Aluminum-iron alloy preparing technology
A preparation process, a technology of aluminum-iron alloy, applied in the field of aluminum-iron alloy smelting process, can solve the problems of increasing the difficulty of production, unevenness, more internal air, etc., to achieve improved stability and yield, uniform particle shape and particle size , easy to evenly distribute the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
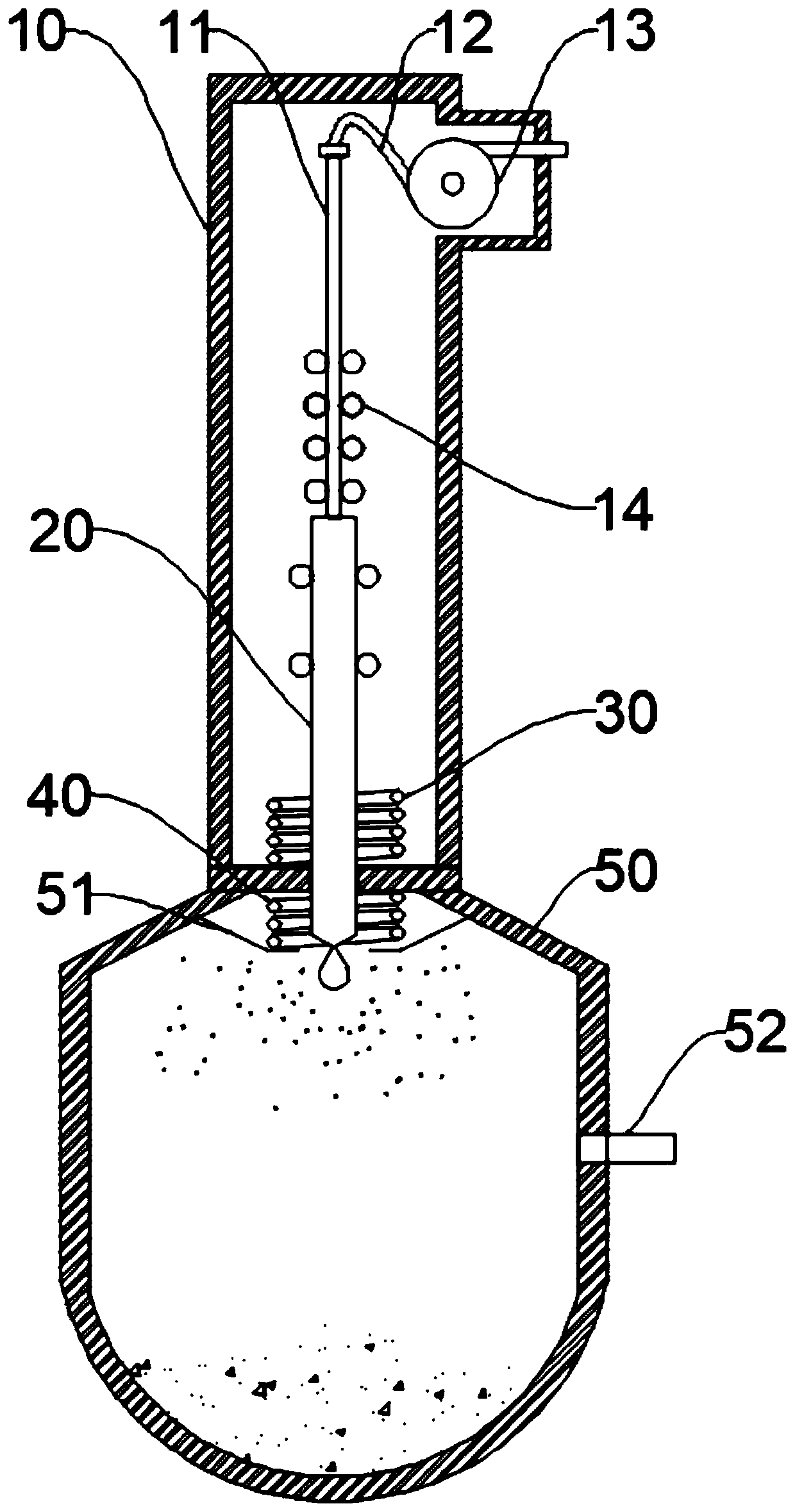
[0049] A process for preparing an aluminum-iron alloy, comprising the following steps,
[0050] 1) Aluminum rod preparation
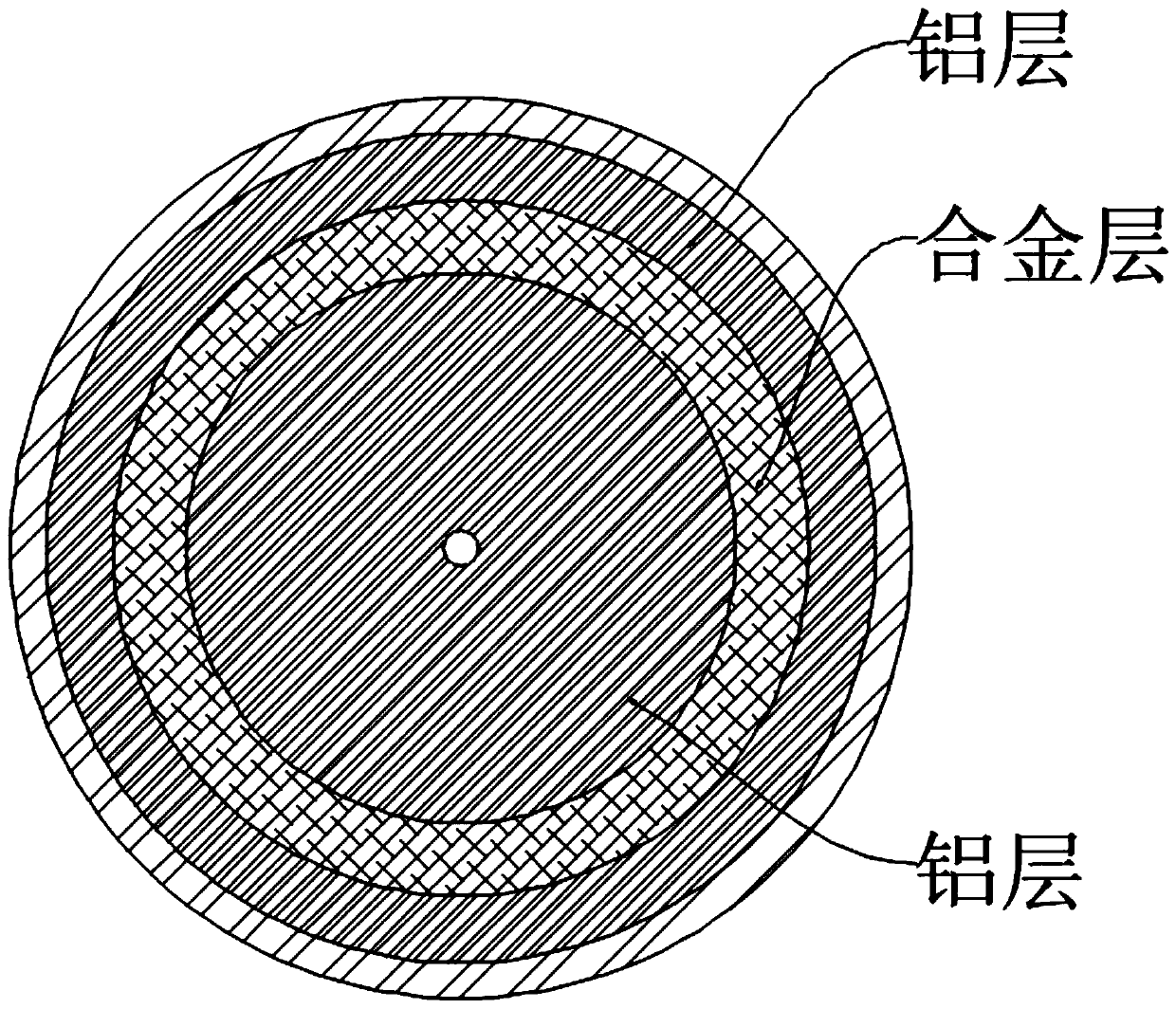
[0051] Calculate the amount of aluminum required for a single powder metallurgy, use 50-100% of all aluminum components, melt it and cast it into a cylindrical shape with a coaxial through hole inside, the diameter of the coaxial through hole is 0.5-1.5mm;
[0052] The cylindrical aluminum rod is for the convenience of uniform melting, and the uniform size is the premise to ensure the uniform composition of the subsequent metal powder. The through holes are for subsequent ventilation.
[0053] 2) Small component smelting
[0054] Melt the components in the alloy other than aluminum and the remaining aluminum that has not been made into an aluminum rod in step 1) in a crucible, at a temperature 10-50 degrees higher than the melting point, and electromagnetically stir for 10-20 minutes;
[0055] When smelting small components, it is best to add each co...
Embodiment 2
[0073] The melting point of aluminum is much lower than the melting point of iron or aluminum-iron alloy. In order to melt the alloy rod quickly, the alloy rod is preheated first, and the preheating temperature is lower than the melting point of aluminum. Then, the alloy layer and the inner aluminum rod are quickly melted together by rapid heating. Avoid using a single heating device for heating, and the heating time is long, which will cause the inner aluminum rod to melt first, and the outer alloy layer to melt later. After preheating, the inner and outer layers can be melted together quickly to make the components more uniform.
[0074] Therefore, in the step 4) the first induction heating ring 30 is fixed at the bottom of the transport box 10, and when the alloy rod 20 advances into the first induction heating exchange 30, the alloy rod 20 is preheated to 600 degrees, and passed through the sealing plate into the collection tank 50.
Embodiment 3
[0076] In order to further reduce the difference between the melting points of the inner and outer layers, in step 1), when the proportion of iron components exceeds 35%, 30-60% of all iron components are smelted together with aluminum; at the same time, in step 2) the small group For the smelting of small fractions, all remaining iron components are used, and aluminum accounts for 11-24% in small fractional smelting. In this way, the internal and external melting points tend to be more consistent, and the components of the molten metal droplets are more uniform, faster and controllable.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com