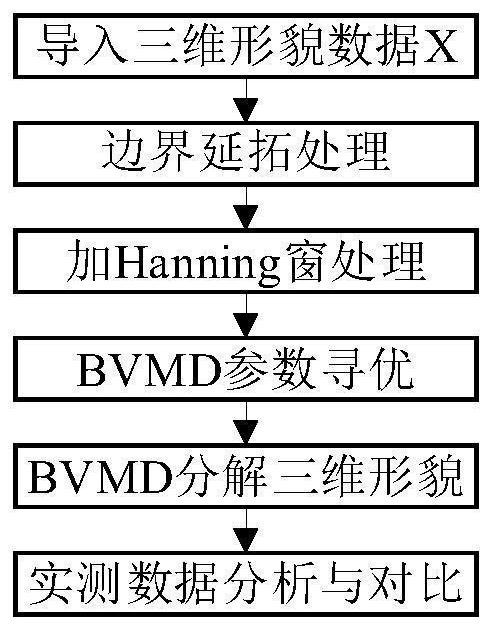
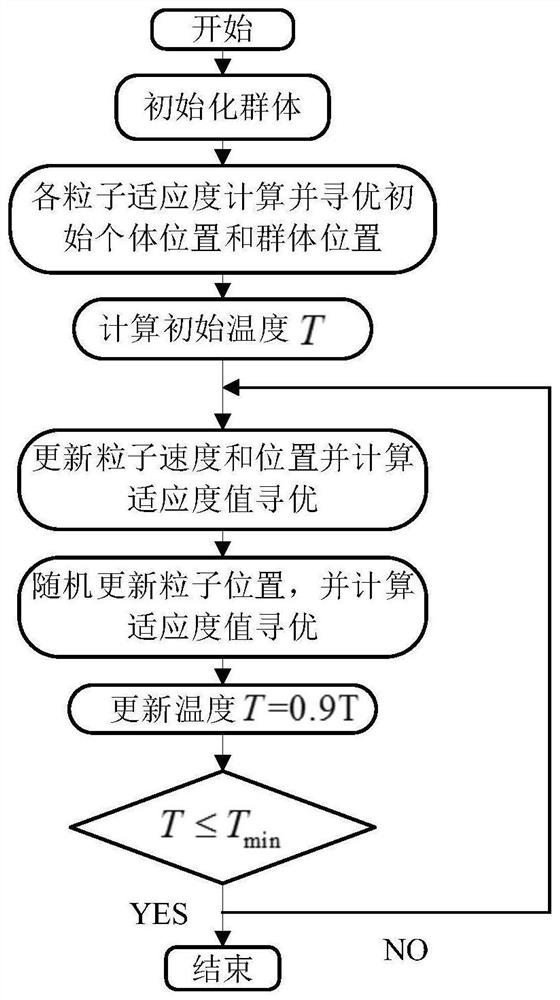
Spatial frequency identification method based on two-dimensional variational mode decomposition of machined surface
A technology of variational modal decomposition and surface processing, applied in character and pattern recognition, instruments, complex mathematical operations, etc., can solve problems such as large reconstruction error, modal aliasing, original signal distortion, etc. Thoroughly solve the effect of modal aliasing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] This embodiment provides a spatial frequency identification method based on two-dimensional variational mode decomposition of ultra-precision machining surface topography, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0071] Step 1, convert the collected 3D topography data into a matrix form, and determine the size of the matrix. The initial 3D topography is as follows Figure 4 shown.
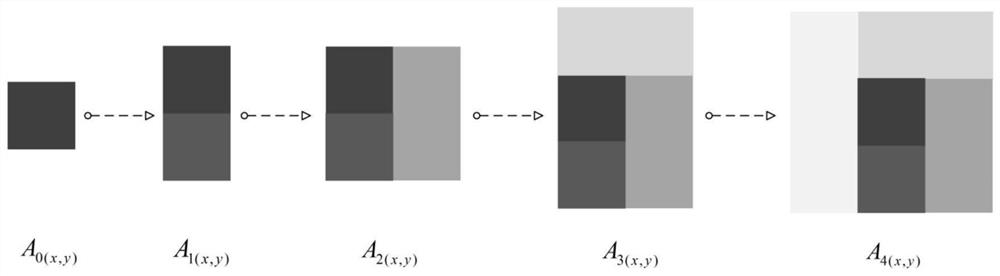
[0072] Step 2, gradually extend the matrix data in step 1, the schematic diagram of the extension is as follows image 3 As shown, the 3D shape data after continuation are as follows: Figure 5 Shown:
[0073] Step 21, record the workpiece surface shape data after ultra-precision machining as A 0(x,y) , where x, y are the sampling points of the row and column of the workpiece surface shape data after ultra-precision machining, (x=1,2,3,...,M; y=1,2,3,...,N) ;
[0074] Step 22, for A 0(x,y) Take its lower boundary as the axis, perform mirror flip, and compare the flipped data with A 0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com