Method for realizing self-adaptive routing protocol of mobile sparse underwater acoustic sensor network
An underwater acoustic sensor and routing protocol technology, applied in the direction of network topology, electrical components, wireless communication, etc., can solve the problems of low delivery rate, blank area, etc., to ensure sustainability and avoid the effect of "void"
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0062] According to the established mobile sparse underwater acoustic sensor network structure, such as figure 1 As shown, the network structure includes underwater sensor nodes, surface buoy communication nodes, and underwater acoustic links. Sensor nodes are sparsely deployed in three-dimensional underwater space at different depths, and are affected by water flow, gravity, buoyancy, resistance, and other environmental factors ( Under the influence of tides, storms, ocean currents and marine life), its function is to acquire, transmit, process and fuse data, and send the collected data to the sea surface buoy node through the underwater acoustic channel in the form of multi-hop, and the sea surface communication The nodes are responsible for forwarding the collected data to the land data processing center.
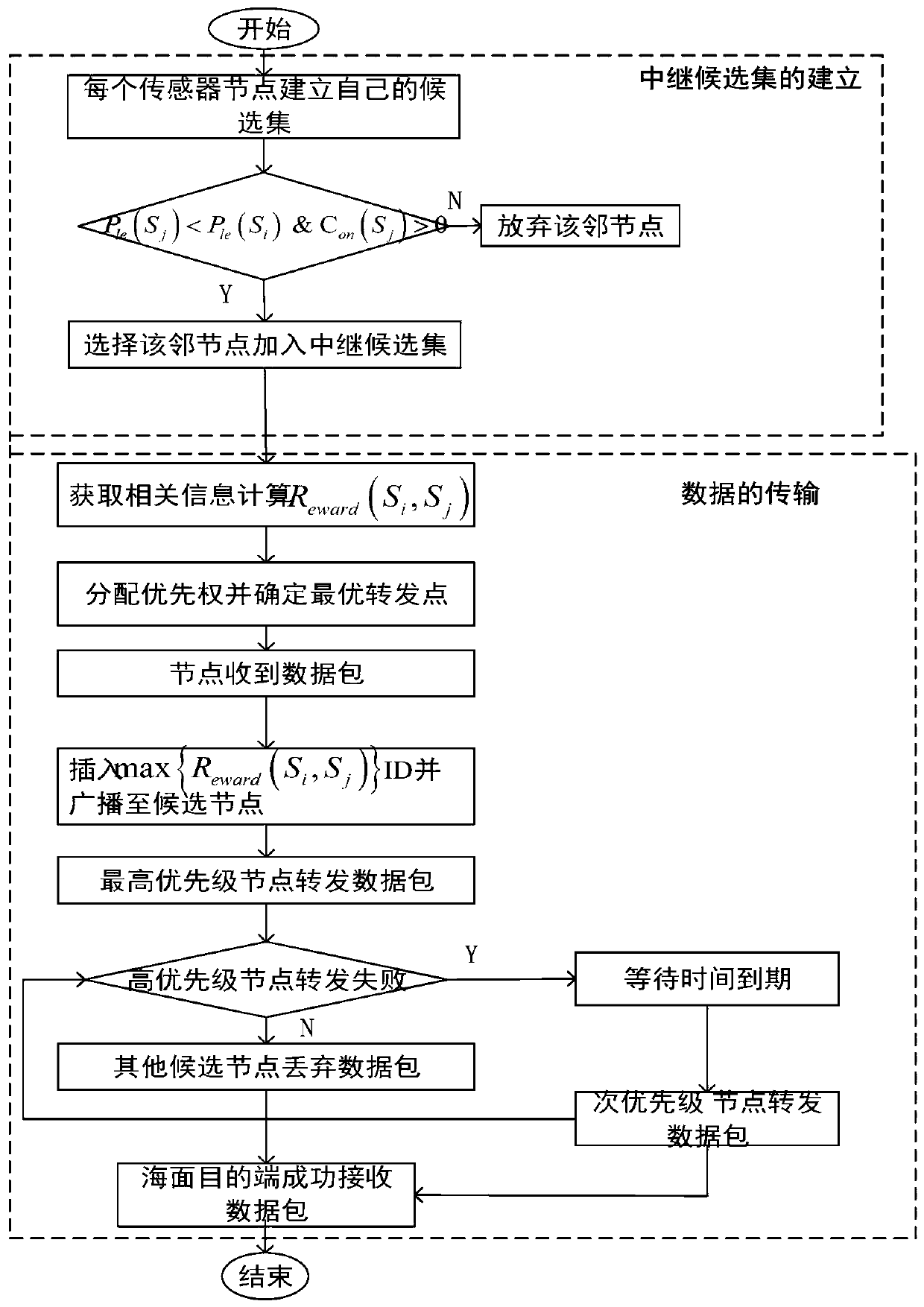
[0063] An implementation method of adaptive routing protocol for mobile sparse underwater acoustic sensor network, such as figure 2 shown, including the following step...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com