Digital signal transmission processing equipment link fault analysis and alarm method
A technology for dealing with equipment and link failures, applied in digital transmission systems, transmission systems, data exchange networks, etc., can solve problems such as complex situations and inconvenient judgments
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
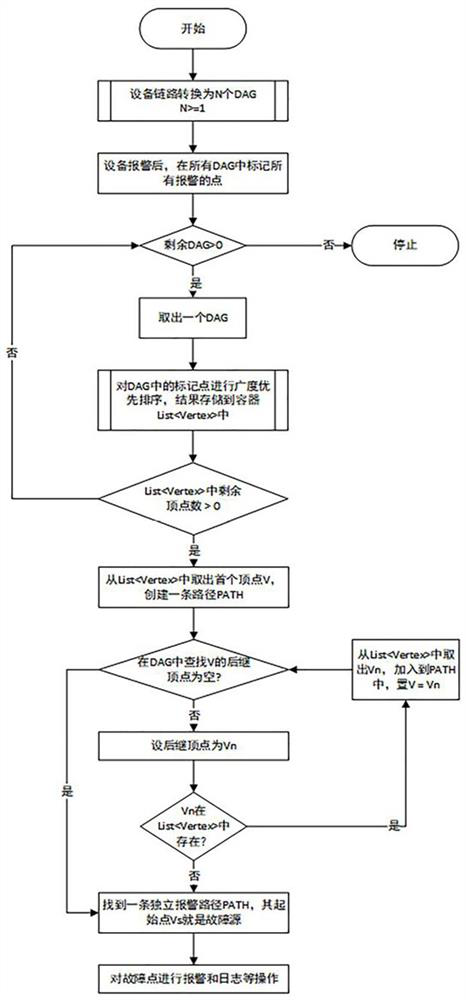
[0036] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, a digital audio and video signal transmission processing equipment link failure analysis and alarm method, including the following steps:
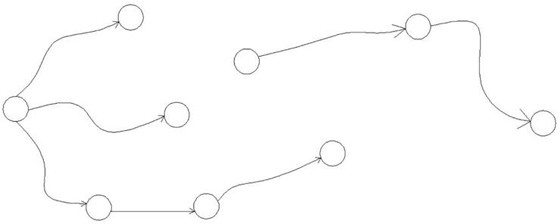
[0037] Step 1: Convert the device link into N DAGs, the device link includes n devices and m signal connections between devices, and n devices (Dev[i]) can be converted into n DAGs Independent node Vertex[i], m signal connection lines can be converted into m edges Edge[j], the edge Edge[j] connects two corresponding nodes in the DAG, and the flow direction of the edge is also the flow direction of the signal , n independent nodes Vertex[i] and m edges Edge[j] constitute the data structure G, if there are N relatively independent sub-links in the device link, and there are no edges connecting the sub-links , then in G, there will also be N independent DAGs (N>=1);
[0038] Step 2: Alarm signal mark. When the monitoring agent detects an abnormality in a certain device, it will report the abn...
Embodiment 2
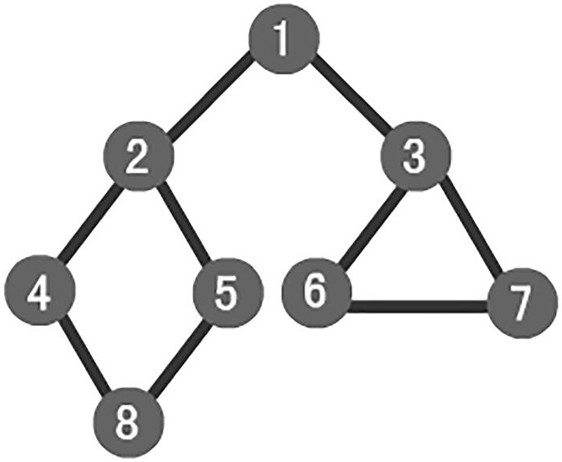
[0046] On the basis of Example 1, such as image 3 As shown, the breadth-first traversal described in step 3 is a traversal strategy for connected graphs, starting from the starting node V0, and traversing the wider area around it radially, that is, starting from V0, Visit the unvisited adjacent points W1, W2, ..., Wk of V0; then, visit the unvisited adjacent points sequentially from W1, W2, ..., Wk. Specific steps are as follows:
[0047] 1: Visit the initial node v and mark the node v as visited;
[0048] 2: Node v enters the queue;
[0049] 3: When the queue is not empty, continue to execute, otherwise the algorithm ends;
[0050] 4: Get out of the queue and get the queue head node u;
[0051] 5: Find the first adjacent node w of node u;
[0052] 6: If the adjacent node w of node u does not exist, then go to step 3, otherwise execute the following three steps in a loop:
[0053] 1). If the node w has not been visited, then visit the node w and mark it as visited;
[...
Embodiment 3
[0059] On the basis of embodiment 1, the concrete steps of described step 4 are as follows:
[0060] A: Create an empty path PATH, and take out the first node V1 in C1 and add it to PATH;
[0061] B: In the graph DAG where V1 is located, find the set of successor nodes {Vnext1, Vnext2,...Vnextm} of V1. If the successor node is in the set C1, take this node out of C1 and add it to the path in PATH;
[0062] C: Repeat steps A and B until there is no successor node belonging to C1, thus finding an independent path PATH;
[0063] D: Repeat steps A, B, and C until the nodes in the C1 set are empty.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com