Methods for the treatment of cysteamine sensitive disorders
A sensitivity, cysteamine technology, applied in the combination of syndromes and diseases, in the field of treatment of cysteamine sensitivity symptoms, can solve the inability to deliver cysteamine preparations in clinical development, and incomplete compliance of cystinosis patients Cystamine therapy, drug barriers at therapeutic levels, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 10
[0439] Example 10 describes a rat pharmacokinetic study of a cysteamine precursor in which renal levels of cysteamine following administration of the cysteamine precursor were much higher than those reported after administration of cysteamine bitartrate at 10.5 hours post administration (Dohil et al. Pharmacol. Drug Dev.) "4:170 (2012)).
[0440] Inherited disorders caused by mutations of arginine to cysteine
[0441] Certain genetic diseases can be treated using the methods and compositions of the invention. For example, a disease-causing mutation includes a DNA sequence change that changes the codon for arginine to a codon for cysteine. A subset of such mutations occur in proteins that retain some function, or are at least stable enough to be fully synthesized by the ribosome and transported to their normal destinations (e.g. plasma membrane, mitochondria, nucleus, etc.). Cysteamine can form disulfide bonds with abnormal cysteine residues and, in doing so, somewhat mimic...
example
[0487] The following examples are presented to provide those of ordinary skill in the art with a complete disclosure and description of how to implement and evaluate the methods and systems claimed herein, and are intended purely to illustrate the invention and are not intended to limit the scope of what the inventors believe to be their invention.
example 1
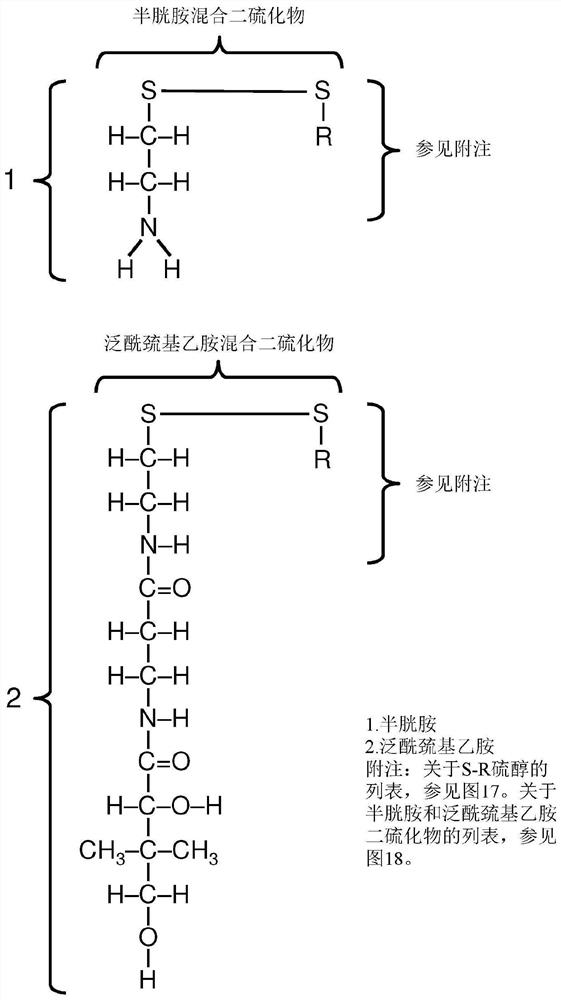
[0488] Example 1. Efficient synthesis of mixed disulfides
[0489] Multiple research groups have described various methods for the efficient synthesis of mixed disulfides (see Witt et al., Langmuir 23:2318 (2007); Musiejuk et al., Organic Preparations and Procedures (Org. Prep.andProc.)" 47.2:95 (2015)), including methods specifically targeting cysteine and cysteine analogs (eg Szymelfejnik et al. "Synthesis" 22:3528 (2007); Gormer et al. J. Org. Chem. 75.5:1811 (2010)). Recent improvements have been reported, for example based on the use of 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyanobenzoquinone (DDQ) to facilitate thiol-disulfide exchange (Musiejuk et al., RSCAdvances )》5.40:31347(2015)).
[0490] These methods allow the preferential synthesis of mixed disulfides (as opposed to two homodimeric disulfides) when combining two different thiols. In this example, the method described by Antoniow et al., Synthesis 3:363 (2007) was used to couple thiol cysteamine and pantetheine. Other thiol ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com