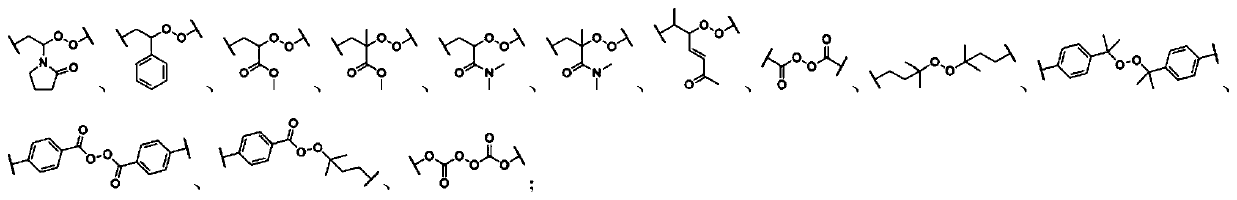
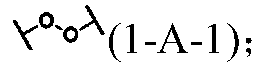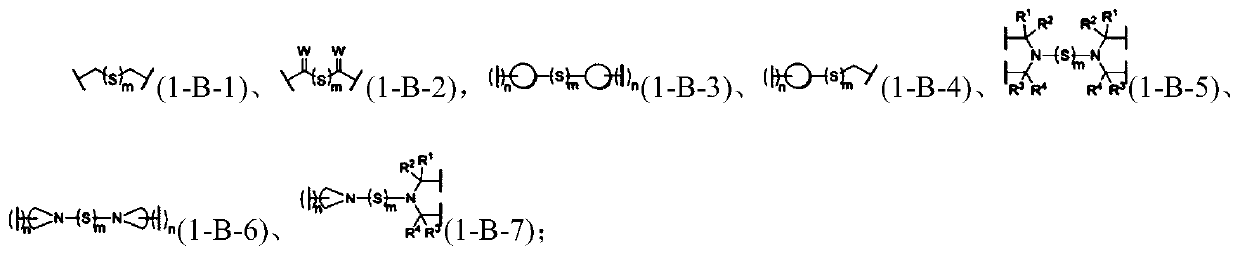Force-induced responsive supramolecular polymer
A technology of supramolecular polymers and supramolecules, applied in the field of force-responsive supramolecular polymers, can solve problems such as difficult to meet the needs of multifunctional and intelligent materials, single properties and performances, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[1663] In the preparation process of the mechanoresponsive supramolecular polymer composition, there is no special limitation on the amount of each component raw material of the mechanoresponsive supramolecular polymer. performance adjustments.
[1664] In an embodiment of the present invention, the form of the mechanoresponsive supramolecular polymer can be solution, paste, glue, common solid, elastomer, gel (including hydrogel, organogel, oligomer swelling gels, plasticizer-swelled gels, ionic liquid-swelled gels), foams, etc. Among them, the content of soluble small molecular weight components contained in ordinary solids and foam materials is generally not higher than 10wt%, while the content of small molecular weight components contained in gels is generally not lower than 50wt%. Ordinary solids have relatively fixed shape and volume, better mechanical strength, and are not bound by organic swelling agents or water. Elastomers have the general properties of ordinary sol...
Embodiment 1
[1677] Example 1 2 molar equivalents of carboxy-terminated polybutadiene (average molecular weight is 1.5kDa) and 1 molar equivalent of diol supramolecule a containing force-sensitive groups in dicycloethylcarbodiimide (DCC) and 4- Under the catalysis of dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP), the polybutadiene whose skeleton contains a force-sensitive group and whose two ends are terminated with carboxyl groups is obtained. 1 molar equivalent of polybutadiene obtained and 2 molar equivalents of ligand compound b are reacted under the catalysis of DCC and DMAP to obtain a polybutadiene supramolecular unit whose skeleton contains a force-sensitive group and both ends are terminated by ligand groups. Body A. Ligand compound b and excess polybutadiene (average molecular weight is 2kDa) terminated by carboxyl groups at both ends are reacted under the catalysis of DCC and DMAP to obtain polybutadiene with ligand group at one end and carboxyl group at the other end . The polybutadiene obtai...
Embodiment 2
[1680] Example 2 A hexafunctional initiator was obtained by reacting 1 molar equivalent of compound a containing a mesensitizing group with excess 2-bromoisobutyryl bromide under the catalysis of triethylamine. Reaction of equimolar equivalents of acryloyl chloride and pyridazine-3-methanol under the catalysis of triethylamine to obtain ligand group-containing acrylate monomer b. With 1 molar equivalent of the obtained hexafunctional initiator as the initiator, cuprous bromide and PMDETA are used as the initiator to initiate the polymerization of 600 molar equivalents of ethyl acrylate, and continue to initiate 150 molar equivalents of dimethylaminoacrylate after the reaction is complete. Polymerization of the mixture of ethyl ester and 150 molar equivalents of monomer b to obtain a six-armed polyacrylate copolymer polymer supramolecular monomer with part of side groups being ligand groups.
[1681]
[1682] Blend the obtained supramolecular monomer with a certain amount of...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com