology arm sequence comprise respective guide RNA target sequences;
[0080] (2) Prepare a replacement donor plasmid or a donor DNA fragment, which includes the following sequentially connected elements: left homology arm sequence, middle exogenous replacement sequence, and right homology arm sequence;
[0081] (3) co-introduce the donor plasmid or donor DNA fragment, 2 guide RNAs or DNA that can form the 2 guide RNAs, Cas9 pro...
Embodiment 3
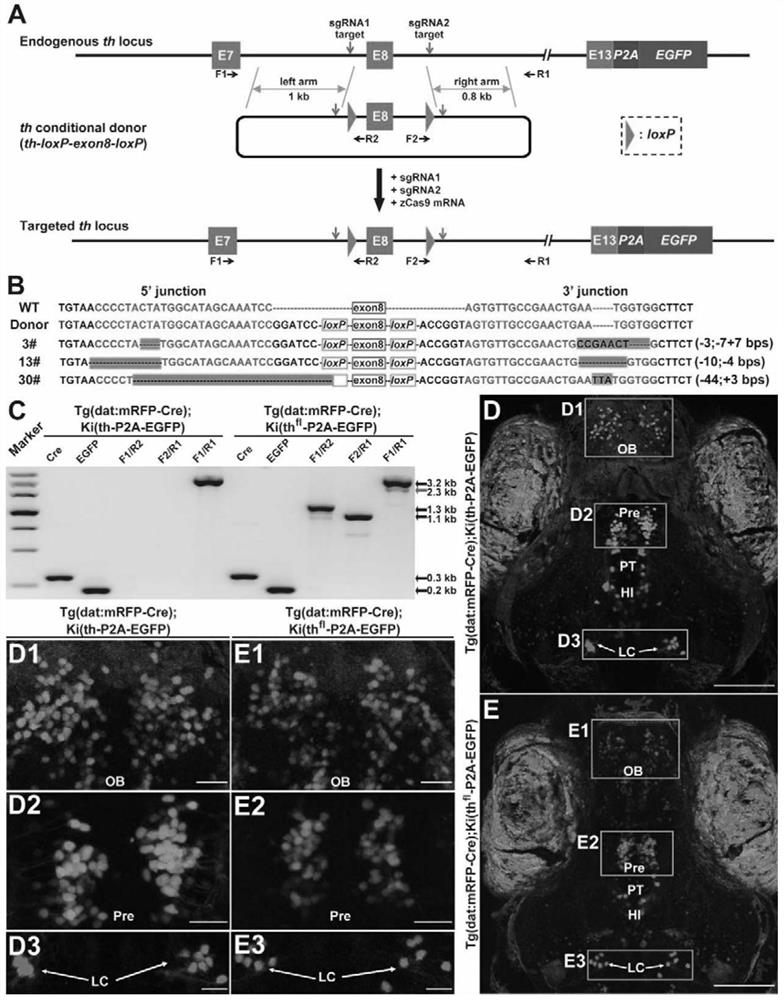
[0096] A method of replacing endogenous th gene fragments in a non-homologous end joining method of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0097] (1) Use the intron of the untranslated segment of the target gene in the genome as the target segment, and determine a guide RNA target sequence (two in total) on both sides of the target segment; determine the left homonym in the genome for the target segment The source arm sequence and the right homology arm sequence, the left homology arm sequence and the right homology arm sequence all comprise respective guide RNA target sequences;
[0098] (2) Prepare a replacement donor plasmid or a donor DNA fragment, which includes the following sequentially connected elements: left homology arm sequence, middle exogenous replacement sequence, and right homology arm sequence;
[0099] (3) co-introduce the donor plasmid or donor DNA fragment, 2 guide RNAs or DNA that can form the 2 guide RNAs, Cas9 protein or mRNA or DNA that ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com