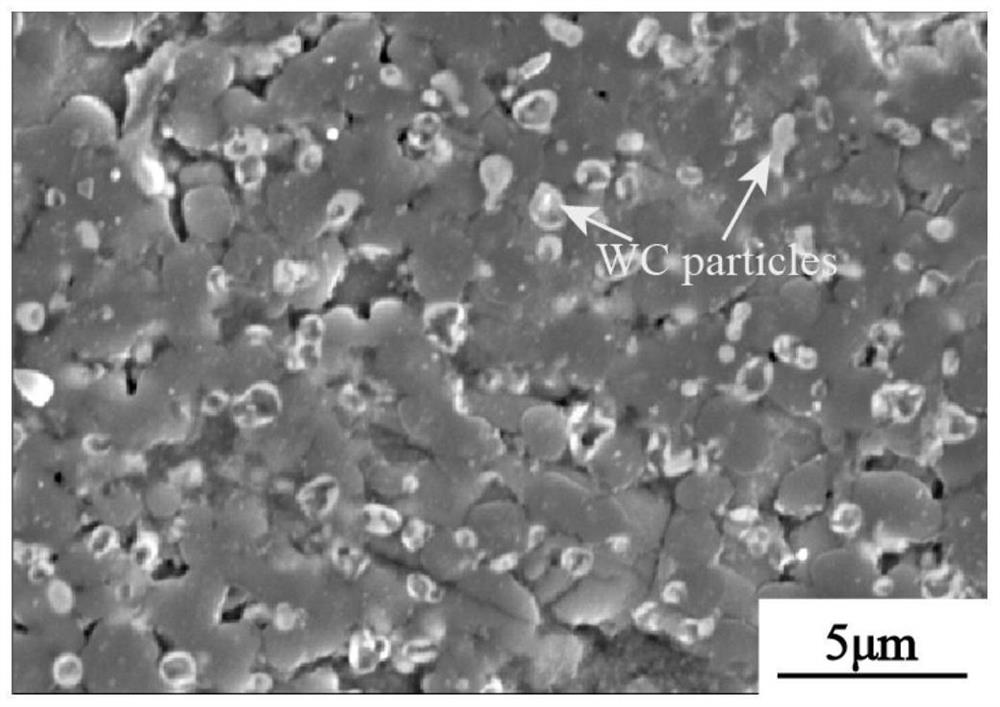
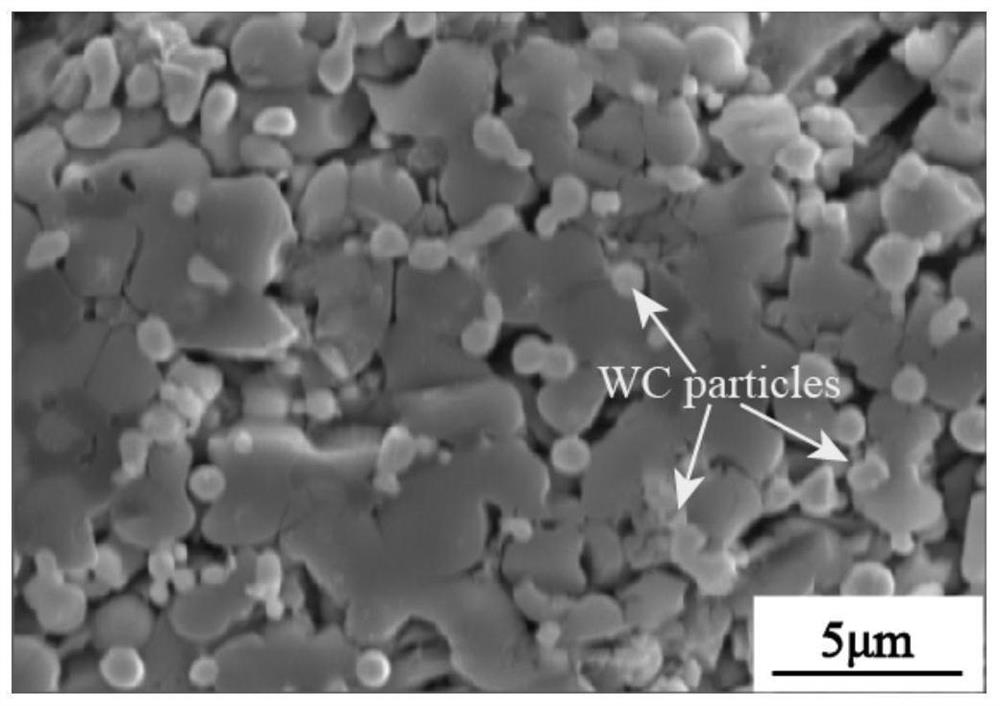
A Method for Promoting Intragranular Distribution of Fine Particles During Laser Shock Melting
A technology of laser shock and fine particles, which is applied in the coating process and coating of metal materials, can solve the problems of insufficient modification of fine particles and large distribution ratio, so as to promote the distribution ratio in the crystal and increase the fluidity , The effect of promoting the injection rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0025] Example 1: The material to be modified is TC11 titanium alloy, the binder is NaCl, and the fine particles are WC particles with an average particle size of 1 μm. First, apply NaCl saturated solution on the surface of TC11 and dry it. The thickness of the insulation layer is 40 μm, and the porosity of the insulation layer is about 55%. Then, the mixed slurry of NaCl and WC is coated and dried, and the thickness of the preset layer is is 400 μm.
[0026] The coated samples were preheated using an induction coil heating unit. During heating, use an infrared thermometer to measure the side temperature of the sample, and stop heating immediately when the temperature reaches 300°C. The heating temperature is about 6s. After the heating is completed, quickly put the sample into a specific fixture and cover the coated quartz glass. This process is controlled within 10s.
[0027] The preheated samples were processed by laser shock melt injection using a continuous fiber laser...
example 2
[0031] Example 2: The material to be modified is TC11 titanium alloy, the binder is NaCl, and the fine particles are WC particles with an average particle size of 1 μm. First, apply NaCl saturated solution on the surface of TC11 and dry it. The thickness of the insulation layer is 30 μm, and the porosity of the insulation layer is about 50%. Then, the mixed slurry of NaCl and WC is coated and dried, and the thickness of the preset layer is is 500 μm.
[0032] The coated samples were preheated using an induction coil heating unit. During heating, use an infrared thermometer to measure the side temperature of the sample, and stop heating immediately when the temperature reaches 200°C. The heating temperature is about 5s. After the heating is completed, quickly put the sample into the specific fixture and cover the coated quartz glass. This process is controlled within 8s.
[0033] The preheated samples were processed by laser shock melt injection using a continuous fiber lase...
example 3
[0035] Example 3: The material to be modified is TC11 titanium alloy, the binder is NaCl, and the fine particles are WC particles with an average particle size of 0.5 μm. First, apply NaCl saturated solution on the surface of TC11 and dry it. The thickness of the insulation layer is 50 μm, and the porosity of the insulation layer is about 60%. Then, the mixed slurry of NaCl and WC is coated and dried, and the thickness of the preset layer is 300 μm.
[0036] The coated samples were preheated using an induction coil heating unit. During heating, use an infrared thermometer to measure the side temperature of the sample, and stop heating immediately when the temperature reaches 350°C. The heating temperature is about 8s. After the heating is completed, quickly put the sample into a specific fixture and cover the coated quartz glass. This process is controlled within 9s.
[0037] The preheated samples were processed by laser shock melt injection using a continuous fiber laser. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com