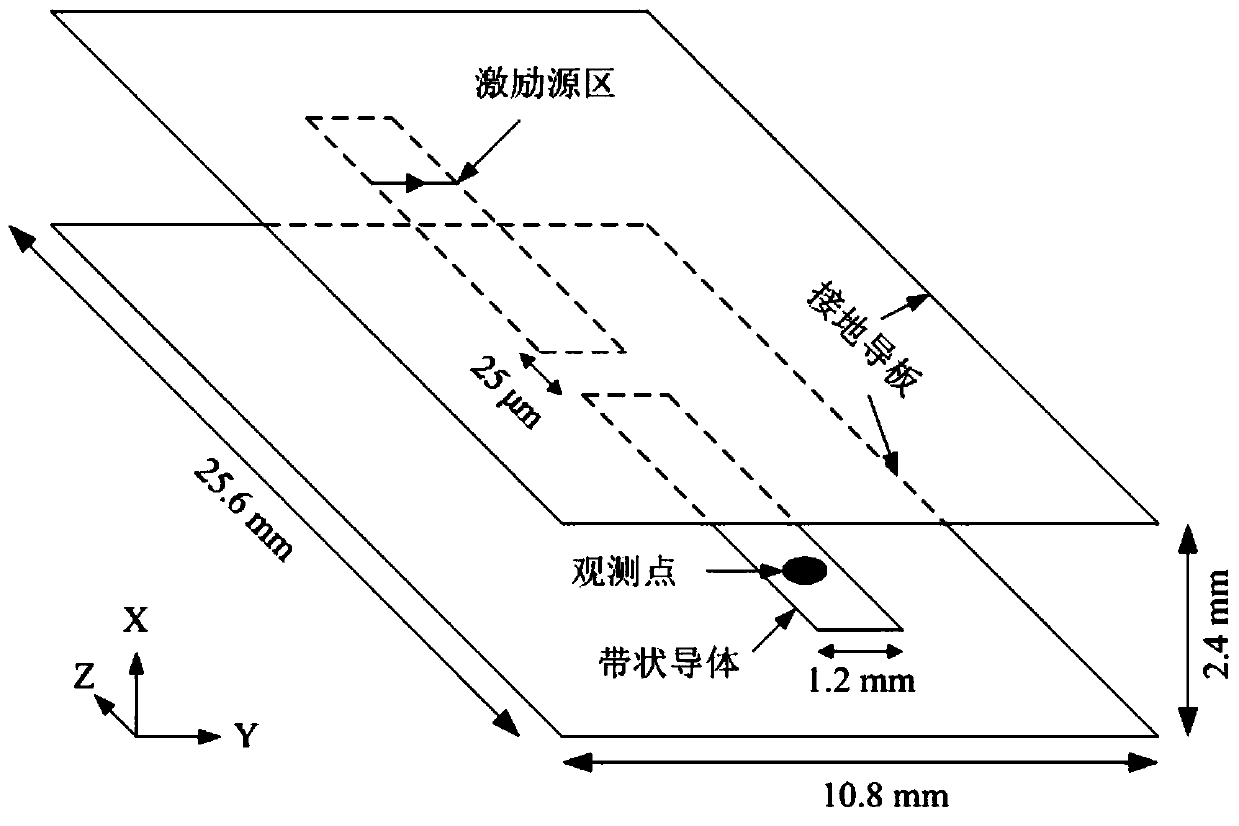
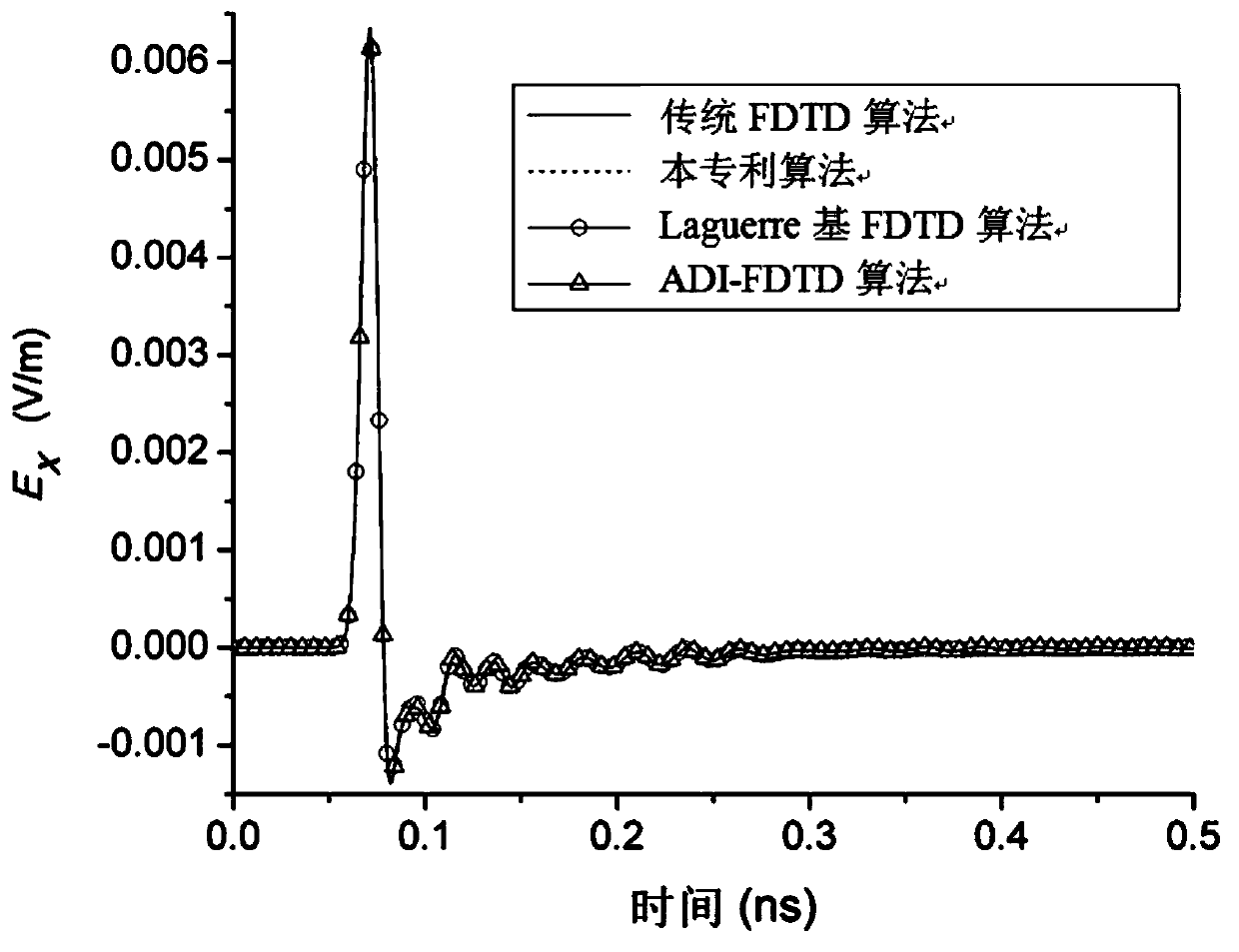
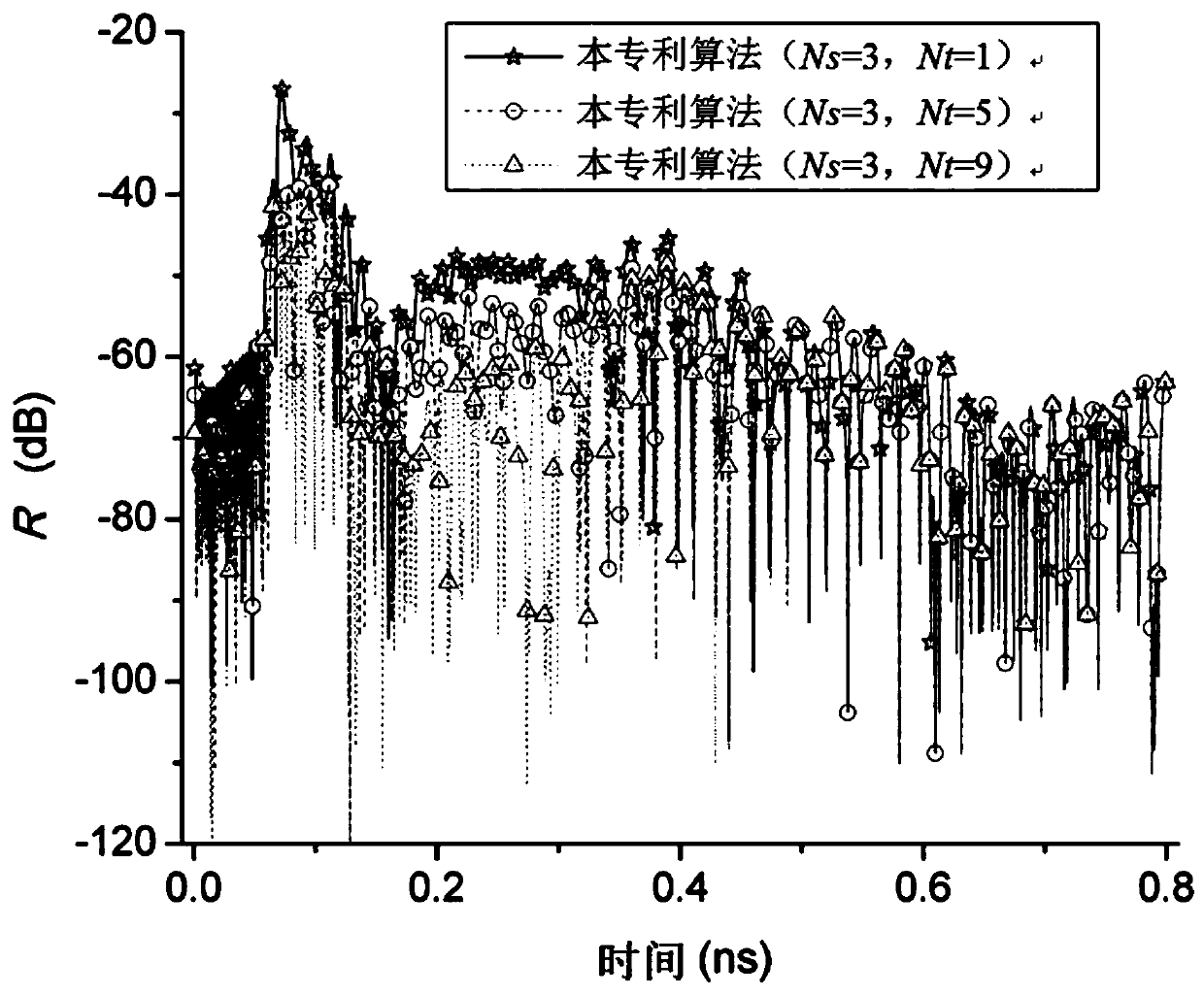
Three-dimensional alternate iteration unconditional stability FDTD algorithm
An alternate iterative, three-dimensional technology, applied in the field of FDTD algorithm, can solve the problems of inappropriate FDTD algorithm and memory resources affecting computing efficiency, and achieve the effect of reducing computing time, improving computing efficiency and high precision.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0052] The specific embodiment of the present invention provides a three-dimensional alternating iterative unconditional stable FDTD algorithm, comprising the following steps:
[0053] Step 1, use the Laguerre orthogonal basis to expand the three-dimensional Maxwell equations to the Laguerre domain, and use the method of constructing variables to write the six Maxwell equations in the Laguerre domain into a matrix equation.
[0054] In a lossless, homogeneous, isotropic medium, the Maxwell equations in the three-dimensional time domain are:
[0055]
[0056]
[0057]
[0058]
[0059]
[0060]
[0061] In the formula, ε is the permittivity, μ is the magnetic permeability, E x ,E y ,E z are the components of the electric field along the x, y, and z directions, H x 、H y 、H z is the component of the magnetic field along the three directions of x, y, and z, J x 、J y 、J z are the components of the current source along the x, y, and z directions.
[0062] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com