Noise reduction method of narrowband active noise control system based on variable step size algorithm
A technology of active noise control and variable step size, applied in active noise control, sounding equipment, instruments, etc., it can solve problems such as difficulty in user parameter selection, restricting the overall performance of the system, high complexity, etc., to enrich the theoretical system and solve complex problems. High degree of noise, the effect of improving the level of noise reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Embodiment 1: Noise reduction method for narrowband active noise control system based on variable step size algorithm
[0054] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a noise reduction method for a narrowband active noise control system based on a variable step size algorithm, including the following steps:
[0055] Step 1: Build a narrowband active noise control system based on the VSS-FXLMS algorithm, such as figure 2 As shown, p(n) is the target noise which usually contains a finite number of frequency components with a mean of zero and a variance of The additive noise v p (n); According to the synchronization signal obtained by non-acoustic sensors (such as tachometers, etc.), the ith reference channel frequency value ω is calculated i ; i=1,2,L,q, q is the number of target noise frequencies; n is the time; S(z) is the secondary channel model, and its coefficient is is the secondary channel estimation model, which can be obtained through offline...
Embodiment 2
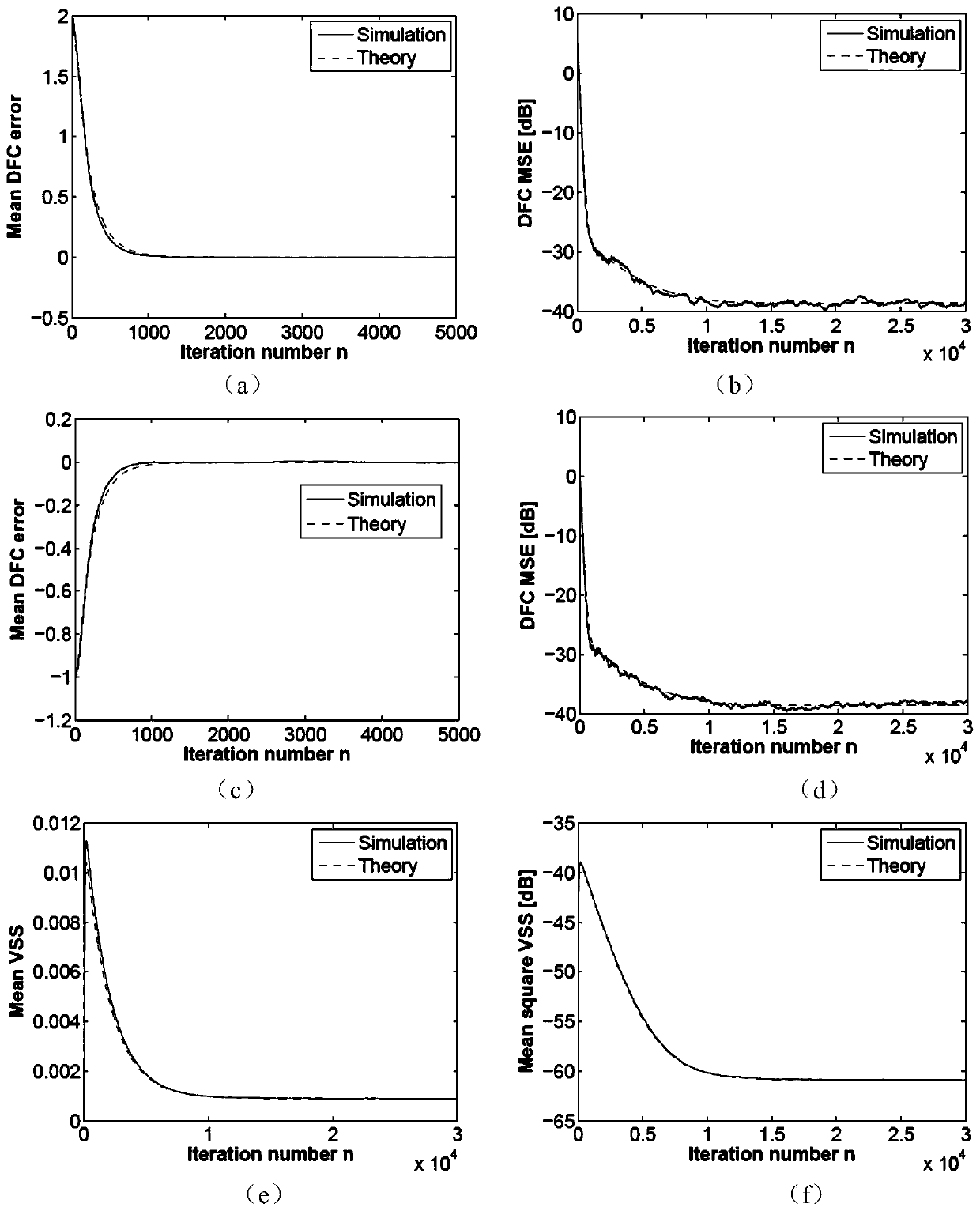
[0106] Example 2: Theoretical verification in the case of simulated noise
[0107] The target noise includes three frequency components and additive Gaussian white noise, and the normalized frequencies of the three frequency channels used are ω 1 = 0.1π, ω 2 = 0.2π and ω 3 =0.3π; the corresponding controller coefficients are respectively a 1 =2.0,b 1 =-1.0, a 2 =1.0,b 2 =-0.5a 3 =0.5,b 3 =0.1; the secondary channel adopts the FIR model, its length and cut-off frequency are 21 and 0.4π respectively; the secondary channel estimates the length of the FIR model to be 31, its coefficients are obtained through offline identification, and the initial value of the step size is 0.0025.
[0108] First of all, in the verification method of the present invention, the dynamic performance analysis results related to the controller coefficient estimation error mean value and mean square value, and the step size mean value and mean square value, the values of the unified user paramet...
Embodiment 3
[0109] Example 3: Experimental verification under actual noise conditions
[0110] The actual noise comes from the noise of a large cutting machine with a rotational speed of 1400rpm. The normalized frequencies of the noise are 0.0804π, 0.1609π, 0.2414π, 0.3218π and 0.4024π. The real secondary channel is an IIR model (S.M.Kuo and D.R.Morgan, Active Noise Control Systems-Algorithms and DSP Implementation, NewYork: Wiley, 1996.), assuming that the secondary channel estimation model is the same as the real secondary channel model. The initial value of the step size is 0.001.
[0111] First, assuming that the user parameter η=0.005 is fixed, change the value of the user parameter ξ, Figure 8 The change curves of residual noise and step size in three different situations are given. When ξ=0.9994, the system noise reduction is 8.79dB; when ξ=0.9996, the system noise reduction is 10.57dB; when ξ=0.9998 , the system noise reduction is 11.51dB. It can be seen that in the case of no...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com