RFID data cleaning method based on lightweight event detection
A data cleaning and event detection technology, applied in the field of RFID data cleaning, can solve the problems of lack of front-end RFID data cleaning, lack of effective context information, difficult deployment, etc., and achieve accurate and reliable results of data cleaning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
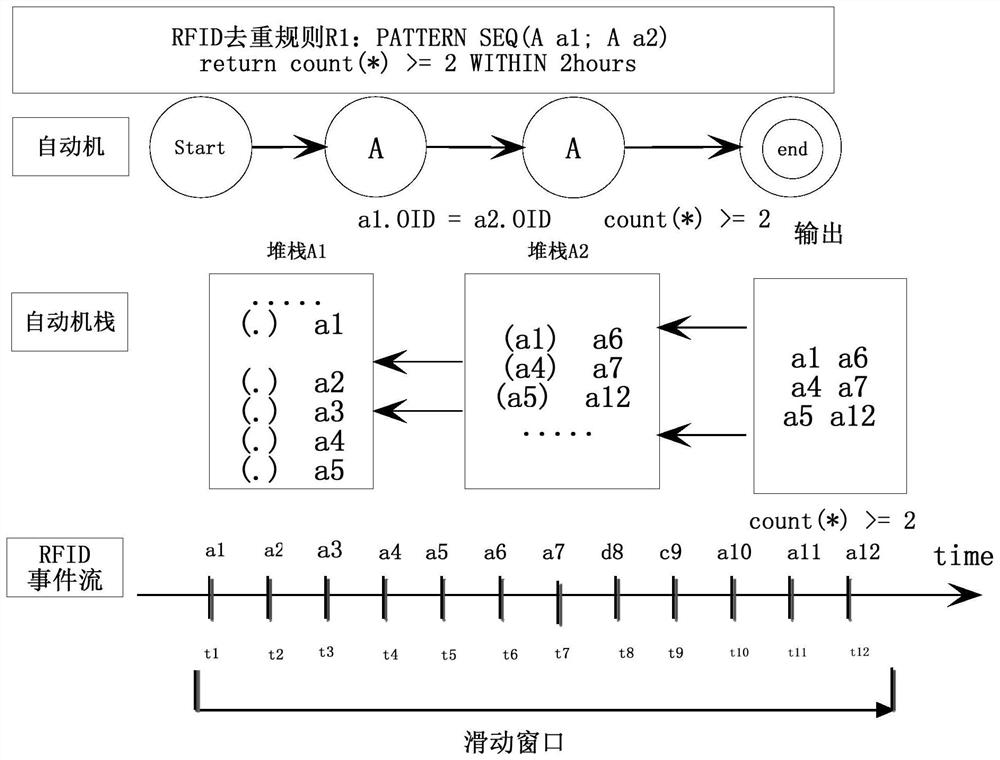
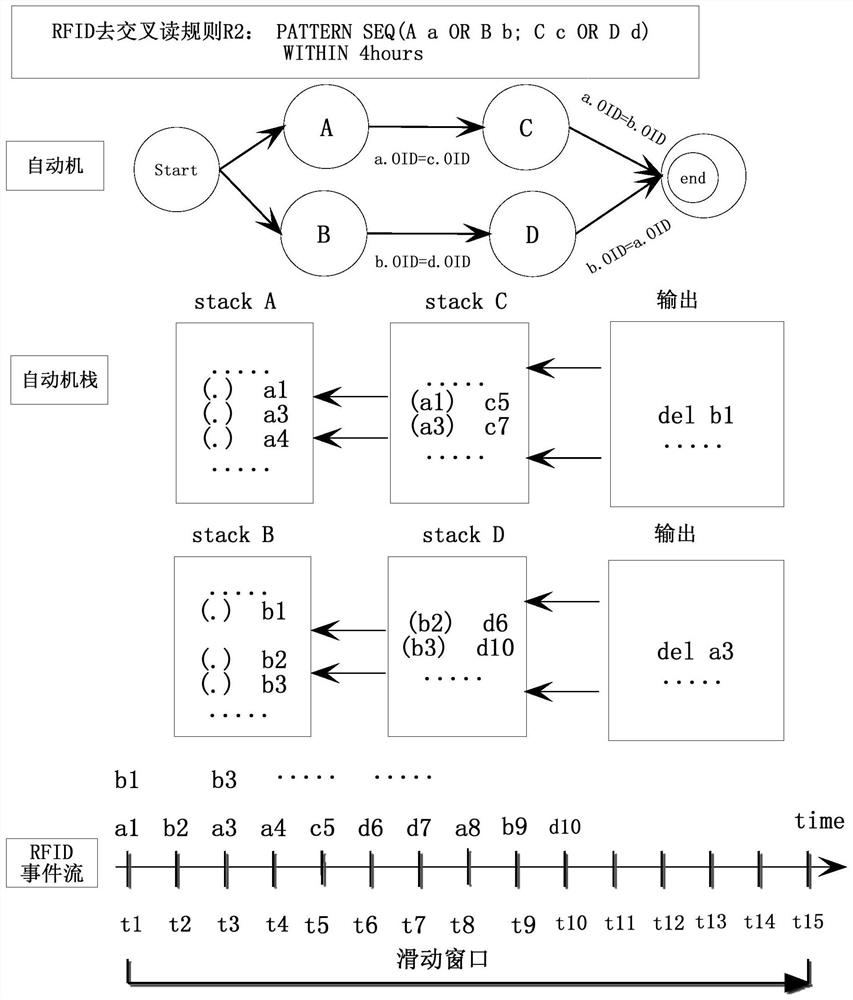
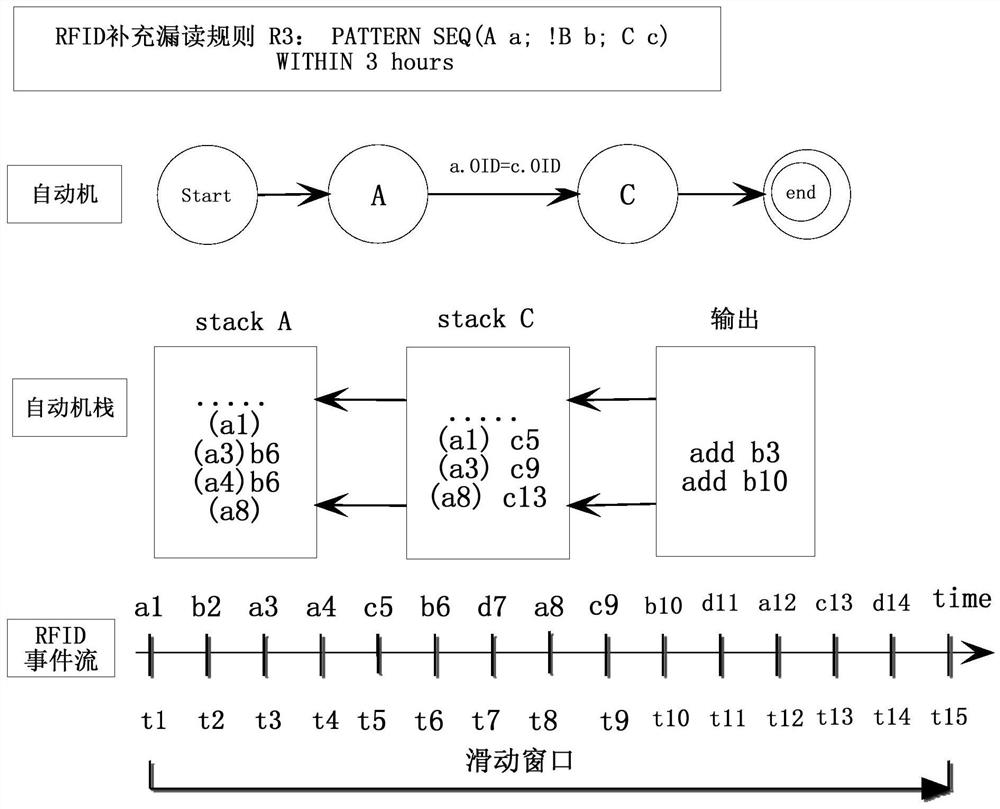
[0030] Event processing (Event Processing) is a real-time data analysis technology that has been widely used in the Internet of Things, workflow and other fields. RFID event detection refers to the process of combining simple or complex RFID events into semantically more complex events through association. An RFID simple event refers to an action in which a RIFD tag is read by a reader. It is an indivisible event (atomic event), represented by a triple (RID, OID, timestamp), where RID is the RFID reader identifier ( event type identifier), OID is the object identifier, and timestamp is the time when the reader reads and writes the tag. Raw events in the RFID data stream use a lowercase letter e i Indicates that the event type (that is, the RFID reader identification) is represented by capital letters A, B, and C, etc. Event detection operators include AND operator, OR operator, NOT operator, and SEQ sequence operator (events appear in sequence), which are used to define comp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com