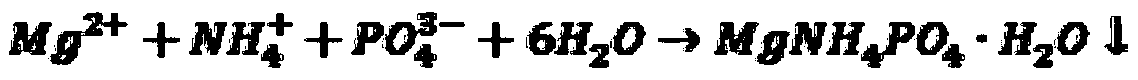Method for recovering phosphorus in blue-green algae in struvite form
A struvite and cyanobacteria technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of long cycle, difficult odor disposal, large land occupation, etc., and achieve short reaction cycle and reduce odor. The effect of producing and producing low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
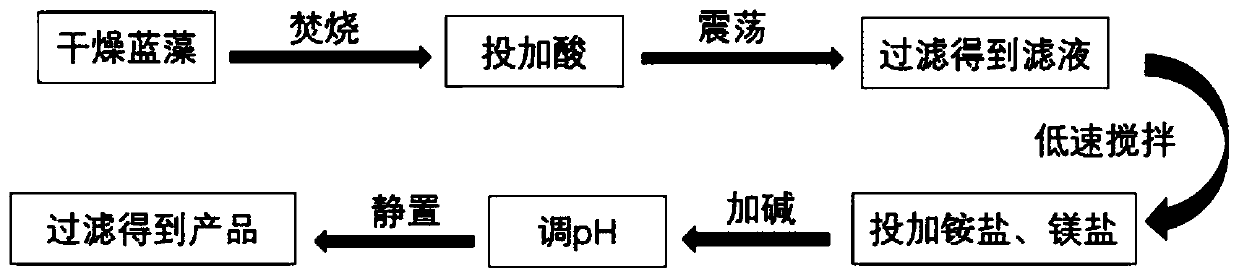
[0028] 1) Dry the salvaged blue-green algae, which can be dried by means of air flotation, pressure, air-drying or sun-drying. After drying, the water content of the blue-green algae is lower than 5%. After ashing and burning in an incinerator at 450°C for 2 hours, the incineration ash of blue-green algae is obtained;
[0029] 2) Add 1 mol / L sulfuric acid extract to the incineration ash of blue-green algae, fully stir for 2 hours, filter to obtain the filtrate, and set aside;
[0030] 3) Add ammonium chloride and magnesium chloride to the filtrate according to the molar ratio of n(N):n(P):n(Mg)=5:1:1.6 while stirring at a low speed;
[0031] 4) Add NaOH solution to adjust the pH value of the reaction solution to 9.0, filter and recover the precipitate, and dry to obtain the struvite crystal product, and the final phosphorus recovery rate is 98.01%.
Embodiment 2
[0033] 1) Dry the salvaged blue-green algae, which can be dried by means of air flotation, pressure, air-drying or sun-drying. After drying, the water content of the blue-green algae is lower than 5%. After ashing and burning in an incinerator at 450°C for 2 hours, the incineration ash of blue-green algae is obtained;
[0034] 2) Add 0.5 mol / L sulfuric acid extract to the incineration ash of blue-green algae, fully stir for 2 hours, filter to obtain the filtrate, and set aside;
[0035] 3) Add ammonium chloride and magnesium chloride to the filtrate according to the molar ratio of n(N):n(P):n(Mg)=5:1:1.6 while stirring at a low speed;
[0036] 4) Adding NaOH solution to adjust the pH value of the reaction solution to 8.0, recovering the precipitate, and drying it to obtain the struvite crystal product, the final phosphorus recovery rate is 99.85%.
Embodiment 3
[0038] 1) Dry the salvaged blue-green algae, which can be dried by means of air flotation, pressure, air-drying or sun-drying. After drying, the water content of the blue-green algae is lower than 5%. After ashing and burning in an incinerator at 450°C for 2 hours, the incineration ash of blue-green algae is obtained;
[0039] 2) Add 0.5 mol / L hydrochloric acid leaching solution to the incineration ash of blue-green algae, fully stir for 2 hours, filter to obtain the filtrate, and set aside;
[0040] 3) while stirring at a low speed, add ammonium chloride and magnesium chloride to the filtrate according to the molar ratio of n(N):n(P):n(Mg)=3.2:1:1.2;
[0041] 4) Adding NaOH solution to adjust the pH value of the reaction solution to 8.5, recovering the precipitate, and drying it to obtain the struvite crystal product, the final phosphorus recovery rate is 99.88%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com